World Religions Notes
advertisement

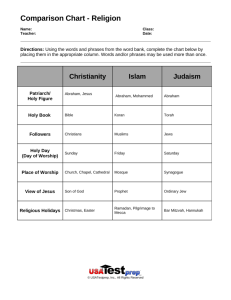
World Religions Terms: Monotheistic – belief in one god Polytheistic – belief in many gods Pious – devout/religious Atheism – belief that there is no god Agnostic – do not know if a god exists or if there is one it is impossible for humans to know it Orthodox – more traditional in their faith. Strict followers of the practices and laws. Resist the contemporary influences. Fundamentalism:. Take the Bible literally, more conservative – stay with the old ways Numbers (2007 – Fact Book) -Christians: 32% - 2,069,883,000 -Muslims 19.6% -1, 254,222,000 -Hindus 12.8% - 837,262,000 -Buddhists 6.0% - 372,974,000 -Jews .2% - 24,295,200 Judaism (Chapter 2:5) - Jewish -Believe they have a covenant (agreement) with God – they promise to obey God and he protects them. History -Abraham was a prophet sent by God to spread the belief of monotheism – one God -Abraham had two sons/two nations Isaac: his line will become the Israelites Ishmael: his line will become the Arabs -Moses led the Israelites out of Egypt/slavery into the land of Canaan -new kingdom called Israel -Great Kings ( Saul, David, and Solomon) -Kingdom divides: Israel (N) and Judah (S) -Driven out by the Assyrians in 722 BC and the Babylonians Teachings: -God is merciful and just -People serve God by studying the scriptures and practicing what they teach -Jacob was also called Israel - descendents “Israelites” -Jews believe that god will send a Messiah to save them – -Do not believe that Jesus was the Messiah Holy Books: The Bible – Old Testament Torah or the Pentateuch: the first five books of the Old Testament -given to Moses by God The rest of the Old Testament The Talmud -a collection of legal and ethical writings -a guide to civil and religious law Branches of Judaism 1. Orthodox -traditional Jewish beliefs and ways of life -Torah and Talmud revealed directly to Moses -men ware Yarmulkas (skullcaps) at all times (respect for God) 2. Reform --moral and ethical teachings more important than ritual -do not follow many of the traditional customs 3. Conservative -In between the Reform and Orthodox Structure: -Synagogue: the Jewish house of worship (aka Temple) -Rabbi : is the spiritual leader -must study to be a Rabbi -Cantor: chants the prayers Worship -in the home and Synagogue -daily prayers -Sabbath –begins Friday and sunset until Saturday and sunset Holy Days -Rosh Ha-Shanah: Jewish New Year – celebrates the creation of the world and God’s rule over it -begins ten days of Penitence ends with Yom Kippur -Yom Kippur -fast and express their regret for bad deeds during the past year and hope to live better the next year -Passover -in the spring: celebrates the Jews exodus Egypt -Hanukkah – Feast of Lights -celebrates God’s deliverance of the Jews (defeated the Syrians) -celebrated by lighting candles in the menorah Customs/Traditions -Kosher: ritually correct -no pork -store meat and milk products separately -ritual slaughter -Bar Mitzvah -celebrates a boy becoming a full member of the Jewish community -Marriage -under a canopy called a huppa – a canopy -divorce is allowed In 132 – the Jews were driven from Israel – Diaspora – scattering of the Jews -Religion survived, the state of Israel ceased to exist for 1800 yrs Christianity (Chapter 5:4) History -at the time of Jesus’ birth, Jews divided -Zealots – wanted to drive the Romans out of Judah -those that believed that the Messiah was coming -Pax Romana – Augustus was the Emperor -Christianity starts as a sect of Judaism -Rome began to recognize Christians around 65 Teachings -monotheism, Ten Commandments -love God, neighbors, enemies -promise of an eternal kingdom after death for those who sincerely repented their sins Savior -Jesus was the son of God and the incarnation of God -appealed to the poor -Most of the information about his teachings come from the Gospels (the New Testament) -many scholars believe these were written about 40 yrs after Jesus’ death Spread of Christianity -eventually broke from Judaism -the Roman road allowed for the spread of Christianity -Peter – spread the teachings throughout Palestine & Syria -Paul – spread Jesus’ teachings -stressed Jesus was the son of God and died for people’s sins -Christianity would welcome all -Rome began to persecute the Christians around the 60s -The religion grew -appealed to those who were put off by Rome’s decadence -Eventually the church evolved into the Catholic Church Holy Days -Early Christians worshipped on Saturday but around the 50s became Sunday (some still consider it Saturday -Christmas – marks the birth of Jesus -took a while to be accepted -Eastern Orthodox celebrate it in January -Easter -celebrates the resurrection of Jesus -Pentecost -celebrates when the Holy Spirit descended upon the disciples after Jesus’ death Branches: Christian Church Roman Catholic Church (West) Eastern Orthodox (1054) Islam Introduction -established by the Prophet Muhammad 610 -he was God’s messenger -only one God – Allah -Muslim: One who submits to God -2nd largest religion Development -began preaching in Mecca– but his preaching angered many and he was forced to flee to Medina – this is called the Hegira -630 he recaptured Mecca: Mecca/Medina – holy cities -soon began to spread throughout the Middle east and North Africa Teachings: -Muhammad’s revelations are preserved in the Koran (the words of God) -The Koran -parts resemble the Bible -stories from the Old and New Testament -Absolute power and unity of God -God is just and merciful -people should repent and purify in order to go to paradise after death -God sends prophets to teach people: Abraham, Moses, Jesus -Do not eat pork or drink alcohol -Against: murder, lying, stealing, adultery, -charity to the poor, hard work, -life is a period of testing and preparation for the life to come -believe in a judgement day: judged by our deeds -good go to heaven; bad to hell Practices: -Five pillars of faith 1. Profess faith in God and his prophet 2. Prayer 3. almsgiving 4. fasting 5. pilgrimage – a hajj to Mecca -Pray five times daily: called to prayer by Muezzin -wash before praying -Holy Day: Friday -Fast in the day during the holy month of Ramadan -House of Worship: Mosque -Iman: leader of the mosque Mecca -where Muslims make their hajj -the Ka’bah is located in the center -40’ x 40’ – The House of God – contains a black stone sent by God to Abraham Sects: Sunni: after the death of Muhammad the leadership passed to the caliphs elected from Muhammad’s tribe Shiites: leadership was restricted to the descendents of Ali (Muhammad’s son in law) – more conservative Today -Many believe that all Muslims are terrorists – not true only a small radical portion believe they are engaged in a holy war with the west – called a jihad – holy war. Hinduism Introduction: -oldest religion in the world -major religion of India and most important cultural influence -developed over thousands of years Beliefs: Sacred Writings: has many -Vedas: oldest sacred writings -prayers and hymns -ritual & theology -mysticism & philosophy -Puranas -long verses (stories) about Hindu myths & Gods -How the world began and periodically ends -Ramayana and Mahabharata -long epics -Bhagavad-Gita -philosophical: the meaning and nature of existence Deities: Polytheistic -Brahman: all divinities are part of this universal spirit -Brahma: creator of the universe -Vishnu: the preserver -Shiva: the destroyer -Shiva’s wife takes many forms: Kali- destroyer, Parvati- motherhood -animals and humans have souls: -some gods take the forms of animals -cows are considered sacred Different schools of philosophy: Yoga: mental and physical exercises designed to free the soul from reliance on the body There are five other schools Caste System: -Strict system of social classes 1. Brahmans: the priests and scholars 2. Kshatriyas: rulers and warriors 3. Vaisyas: the merchants & professionals 4. Sudras: the laborers and servants 5. Untouchables -today the caste system is weakened After life: -Reincarnation: -the soul never dies but reborn -Karma: -every action influences how the soul will be born in the next life -reincarnation continues until spiritual perfection is achieved: moksha Worship: -Hindus worship in temples -worship as individuals -families often have shrines to a chosen divinity Buddhism Introduction: -established around 500 bc -very influential in Asia -has combined elements of Shinto & Hinduism -Buddha means: enlightened one Establishment: -Siddhartha Gautama was from a wealthy family but he became overwhelmed that life was filled with suffering -He left his family and lived as a poor monk seeking enlightenment -He experienced enlightenment: -there is an endless cycle of reincarnation because we desire things -when he ceased to desire enlightenment, it came to him Beliefs -believed in Karma -we should eliminate attachment to worldly things -eventually we will reach the state of peace and happiness: Nirvana -to break this cycle of reincarnation and achieve Nirvana we must; Follow the Middle Way – avoid extremes Eightfold Path: knowledge & truth, resist evil, respect life, do no harm to others, hold a job that causes no harm, control feelings & thoughts, meditation Four Noble Truths -Spiritual Literature: The Tripitika -The Sangha: is the community of monks and nuns -People should seek enlightenment on their own Sects: -Theravada Buddhism: -very pious, virtues of monastic life, shave heads -Mahayana -believe there are many Buddhas -seek future Buddhas -try to be a bodhisattva: a person who vows to become a Buddha by leading a life of virtue and wisdom. -the postpone Nirvana to help others -Zen (mainly in Japan) -emphasis on a close relationship with a master and his disciples -truth is comes in a sudden flash of insight Other: The Dalai Lama – peculiar to Tibetan Buddhism -Lama means superior one -the leader of Tibet -when one Dalai dies there is the search for his successor: believed that he will immediately reincarnate into the body of his successor. -Tibet was taken over by the Chinese in 1959 and the Dalai was forced to flee to India Holy Days -Various among the different sects Questions Look at the three monotheistic religions: What is the difference between Judaism and Christianity? What is the difference between Christianity and Islam? What determines if one is living pious life? Going to heaven In Judaism: Christianity: Islam What is the attitude of each about the Judgment Day How does each religion treat the poor? What are examples in each where there has been killing the name of religion? You are logged in as Jackie Christian (Logout) WH