The history of the Silk Road Final Project LSEC 1103 Early history
advertisement

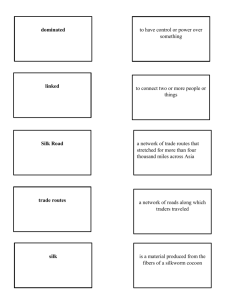
The history of the Silk Road 1 Final Project LSEC 1103 Early history The story of the Silk Road relates to a network of trade routes which were known as the Silk Route. This great East to West route began well over 2,000 years ago in the 2nd century BC. It was not until the 1870s that a German geographer gave it the name of ‘The Silk Road’. Trade using this route is regarded as playing an important role in the development of the great civilisations of China, Egypt, Persia, Arabia and Rome. “Even before the discovery of silk there was a vast amount of trade already taking place in Central Asia and China” (Rowan, N. 2006) The Silk Road is actually a misnomer as it is actually a network of caravan tracks which connected Asia, Africa and Europe. Although it is named after the profitable Chinese silk trade many other goods were traded. Heading west to Europe were luxury goods such as porcelain, furs and spices as well as gunpowder and paper products. Moving in the other direction were cosmetics, gold, silver and glass. Animals such as horse, camels and elephants made the trip. Not only goods travelled between east and west but also culture, art, philosophies and beliefs. 2 Development These trade routes extended for around 6,500 kilometres and the overland routes stretched from the ancient cities of China and divided into northern and southern routes. The northern route travelled from the Shaanxi Province in central China which branched into separate routes across mountains and deserts before rejoining in Turkmenistan. This was a route for caravans which brought in delicacies such as dates and saffron from Persia, frankincense and myrrh from Somalia, glass from Egypt and sandalwood from India. In exchange caravans returned with item such as silk brocade and lacquer ware. The southern route was basically a single route running through China to Karakoram and is now a paved road which connects China and Pakistan. The ancient route continued through Afghanistan to Mesopotamia, through the Arabian desert to the Mediterranean and thence to Rome. The land route continued to North Africa. The most important period for the Silk Road was during the Tang dynasty in the th 7 century AD. The city of Changan - the starting point of the road – had grown into a large cosmopolitan city of city. By 742 AD the population had reached almost 2 million and the census of 754 AD showed 5,000 foreigners living there. Turks, Indians and Indians had come along the road as well as Koreans and Japanese from the East. All manner of rare plants could be found in the local bazaars. The Silk Road began to decline after this period, partly due to the development of sea routes. Another factor was desertification which meant that many of the settlements along the road simply disappeared: swallowed up by the desert. Another contributing factor was the closing up of China by the Ming and Qing dynasties and it would not be until the 19th century that Western powers made inroads into China. 3 Modern developments After a lengthy period of hibernation the Silk Road is beginning to regain its importance. With the opening up of China the route itself is being reopened. The latest link in the history of the Silk Road happened when China and Kazakhstan were connected by rail in 1990. Since 2008 this line has been used as a direct passenger service between the two countries. With the opening of the USSR trade has begun to flow again in Central Asia. Nowadays the trade is not silk and furs but oil. The Silk Road is also becoming a tourist destination. 601 words Bibliography Hirst, �. K. (n.d.). Along the Silk Road - Archaeology and History Along the Silk Road. Archaeology - The Study of Human History in Archaeology. Retrieved October 4, 2011, from http://archaeology.about.com/cs/asia/a/silkroad.htm Rowan, N. (2006). The Silk Road Society - A Detailed History of the Silk Roads. The Silk Road Society - Home. Retrieved October 4, 2011, from http://www.travelthesilkroad.org/content/view/15/29/ Silk Road - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Retrieved October 4, 2011, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silk_Road The Silk Road: History. (n.d.). The Silk Road: Luxury Travel Through An Ancient Land. Retrieved October 4, 2011, from http://www.silkroad-hotels.com/history.html "The Silk Road." ThinkQuest : Library. N.p., n.d. Web. 4 July 2011. <http://library.thinkquest.org/13406/sr/>. The Silk Road Project - Silk Road Maps. (n.d.). The Silk Road Project. Retrieved June 24, 2013, from http://www.silkroadproject.org/tabid/177/d Wild, O. The Silk Road . UCI Department of Earth System Science. Retrieved October 4, 2011, from http://www.ess.uci.edu/~oliver/silk.html