Animals!! - ywillard
advertisement

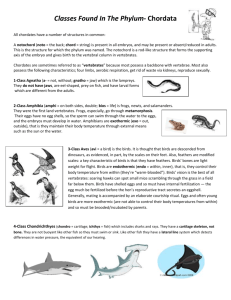
Animals!! Characteristics Cannot make their own food Digest their food Move from place to place Many celled Eukaryotic Classicfication Vertebrates: animals with a backbone Fish, birds, mammals Invertebrates: animals without a backbone Sponges, jellyfish, worms and insects. Symmetry Radial symmetry: body parts are arranged in a circle around a center point. Bilateral symmetry: body parts arranged in the same way on both sides of its body. Invertebrates Sponges Live in water Get food from water through pores No symmetry Cnidarians Sting food and eat it Live in water Have tentacles Radial symmetry Example: Jellyfish Flatworms Flat Live inside something else (parasites) Bilateral Symmetry Examples: Tapeworm and planarian Roundworms Round Live inside something else (parasites) Bilateral symmetry Examples: Hookworms Segmented Worms Body has segments Bilateral Symmetry Examples: Earthworm and leeches Mollusks • • • • • Live in water Many have shells Have soft bodies Bilateral Symmetry Examples: Snail, Clam, Slug, Octopus, Oyster, Scallop Echinoderm Spiny body Live in the oceans Radial symmetry Starfish, sea urchin, sea cucumber, sand dollar Arthropods Jointed legs Harder outer coat Have segmented bodies Examples: Spiders, Flies, Crabs Crustaceans Large claws 2 body parts Most live in water 8 legs Examples: Crab, Lobster, Shrimp Centipedes and Millipedes Centipedes: Flat, 2 legs on each segment Millipedes: Round, 4 legs on each segment Spiders and their relatives 2 body parts 8 legs Examples: spiders, ticks, scorpions Insects 3 body parts 6 legs Sometimes antenna: used for feeling Sometimes they have wings Vertebrates Vertebrate Characteristics: They have backbones. They belong to the phylum Chordata. Chordates are: A huge phylum that has subphyla called vertebrata, tunicates and lancelets All chordates have a notocord, which is a: flexible rod-like structure along the dorsal side of an animal They also have a Dorsal hollow nerve cord: tubular bundle of nerves that lies above the notocord. Lastly, they have gill slits: paired openings located in the throat behind the mouth. What is an endoskeleton? Vertebrae (bones that cover the dorsal nerve cord) and other bones that are internal. Endomeans within. Supports and protects the internal organs What is an ectotherm? An animal whose internal body temperature changes when the environment temperature changes. Otherwise known as cold blooded. What is an endotherm? Animals that keep a constant internal body temperature even when the environment temperature changes. Fish They are ectotherms. They have gills for breathing. Most fish are going to have fins. These are used for steering, balancing and moving. Fish have scales. These are: hard, thin, overlapping plates that cover the skin and protect the fish’s body. They are made of bone. Fish are broken up into 3 groups. These groups are the jawless fish, the cartilaginous fish and the bony fish. An example of a jawless fish is a sea lamprey. They have round mouths and their bodies are long and tubelike. They have slimy skin and no scales. Their bodies are made of cartilage. Cartilage: tough, flexible tissue that is not as hard as bone. Cartilaginous fish have skeletons made of cartilage. Unlike the jawless fish though, these fish have moveable jaws and they have scales that feel like sandpaper. An example would be a shark. Bony fish have skeletons made of bone. Gills are covered with a Hard gill cover. Some examples of bony fish are tuna, yellow perch, and salmon. Amphibians: Amphibians are: ectothermic vertebrates that lives part of this life in the water and part of its life on land. They have moist skin, which is smooth and does not have scales. oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged through the skin. They also have sac-like lungs in their chest that they use for breathing. Amphibians hibernate during the winter. Hibernation: that period of inactivity and lower metabolic needs during the winter. They also do something called estivation during the summer months when the weather is extremely hot. Estivation: a period of inactivity and lower metabolic needs during the hot, dry summer months. Their skeleton is made of bones. Some examples are frogs, toads, salamanders and newts. What is metamorphosis? A series of changes that a larva goes through to become an adult. Their larva stage is spent in water and their adult stage is on land. Reptiles: A reptile is: ectothermic, vertebrate with dry, scaly skin. Examples of reptiles are lizards, snakes, turtles, crocodiles and alligators. They have a thick, waterproof skin. They also have scales that prevent them from drying out. Most reptiles have four legs. Which ones don’t? SNAKES! The four legs are have claws that help them to hold their body off the ground which helps them walk faster. They also use their claws to dig and climb. Reptiles breathe with lungs. The young develop in an amniotic egg: leathery egg that provides a complete environment for the developing embryo. Turtles: found on almost every continent and most of the world’s oceans. They are covered by a thick, hard shell. They do not have any teeth. They feed on insects, worms, fish, and plants. Crocodiles and alligators: largest reptiles. Found in or near water. Crocs have long, slender snouts and are very aggressive. Alligators are less aggressive and have very broad snouts. Lizards and snakes: largest group of reptiles. Lizards have movable eyelids, external ears, legs with claws on each foot. They eat meat and vegetables. Snakes hear vibrations not sound waves. They smell with their tongue. They eat meat. Birds: Birds are vertebrates. They are also endotherms. Birds have feathers and scales. As you may know they are the only animal that has feathers. Birds also lay eggs. The eggs that they lay though are not like reptile eggs. They are not leathery. They have a hard shell instead. The parents incubate their eggs. What does it mean to incubate? Keep the eggs warm by sitting on them. Birds have four legs but their front legs are actually wings. Their back legs support them and they usually have claws on their toes. Birds also do not have teeth. They have a beak instead. If you eat eggs, you know what an egg looks like. The eggs that they lay are also called amniotic eggs. Birds can lay two to eight eggs at one time. Birds have two types of feathers. They are contour feathers and down feathers. Contour feathers: strong and lightweight. Give birds their color and their shape. Use these to fly. They help with steering and keeps them from tipping over. Down feathers: soft and fluffy. Provide insulation in adult birds and cover the body of baby birds. Help birds to keep their constant temperature. Something that you might not know about birds is that their bones are hollow. This is going to make the bird lighter making it easier for the bird to fly. Birds generate their body heat from their food. This is how they maintain their body temperature. Mammals: Mammals are: endothermic vertebrate. Have hair and produce milk to feed to their young Mammary glands: produce the milk female mammals use to feed their young. Oil glands are used to lubricate hair and skin. Sweat glands are used to help an animal stay cool. Animals also have scent glands which can be used to marking territory, attracting mates and for defense. Mammals all have hair at sometime in their lives. Some have a lot of fur. This fur is going to traps air to keep them warm. Some only have little hairs. Some have hairs that have changed over time into quills. What kinds of animals have quills? porcupines All animals have teeth. You can tell what an animal eats by looking at its teeth. There three ways to classify animals by the way that they eat. Herbivores: animals that only eat plants Carnivore: animal that only eats other animals Omnivore: animals that eat both plants and animals. There are three different ways that animals can be classified. They are monotremes, marsupials, and placental mammals. Monotremes: mammals that lay eggs with tough, leathery shells. Marsupials: pouched mammals that give birth to tiny, immature offspring. Placental Mammals: embryos develop inside the uterus of the female. The time that it takes for the embryo to develop is called the gestation period. Have a placenta: a sac-like organ developed by the embryo that attaches to the uterus. It absorbs oxygen and food from the females blood. It does this through the umbilical cord: attaches the embryo to the placenta.