Using Context Clues
advertisement

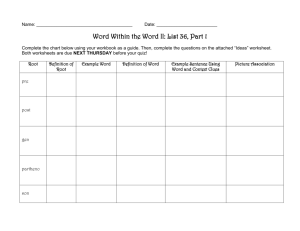
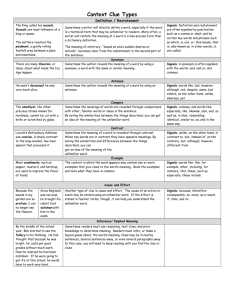
Using Context Clues Types of Clues Writers often help readers with unfamiliar words by giving clues through the use of: • punctuation marks (commas or dashes) • “signal” words (that clarify) or • whole sentences before or after the word which form a “context” that can help define the unfamiliar word. Punctuation Marks Commas, dashes, and parentheses are sometimes followed by a word or words that have the same meaning, a short definition, or an example, to help the reader. Commas, Dashes, and Parentheses Examples: •Stealthily, slowly and secretly, he crept up on his victim. •At 3:00 we’ll take a brief intermission--- a short break---and get some refreshments. •The incinerator (which is the place we burn our trash) was causing the air to heat up. Signal Words These words signal a definition, example, or synonym : or, such as, for example, which is, especially, like, that is, and in other words. Signal Words Examples: (notice the signal words) The boy stood there stolidly or with little emotion or movement. The girl cried in anguish, like a dying animal. Enunciation is extremely important in a speech. In other words, you must always speak clearly to be understood. Context of the Text When a reader encounters an unfamiliar word, he/she must use all of the clues around the word to figure it out. These are the “context” clues. Context of the Text Example: The students were exhilarated when their football team won the championship game. They celebrated, laughing and cheering, all night. What does exhilarated mean? What are the clues in the sentence that tell you this? Practice Using Context Clues Copy the following sentences in your journal. Write a definition or synonym for each underlined word. Circle the clues in the text that helped you guess the meaning of the word. 1. The indigenous (native) animals of this area are at risk due to the new construction. 2. His indisposition made him turn down the invitation. He was truly sick that day. 3. Her words were really lyrical, her friends thought she could become a poet. 4. The first class to secede, or break away, from the school group was the fifth grade class. 5. The genre, such as fiction, should be labeled on your book report. 6. She was of an indeterminate--hard to identify--age. 7. He is a skeptic, he doesn’t believe anything until you can prove it to him. 8. The impudent child got scolded by her parents for her rudeness to her brother. 9. His help was incalculable, without his countless efforts we couldn’t have done what we did. 10. The luminous light brightened our path so well that we easily found our way out. Answers 1. Native or natural to that area; clues are the parentheses ( ) around the synonym. 2. Illness; clue is the word sick. 3. Poetical; clue is the word poet. 4. Separate or break away; clue is the word or before a synonym. Answers continued 5. Type of writing; Clues are the words such as followed by an example. 6. Hard to identify or determine; clues are the dashes before and after the synonym. 7. A person that doesn’t believe easily; clues are the words/phrases believe and until you can prove it. 8. Rude; clue is the word rudeness. Answers continued 9. So much it can’t be measured, immeasurable; clue is the word countless. 10. Bright; clues are light and brightened.