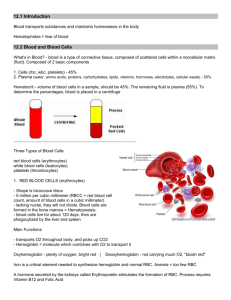
Describe the function of red blood cells.
advertisement

Topic: Circulatory system Aim: Describe the components of the blood and their functions. Do Now: Take out your blood reading notes and the Flamin’ Hot Cheetos article. What is the correct sequence or order of organs food passes through in the digestive system? HW: Read page 553 about Blood types. Copy Table 2 into your notes section. Flamin’ Hot Cheetos Why are they not recommended for children? • They lack nutritional value. Flamin’ Hot Cheetos Why are they not recommended for children? • They lack nutritional value. • Contain a lot of red food dye can turn stool of people who eat large quantities of it red • Can be a sign of over-eating • Complaints of pain in their upper abdomen, rising into their chest • People with gastroesophageal reflux should avid it bc it can lead to a flare-up. • Significant inflammation of stomach lining abdominal pain • Kids are et up for ulcerations, erosions and peptic ulcer disease • Cause gastritis bloating, burning and vomiting https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R-sKZWqsUpw • Adult = about 5L • Blood is produced in BONE MARROW Did you know… • A newborn baby has about 1 cup of blood in his body. • It would take 1,200,000 mosquitos, each sucking once, to completely drain an average human of blood. • Blood makes up about 7% of your body weight. • It only takes 20 to 60 seconds for a drop of blood to travel from the heart, through your body, and back to the heart again. Describe blood. • Liquid tissue • Transports SUBSTANCES throughout the body 1. Identify the 3 types of blood cells. • Red blood cells • White blood cells • Platelets 2. Identify another name for red blood cells. • Erythrocytes 3. Describe the function of red blood cells. • Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from cells • HEMOGLOBIN (protein) 4. Describe the shape of RBC’s. (What do they look like?) • Circular • No nucleus • Disc shaped • Biconcave • Most numerous https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_ZV5140OykE Did you know… • A red blood can make a complete circuit of your body in 30 seconds. • There are 150 Billion red blood cells in one ounce of blood 5. Identify another name for white blood cells. • Leucocytes 6. Describe the function of white blood cells. • Identify and destroy pathogens (disease-causing organism) • Produce antibodies • ENGULF pathogens • Produce ANTIBODIES 7. Describe the shape of white blood cells. (What do they look like?) • Circular • Have a nucleus • Larger than rbc’s https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z_pJBsqw8v k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0TvTyj5FAaQ 8. Identify another name for platelets. • Thrombocytes 9. Describe the function of platelets. • Involved in blood clotting and repair and regeneration of connective tissue https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=--bZUeb83uU A. Platelets stick to edge of cut B. FIBRIN is produced (long, sticky string) that sticks to cut vessel C. Web like complex of strands forms to stop bleeding CLOT D. Clot becomes hard & dry (SCAB) E. Skin cells repaired under scab and scab falls off 10. Place the blood cells in correct sequence (order) from largest to smallest. • WBC’s RBC’s Platelets 11. Identify the liquid that transports red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. • Plasma • 90% water 12. Identify other substances that are transported by plasma. • • • • • • Nutrients Metabolic wastes Enzymes Salt Proteins Antibodies https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_WrGROWd3KI Did you know… • Coconut water can be used (in emergencies) as a substitute for blood plasma. You can donate your plasma. During the actual blood donation process, your blood is drawn through a needle placed in a vein in one arm. Then a special machine separates the plasma (and often the platelets) from your blood sample. This process is called plasmapheresis. The remaining red blood cells and other blood components are then returned to your body, along with a little saline (salt) solution. Plasmapheresis is also used to treat the following: • Autoimmune diseases • Neurological diseases • Very high levels of cholesterol that are not reduced by diet and medications • Toxins that can get into your blood An average adult’s body normally contains over 35 billion WBC’s. That’s 1 for every 600-700 RBC’s. One grain of rice = 1 cubic mm • 5 million RBC’s • 5,000 – 10,000 WBC’s • 400,000 platelets Let’s summarize… 1. Identify the four parts of the blood. 2. Describe the function of plasma. 3. Describe the function and shape of red blood cells. 4. What do red blood cells contain? 5. Describe the function and shape of white blood cells. 6. Describe the function and shape of platelets. Review: Identify the part of blood being described. 1. Most numerous blood cell. Red blood cells 2. Carries enzymes and nutrients. Plasma 3. Involved in blood clotting. Platelets 4. Carries oxygen. Red blood cells 5. Largest blood cell. White blood cells 6. Made up of 90% water. Plasma 7. Involved in blood clotting. Platelets 8. Protect the body against disease. White blood cells 9. Carries hormones. Plasma 10. Contains hemoglobin.Red blood cells https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CRh_dAzXuoU&index=2&list=PL23D6FD0A9F7DB51D 1. Identify structures A, B and C. 2. Identify the function of each structure. 3. Identify the fluid that transports these structures. A B C C What is a major difference between red blood cells and white blood cells? 1. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, but white blood cells do not. 2. Red blood cells can move, but white blood cells cannot. 3. Red blood cells contain nuclei, but white blood cells do not. 4. Red blood cells engulf foreign bacteria, but white blood cells do not. What component of blood is important in healing wounds on the skin? 1.red blood cells 2.urea 3.platelets 4.white blood cells Where are red and white blood cells made in the body? 1.in lymph nodes 2.in bone marrow 3.at the sinoatrial node 4.in the heart What component of blood plays a role in protection against disease? 1.white blood cells 2.platelets 3.urea 4.red blood cells Which blood component is a liquid? 1.platelets 2.white blood cells 3.plasma 4.red blood cells What is a pickup function of blood? 1. picks up urine from the bladder 2. picks up undigested food from the large intestine 3. picks up carbon dioxide from the air in the lungs 4. picks up carbon dioxide waste from cells. Oral cavity A Esophagus C B Salivary glands Liver H I Gall bladder J Large intestine D Stomach E Pancreas Small intestine F G Rectum