MT: Ch. 7: Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System
advertisement

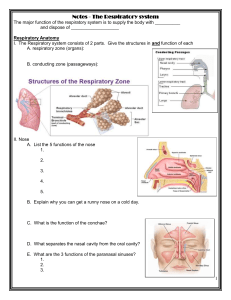
MT: Ch. 7: Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System __________ fresh __________ into lungs ____________ __________ for _____________ ____________ ________ air Organs of the Respiratory System Nasal cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchial tubes Lungs Respiratory System Combining Forms alveol/o alveolus; air sac anthrac/o coal atel/o incomplete bronch/o bronchus bronchi/o bronchus bronchiol/o bronchiole Respiratory System Combining Forms coni/o dust diaphragmat/o diaphragm epiglott/o epiglottis laryng/o larynx lob/o lobe nas/o nose orth/o straight, upright ox/o, ox/i oxygen pharyng/o pharynx pleur/o pleura pneum/o lung, air pneumon/o lung, air pulmon/o lung rhin/o nose sinus/o sinus, cavity spir/o breathing trache/o trachea, windpipe Respiratory System Suffixes –capnia carbon dioxide –ectasis dilated, expansion –osmia smell –phonia voice –pnea breathing –ptysis spitting –thorax chest Anatomy and Physiology Cells of body require ____________ gas exchange Delivery of ______________ Removal of ________________ Respiratory system works in conjunction with ______________________ to meet this need Respiration Must be _______________ to meet cells’ needs (O2 is NOT stored in body) Subdivided into three distinct parts: 1: Ventilation Flow of air between ___________ environment and ____________ 2: Inhalation Flow of air into ____________ Brings fresh ____________ into air sacs 3: Exhalation Flow of air out of ____________ Removes __________________ from body External Respiration Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in _________ Gases diffuse in opposite directions Oxygen Leaves ___________ and enters ___________ Carbon dioxide Leaves _____________ and enters __________ Internal Respiration Oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange at ____________ Oxygen Leaves _____________ and is delivered to _________ Used immediately for _______________ Carbon dioxide Waste product of metabolism Leaves ____________ and enters ____________ Respiratory System Organs Nasal Cavity Air enters through ________________ Nasal cavity divided by ______________ ___________ in roof of mouth separates nasal cavity above from mouth below ___________ Small ________ line opening to nasal cavity _________ out large dirt particles before they can enter lungs Walls of nasal cavity and nasal septum Made of flexible ____________ Covered with ______________________ Much of respiratory tract is covered with mucous membrane ___________ is thick and sticky secretion of membrane _________ air by trapping dust and bacteria ____________ in mucous membranes ____________ air _____________ air Paranasal sinuses Located within _________________ Echo chamber for ____________ production 1 Gives resonance to voice Pharynx Commonly called ______________ Used by respiratory and ____________ systems At end of pharynx Air enters _____________ Food and liquids enter _______________ Three Subdivisions of Pharynx 1: _________________ Upper section by nasal cavity 2: __________________ Middle section by oral cavity 3:___________________ Lower section by larynx Tonsils _______________ tissue Removes _____________ in air and food Three pairs 1: _____________ 2: ______________ 3: _______________ Eustachian or Auditory Tube Opening found in ______________ Other end opens into ______________ Tube opens with each ______________ Equalizes __________ pressure between middle ear and outside atmosphere Larynx Commonly called _____________ ____________ tube between pharynx and trachea Contains ______________ Walls of larynx Composed of ____________ plates Held in place by ligaments and muscles Thyroid cartilage forms the _____________ Vocal Cords Folds of membranous tissue Not actually cord-like in structure ___________ to produce _____________ as air passes through opening between folds Called glottis Epiglottis Flap of ______________ Sits above glottis Covers ________ and __________ during _____________ Food goes into esophagus - Not into trachea Trachea Commonly called ________________ Carries air from larynx to main ______________ Approximately four inches in length Tube composed of: Smooth ____________ _______________ rings Lined with ___________________ and ___________ Assists in ____________, _____________, and _______________ air as it travels to lungs Bronchial Tubes Distal end of ______________ divides Forms left and right main or ________________ Each bronchus enters a lung ____________ to form secondary bronchi Alveoli Bronchi continue to branch to form narrow __________ Bronchiole terminates in ______________ Approximately 150 million alveoli in each lung Respiratory Membrane ___________________ encase each alveolus Alveoli wall + capillary wall forms respiratory membrane ______________ respiration takes place across respiratory membrane Lungs Each is total collection of ____________, ___________, and _____________ Two lungs Right lung has ____________ lobes Left lung has ___________ lobes Spongy because they contain __________ Apex Pointed ____________ portion Base Broad ____________ area Hilum _________ and __________ point Bronchi, blood vessels, nerves Protected externally by the ____________ Protected internally by double membrane called ______ Pleura ____________ pleura ______ membrane that lines wall of chest cavity ______________ pleura _____ membrane that adheres to surface of lungs Pleura is folded to form a sac around each lung called ____________ ______________ between two pleural layers reduces ___________ when two layers rub together during ventilation 2 Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) It is important to measure actual ___________ of air flowing in and out of lungs Can then determine lung ____________ Respiratory therapist Measures lung volumes Pulmonary function tests Respiratory Muscles - Inhalation Diaphragm ________ separates abdomen from thoracic cavity Contracts and moves down into abdominal cavity Causes decrease of pressure, ___________________, within chest cavity Air ______________ lungs (inhalation) to equalize pressure Intercostal muscles Located between ______________ ____________ rib cage to further enlarge thoracic cavity Increases ______________ pressure Assists with _____________ inhalation Respiratory Muscles - Exhalation Unforced exhale results when: ___________ and ___________ muscles _________ Thoracic cavity becomes smaller Creates _____________ thoracic pressure Air flows _________ of lungs to equalize pressure For forceful exhale Use ___________ chest and neck ___________ to further decrease size of thoracic cavity Create greater ___________ pressure Word Building p. 217-218 Respiratory System Vocabulary p. 218-220 Respiratory System Pathologies p. 220-223 - Take notes during class Diagnostic Procedures p. 223-224 Take notes during class Therapeutic Procedures p. 225-226 Take notes during class Pharmacology p. 227 Take notes during class Abbreviations to know p. 227: ABGs ARDS Bronch Co2 COPD CPR C&S CXR ENT LLL LUL O2 RA RLL RML RUL SARS SIDS SOB TB URI Respiratory Rate One of the vital signs (_________), along with heart rate, temperature, and blood pressure Respiratory rate dependent on level of _________ in blood When CO2 level is ___________, we breathe more ______________ to expel excess If CO2 levels _____________, respiratory rate will also __________ until CO2 builds up in bloodstream Respiratory Rates by Age Group Age Respirations per Minute Newborn 30–60 1-year-old 18–30 16-year-old 16–20 Adult ____________ 3