Chapter 8-4, 8-6, 8-17, 8-18, 8-19, 8-20 and 8-24
advertisement

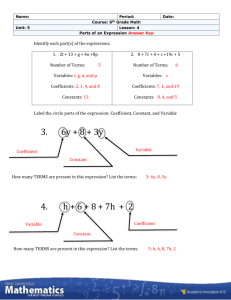
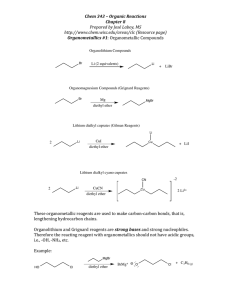
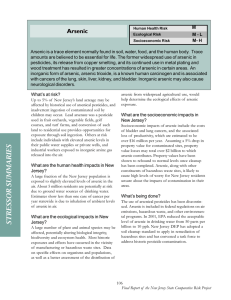
8-4. Find the activity coefficient of each ion at the indicated ionic strength: (a) (μ = 0.01 M) 3+ (b) Sc (μ = 0.005 M) 3+ (c) Eu (μ = 0.1 M) + (d) (CH3CH2)3NH (μ = 0.05 M) 8-6. Calculate the activity coefficient of Zn 2+ when μ = 0.083 M by using (a) Equation 8-6; (b) linear interpolation in Table 8-1. + − 2+ 8-17. Write a charge balance for a solution containing H , OH , Ca , + , + + , Ca(HCO3) , Ca(OH) , K , and . 8-18. Write a charge balance for a solution of H2SO4 in water if the H2SO4 ionizes to and . 8-19. Write the charge balance for an aqueous solution of arsenic acid, H3AsO4, in which the acid can dissociate to , and structure of . Look up the structure of arsenic acid in Appendix G and write the . 2+ − + + 8-20. (a) Write the charge and mass balances for a solution made by dissolving MgBr 2 to give Mg , Br , MgBr , and MgOH . 3+ 2+ 8-24. Write a mass balance for a solution of Fe2(SO4)3 if the species are Fe , Fe(OH) , , , − , and HSO 4. ,