Part I Review for SS8A
advertisement

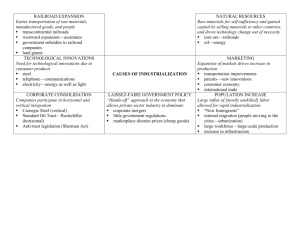
AIM: What do we need to study for the midterm? Do Now: List 3 topics we have studied so far. HW: Study Transcontinental Railroad • Opened new markets in the west and brought products of western farms and mines east. Capitalism • The economic system based on private initiative, competition, profit, and the private ownership of the means of producing goods and services. Laissez-Faire • Noninterference; has come to mean a policy by which the government minimizes its regulation of industry and the economy. Free Enterprise System • An economic system based on private ownership, individual enterprise, and competition. Rise of Corporations • After the Civil War – many businesses became corporations to raise capital for expansion. Andrew Carnegie • Industrialist and philanthropist who built Carnegie Steel Company, later part of US Steel John D. Rockefeller • Industrialist and philanthropist • Founder of the Standard Oil Company J.P. Morgan • Banker • Controlled electrical, insurance, and shipping companies • Morgan bought Carnegie Steel in 1901, merged it with other companies and created the US Steel Corporation, the worlds largest. Cornelius Vanderbilt • Started with steamship lines • Began to buy up railroad lines in NY state. • Eventually bought up most of the lines between Chicago and Buffalo. Monopolies • Company that controls all or nearly all the business of an industry Government’s Response to Big Business • Interstate Commerce Commission – regulate railroads. • Sherman Anti-trust Act – prohibits monopolies in “restraint of trade” Interstate Commerce Act • Regulates Railroads • Forbade the practice of pools and rebates. Sherman Anti-trust Act • Prohibited trusts or other businesses from limiting competition. Labor Unions • Knights of Labor – Terence Powderly – open to skilled and unskilled workers • American Federation of Labor – Samuel Gompers – Skilled workers in specific trade unions. Urbanization • A process by which more of a nation’s population becomes concentrated in its cities. Strikes, Picketing, Boycotts • Strikes: Union workers refuse to do their jobs. • Picketing: • Boycotts: refusal t buy or use a product or service Child Labor Laws • Knights of Labor called for end to child labor. Immigration • Old: up to 1850, came from northern and western Europe, especially Ireland, Germany, and Scandinavia. Some settled in the cities, but most went out west to start farms. • New: 1850-924, came from southern and eastern Europe, especially Italy, Poland, and Russia. Did not assimilate well. Settled in cities – ghettos. Ellis Island • Receiving station – immigrants would be given a medical inspection Ethnic Ghettos • Urban areas that are dominated by a single ethnic group. Homestead Act • Provided for the settlement of western lands – gave 160 acres had to work the land for 5 years (build a well and put up a fence) Causes and Results of Great Depression • • • • • • Stock market crash Overproduction Unequal distribution of wealth Buying on Margin/Installment buying New Deal – relief, recovery, reform End - WWII Populist Party • Farmers formed this party – goals were: graduated income tax, direct election of United States senators, and government ownership of railroads, telegraphs, and telephones. Progressive Party • Progressives supported the use of government power to bring about reform. – – – – – Secret ballot Initiative Referendum Recall Direct primary