Role of the President
advertisement

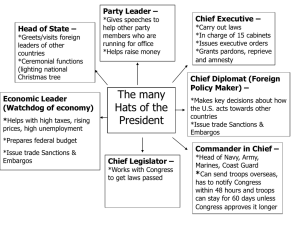
What do we like to do? Review! Review! •What is one of the three Constitutional qualifications to become the President of the United States? •What do we call the indirect system used to elect our President? •How many total electors do we have? Where does that number come from? •How many votes does one have to get in order to be elected President? •How long is a presidential term? How many can they serve? •Where does the President live and work? •What Constitutional qualifications are needed to become the Vice President? •Who follows in order of succession if the President dies or becomes incapacitated? (_________, ________, __________) “The Role of the President” Constitutional Government In the United States, we have a constitutional government. This is a government that is based on the written plan of government as stated in the constitution. Where in the Constitution can we find out about the roles and powers of President of the US? Role of the President The President is the most powerful public official in the United States. The Constitution says that “Executive Power shall be invested in a President…” This means that his/her main job is to “execute” or carry out laws that are passed by Congress. The president has several jobs to fulfill. In Article II, the Constitution also gives the President the power to… Presidential Powers The Constitution lists (or “expresses”) certain powers that are set aside for the President. They are listed in Article II. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. “Veto”, or reject, bills passed by Congress. Call Congress into special session. Serve as “commander-in-chief” of the armed forces. Receive/make agreements with foreign leaders or dignitaries. (With Senate Approval) Make treaties with other nations (With Senate Approval) Appoint heads of executive agencies (With senate approval) Pardon, forgive or reduce the penalties against people convicted of federal crimes. Required to give ‘State of the Union’ Address to Congress “State of the Union” The “State of the Union” address is the President’s way of keeping the Congress informed about the nation and government. This “informing” is required by the Constitution Roles of the President The President has several roles that they play as the leader of the United States. Role #1: Chief Executive This is the President’s most important job. As Chief Executive the President must carry out laws that are passed by Congress. The President’s “Cabinet” was created to help the with this task. Role #1: Chief Executive An “executive order” is a rule or command that has the force of law. This power is used by the president to “take care of laws that are faithfully executed.” In 1948, President Truman issued an order to integrate the U.S. Armed Forces. Executive Orders Executive Order #9066 was issued by President F D Roosevelt during WWII that forced many Japanese Americans into internment camps as a result of the bombing of Pearl Harbor. – Now, therefore, by virtue of the authority vested in me as President of the United States, and Commander in Chief of the Army and Navy, I hereby authorize and direct the Secretary of War, and the Military Commanders… deems such action necessary or desirable, to prescribe military areas in such places and of such extent as he or the appropriate Military Commander may determine, from which any or all persons may be excluded,…, the right of any person to enter, remain in, or leave shall be subject to whatever restrictions the Secretary of War or the appropriate Military Commander may impose in his discretion. (1942, Executive Order 9066) The act of making people relocate for a certain amount of time is Forced Internment. Role #1: Chief Executive The President also has the power to appoint federal judges to Federal Courts and justices to the U.S. Supreme Court (but must receive approval from the Senate). Not all appointees are approved… Role #1: Chief Executive Finally, Presidents can issue or grant – “pardons” (or declarations of forgiveness) – “reprieves” (or orders to delay punishment until heard by a higher court – “amnesty” (or a pardon toward a group of people) Role #2 - Chief Diplomat/Foreign Policy Leader As Chief Diplomat, the President directs the foreign policy of the United States. This is done by negotiating treaties with leaders of other nations and securing relationships with other nations – this is also called foreign affairs. Role #2 - Chief Diplomat/Foreign Policy Leader The President utilizes his Secretary of State and ambassadors/diplomats (people who work for the government and are assigned to a foreign nation) to create better relations and build diplomacy with other countries. Role #3: Commander-in-Chief The President has complete control of the armed forces. However, as a part of “checks & balances” only Congress has the power to declare war. This has only happened 5 times – the last official declaration of war was Dec. 7, 1941 (World War II). Role #3: Commander-in-Chief Even without a declaration of war, the President has the authority to send troops into action. Since 1789, the presidents have sent troops into action over 150 times. Role #3: Commander in Chief For example, during the conflicts in both Korea and Vietnam, the President got involved in these conflicts and sent troops into battle without a declaration of war from our Congress. Role #3: Commander-in-Chief After the Vietnam War, in 1973, Congress passed the “War Powers Resolution” which forced the President to notify Congress within 48 hours of sending troops into action. Additionally, troops must be back in 60 days unless Congress: – approves an extension or – war is declared. BRAIN BREAK! Which of the roles of the President discussed so far is his most important role? Which of the roles of the President discussed so far allows the President to call troops into action? What do we call the federal powers that are listed in the Constitution? Role #4: Legislative Leader Many bills that Congress considers each year come from the President or “Executive Branch”. The President cannot make laws, but he can encourage Congress to pass laws that he supports and veto bills that he is not in favor of. Role #4: Legislative Leader Every President creates a “legislative program”, or a list of new laws the President wants Congress to pass. A special staff is created to work with Congress on these bills. Role #4: Legislative Leader The President represents the entire nation, while members of Congress represent their own constituents (the people back home who voted for them). This causes conflicts from time to time… Role #4: Legislative Leader Time is a major issue as the President can only serve two terms, but members of Congress have no term limits. The president is the “living symbol” of the United States. His or her role is to carry out the ceremonial functions for American citizens. The president meets visiting foreign leaders and presents medals to our country’s heroes. The President is interested in domestic affairs – all things socially, politically, and economically related to the US. Role #5: Head of State Role #6: Economic Leader Each president hopes to help the country’s economy prosper. To do this, the president plans the federal budget – a statement of our government’s economic plans for the year. Role #7: Party Leader Our current President is the head of the Democratic party. The president is considered the leader of their political party. How can a president help their political party? – Give speeches on behalf of candidates. – Raise money for elections – Use their constant media coverage to get people in the spotlight at big events (free air time).