Nucleic Acids
advertisement

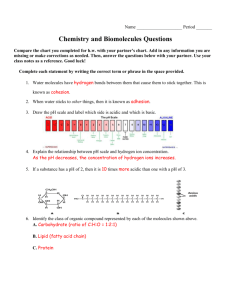
1 Name: _________________________ Date: __________ Unit 2: Ecological Biochemistry 2B Biochemistry Part 1 NOTES Organic Chemistry The study of compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Inorganic chemistry- the study of all other compounds Why is carbon so special? Carbon has four valence electrons, allowing it to form up to four bonds with many other elements. One carbon atom can bond to another, giving it the ability to form chains that are almost unlimited in length. These carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double or even triple covalent bonds. Chains of carbon atoms can even close up on themselves to form rings. HONC 1234 Organic Compounds vs. Inorganic Compounds Organic Are usually defined as compounds which contain _____________ with __________________. (May contain additional elements as well) Are produced only by living things (biotic). Range from simple to very complex. Contain strong, _____________________ bonds. Examples: CH4, C6H12O6, SUGARS, PROTEINS, FATS, OILS, DNA Inorganic Usually defined as compounds that _______________ contain carbon with hydrogen. (May contain just carbon.) Often can be formed in the non-living (abiotic) environment, but : Can also be made by/found in living things. Examples: H2O, NaCl, O2, NH3, CaCO3, CO2 Summary/Additional Notes: 2 Substance Organic? 1. sodium chloride (table salt): NaCl 2. glucose: C6H12O6 3. water: H2O 4. heating oil: C14H30 5. chitin (a protein): C8H12NO5 6. thymine (a nitrogenous base): C5H5N2O2 7. sulfuric acid: H2SO4 8. oxygen gas: O2 9. ethanol: C2H5OH 10. adenosine triphosphate (ATP): C10H16N5O13P3 11. carbon dioxide: CO2 Macromolecules The main organic molecules of living things Are ________________ made from _______________ o Monomers are small repeating units o Polymers are larger molecules made from putting the monomers together. 4 major groups of macromolecules: A. Carbohydrates B. Lipids C. Nucleic Acids D. Protein Summary/Additional Notes: Inorganic? 3 GROUP Basic Building Blocks (Monomers) Macromolecule (Polymer) Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins The exception: Lipids are not composed of monomers and polymers. Instead, they take different forms which we will discuss. Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Proteins Foods in which they are found Building and Breaking Down Macromolecules 2 major chemical processes (metabolic reactions) occur to ______________ or ____________________ organic molecules into larger or smaller units These reactions occur to build and break all four types of macromolecule (carb, lipid, nucleic acid, and protein) Dehydration synthesis Hydrolysis Summary/Additional Notes: 4 Dehydration Synthesis The chemical reaction where a large molecule is from smaller molecules by taking away a water molecule _________ Hydrolysis The chemical reaction where a large molecule is into smaller molecules by adding a water molecule disaccharide + water → yields monosaccharide + monosaccharide A. Carbohydrates Are molecules Made of the elements C, H, O in the ratio of 1:2:1 Main source of _____________ for living things They range from small, monosaccharides (_____________________) to ____________________ molecules such as disaccharides, to large polysaccharides (________________________________). Summary/Additional Notes: _____ 5 Monosaccharides smallest unit or monomer of a carbohydrate can be combined by dehydration synthesis to form larger molecules like disaccharides and polysaccharides • Examples: Glucose, Galactose, and Fructose • Chemical Formula: C6H12O6 galactose fructose glucose C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C6H12O6 Structural Isomers – same formula, but _______________ structures Another monosaccharide is ribose. It is a component of RNA (ribonucleic acid) ribose CH O 5 10 Disaccharide- a compound made by joining ___________ monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis Examples: 1. Sucrose (table sugar)- made from a glucose combined with a fructose 2. Lactose (milk sugar)- made from a glucose combined with a galactose Polysaccharides- large molecules made by combining _____________ monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis Summary/Additional Notes: 5 6 3 main examples of polysaccharides: Polysaccharide: Found in: Made of: Used for: Starch Glycogen Cellulose Structure of Polysaccharides All made of glucose monomers but in different arrangements: _________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ Why do endurance athletes often consume a diet high in complex carbohydrates while training? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ If a starch polysaccharide 100 glucose molecules long is hydrolyzed, how many water molecules are needed to break the bonds? _________________ B. Lipids Are important for energy, cell structure, and waterproof coatings. Generally _______________________ in water Contain C, H, O (NOT in a 1:2:1 ratio) Lipids do not have a repeating structural monomer unit. They do not technically form polymers. Different lipids have different structures. Summary/Additional Notes: 7 Types of Lipids *1)Fats- triglycerides that are solid at room temperature; usually from animal sources Examples: butter, shortening, lard *2) Oils- triglycerides that are liquid at room temperature; usually from plant sources Examples: sunflower oil, olive oil, corn oil 3) Waxes - ear wax, beeswax, and the waxy layer on the surface of plant leaves. 4) Steroids - cholesterol; hormones such as testosterone; pigments used in animal vision and in photosynthesis. 5) Phospholipids – important structural component of cell membranes Triglycerides Triglycerides are lipids that form when a glycerol molecule combines with 3 molecules called fatty acids. The structure of the fatty acid determines the function of the triglyceride ___________ Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty acids 1) A fatty acid is SATURATED if each carbon in a lipid’s fatty acid chain is bonded to another carbon atom by a ______________ bond (no C=C double or triple bonds) tend to form molecules called saturated fats which are at room temperature. contain the maximum amount of hydrogens possible. unfortunately, NOT very 'heart-healthy'! Summary/Additional Notes: 8 2) A fatty acid is UNSATURATED if there is at least one carbon-carbon ______________ bond (monounsaturated). A fatty acid is said to be POLYUNSATURATED if there are more than one carbon-carbon double bond tend to form molecules called oils which are _______________ at room temperature. contain fewer hydrogens these are more "heart-healthy"! Formation of Triglycerides Fatty acids are attached to the glycerol molecules by dehydration synthesis. This occurs at the carboxyl end of each fatty acid The carboxyl group can be written as COOH or -COOH. The carboxyl group contains a carbonyl (C=O) group and a hydroxyl (–OH) group. __________ __________ How many water molecules are removed in the formation of 1 triglyceride? _________ Why do you think saturated fats are solid and unsaturated fats are liquids? Think about the structure/layout of each. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Summary/Additional Notes: 9 Melting point is the temperature at which a substance melts. Which one of the fatty acids in the table is saturated? -5 ________________________ -11 Which is monounsaturated? ________________________ Which are polyunsaturated? ______________________________________ How does the number of double bonds affect the melting point? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ C. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids store and transmit hereditary, or _______________, information (EXAMPLES: DNA and RNA) Contain C, H, O, N, P. Made of monomers called ___________________ Many nucleotides come together by dehydration synthesis to form the nucleic acid polymers (DNA or RNA) Three parts to a nucleotide Nitrogenous base 5-carbon sugar Phosphate group Exception: A special nucleotide called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) stores & releases energy. ATP molecules are nucleotides but do not come together to make polymers. Notice 3 phosphate groups instead of one in the ATP nucleotide Summary/Additional Notes: 10 DNA and RNA DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid Nucleic acid that stores genetic information Holds the codes (genes) for proteins Contains the 5-carbon sugar _________________________ RNA- Ribonucleic acid The helper molecule for DNA in the making of proteins Contains the 5-carbon sugar __________________ How many nucleotides are in the nucleic acid above? _____________ Central Dogma of Molecular Biology ______________ → ______________ → _____________ → ____________ Summary/Additional Notes: