File
advertisement

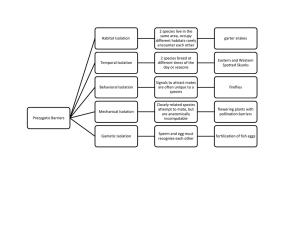
Unit Test: Evolution Study Guide Origins of Life: • Difference between a Law and a Theory • Know who Alexander Oparin, Louis Pasteur, Miller & Urey, Charles Darwin, and Lynn Margulis were and what their major contributions were to science • Primordial Soup Theory • Endosymbiotic Theory Theory of Evolution • Evidence of Evolution • Fossil record, Comparative Anatomy, Comparative Embryology, Biogeography, and Molecular Biology • Homologous, vestigial, and analogous structures • Theory of Superposition • Identify the changes through out time in human evolution in the brain size, jaw size, language, and manufacturing of tools • Know the theories behind why these changes might have occurred • Label the parts of the brain • The brain lobes • The brain stem Mechanisms of Evolution • Difference between acquired and inherited traits (Lamarck) • Geological change and overpopulation/resources theories (Lyllel & Hutton, Malthus) • Darwin’s Discoveries on the Galapagos Islands • Finches • Adaptive Radiation • The 4 conditions for natural selection • (1) Overproduction of offspring, (2) Inherited Variation, (3) Struggle to survive, and (4) differential reproduction • Mechanisms of evolution • Genetic drift, gene flow, non-random mating, mutation, natural selection • Rates of Evolution • Punctuated Equilibrium and Gradualism • 3 Types of Natural Selection • Disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection • Macro Evolution patterns • Speciation • Types of reproductive barriers: • Habitat isolation, Geographic isolation, behavioral isolation, gametic (reproductive) isolation, Mechanical Isolation, temporal isolation, Hybrid sterility, and reduced hybrid viability • Extinction • Adaptive radiation • Convergent evolution • Co-evolution Reproductive Barriers Habitat Isolation: When two species live in the same area but in different habitats Geographic Isolation: When two species live in different regions or are separated by a geographical barrier such as a mountain range, river, valley, etc. Mechanical Isolation: when two species cannot mate because they are structurally incompatible. For example, two insect species who cannot mate because the male counterpart cannot hold on to the female due to their body structure. Behavioral Isolation: When two species do not mate because they do not respond to each others mating signals or mating calls Temporal Isolation: When two species mate at different times of the day or different times of the year and thus do not interact Gametic (Reproductive) Isolation: When the egg and sperm of two species are incompatible and the sperm will not fertilize the egg. Hybrid Sterility: When two species mate and produce a hybrid offspring, however the offspring are sterile Reduced Hybrid Viability: When two species mate and produce offspring that will not survive to reach sexual maturity