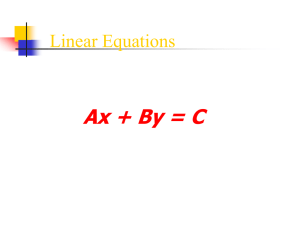x - Linear Equations
advertisement

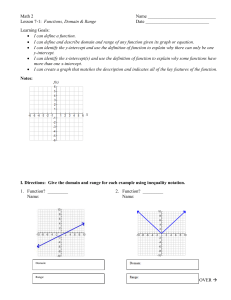
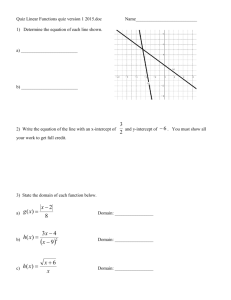
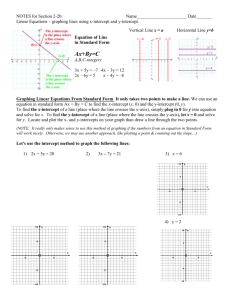
The exponent of each variable is 1. The variables are added or subtracted. A or B can equal zero. A>0 Besides x and y, other commonly used variables are m and n, a and b, and r and s. There are no radicals in the equation. Every linear equation graphs as a line. Equation is in form When B=0, then Rewrite with both variables 6y = 3 – x (add x on both sides) Multiply both sides of the equation by Multiply both sides of the equation by 3 … The following equations are NOT in the standard form of : x4 The is the point where a line crosses the . The general form of the x-intercept is (x, 0). The y-coordinate will always be zero. The is the point where a line crosses the The general form of the y-intercept is (0, y). The x-coordinate will always be zero. For the equation 2x + y = 6, we know that must equal 0. What must x equal? Plug in 0 for y and simplify. 2x + 0 = 6 2x = 6 x=3 So (3, 0) is the x-intercept of the line. y For the equation 2x + y = 6, we know that x must equal 0. What must y equal? Plug in 0 for x and simplify. 2(0) + y = 6 0+y=6 y=6 So (0, 6) is the y-intercept of the line. To find the x-intercept, plug in 0 for y. To find the y-intercept, plug in 0 for x. x-intercept: Plug in y = 0 x = 4y - 5 x = 4(0) - 5 x=0-5 x = -5 (-5, 0) is the x-intercept y-intercept: Plug in x = 0 x = 4y - 5 0 = 4y - 5 5 = 4y =y 5 (0, ) 4 is the y-intercept x-intercept Plug in y = 0 6x - 3y = -18 6x -3(0) = -18 6x - 0 = -18 6x = -18 x = -3 (-3, 0) is the x-intercept y-intercept Plug in x = 0 6x -3y = -18 6(0) -3y = -18 0 - 3y = -18 -3y = -18 y=6 (0, 6) is the y-intercept https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TNR5j9m9 yt4