Jewish Americans
advertisement

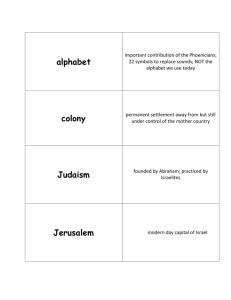
Jewish Americans HIS 206 Jewish Identity • Can be both religious & ethnic/cultural identity ▫ Use of religious symbols may be sign of cultural identity rather than religious observance ▫ 41% of Jewish Americans belong to synagogue 11% attend services weekly 28% attend at least once a month 59% attend on High Holy Days • 3 main branches of Judaism in U.S.: ▫ Orthodox (7%) – accept divine authorship of Torah & interpret it literally, maintain full observance of Law ▫ Conservative (38%) – founded in 1913 by Solomon Schecter; accept divine authorship but interpret Torah flexibly ▫ Reform (42%) – deny divine authorship of Torah & do not obey Law literally Jewish Faith • Scripture = Tenakh – acronym for Torah (Law), Nevi’im (Prophets) & Kethuvim (Writings) ▫ Orthodox also accept Talmud (Rabbinic commentaries) • In U.S., worship influenced by Christian styles ▫ Synagogue is house of worship (Beth T’filoh), study (Beth Hamidrosh), & community gathering (Beth Haknesseth) ▫ Rabbi has taken on roles of Christian minister/priest – performing rituals, preaching sermons, visiting sick, etc. ▫ Beth Din = rabbinical courts which can resolve disputes ▫ Kashruth (Kosher) = dietary laws enforced by shohets Jewish Holidays • Rosh Hashanah – New Year; begins 10 Days of Awe • Yom Kippur – Day of Atonement • Sukkot – Feast of Tabernacles to commemorate 40 years in wilderness • Pesach – Passover; commemorating escape from Egypt • Shavu’ot – Pentecost; celebrates harvest & giving of Law to Moses • Purim – commemorates Esther’s rescue of Jews in Persian Empire • Channukah – commemorates Maccabean revolt against Seleucid Empire Jewish Immigrants • 4 waves of Jewish immigration to U.S.: ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Colonial – mostly Sephardic Jews Mid-19th century – German Jews 1890-1910 – over 1 million Russian Jews Post – WWII – refugees & Holocaust survivors • Jewish-American organizations formed for various purposes ▫ Landsmanschaftn – mutual aid societies ▫ Hebrew Benevolent Society (1828) & B’nai B’rith (1845) directed charity efforts ▫ Hebrew Immigrant Aid Society helped newcomers ▫ American Jewish Committee & Anti-Defamation League combat prejudice & discrimination Anti-Semitism in America Assimilation • Ghettoes delayed assimilation ▫ In Europe, ghettoes imposed by Christians ▫ In U.S., voluntarily chosen to maintain culture & keep kashruth ▫ Often faced de facto segregation • Widespread acceptance & assimilation began during WWII ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Holocaust created great sympathy Prior to 1965, exogamy rate was 9% 25% by 1974, 52% by 1985 Black – Jewish relations often strained due to Jewish role as middlemen (landlords, shopkeepers) Hank Greenberg, Detroit Tigers