Topic F: Chemical Bonding
advertisement
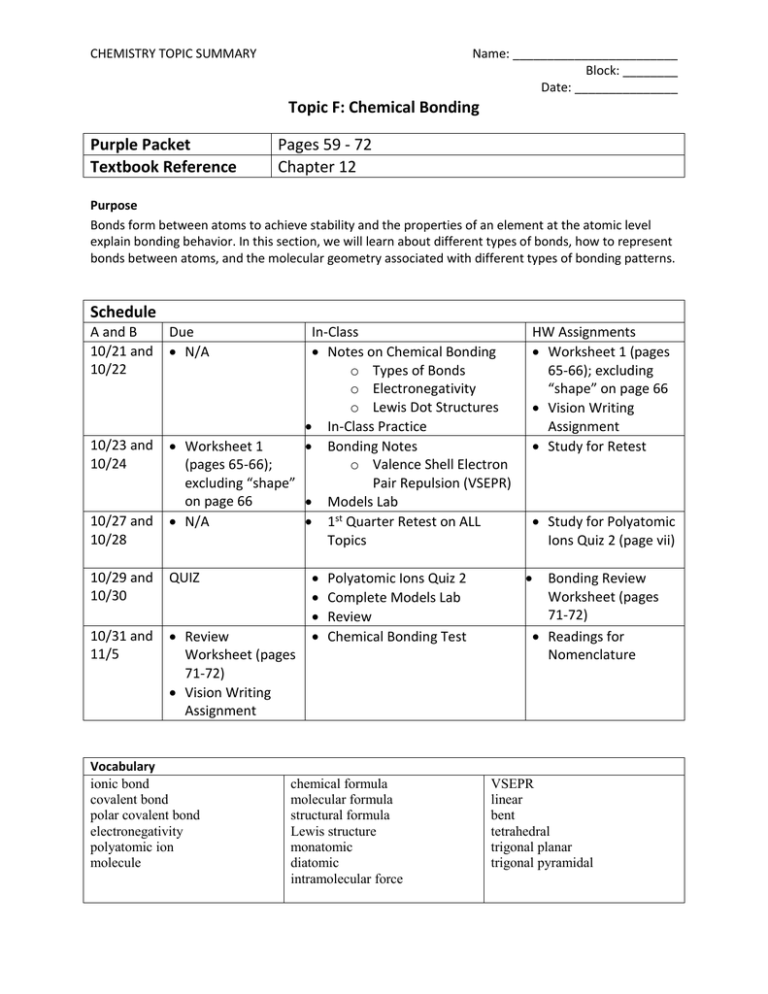
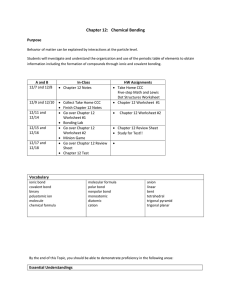
CHEMISTRY TOPIC SUMMARY Name: ________________________ Block: ________ Date: _______________ Topic F: Chemical Bonding Purple Packet Textbook Reference Pages 59 - 72 Chapter 12 Purpose Bonds form between atoms to achieve stability and the properties of an element at the atomic level explain bonding behavior. In this section, we will learn about different types of bonds, how to represent bonds between atoms, and the molecular geometry associated with different types of bonding patterns. Schedule A and B 10/21 and 10/22 10/23 and 10/24 10/27 and 10/28 Due N/A In-Class Notes on Chemical Bonding o Types of Bonds o Electronegativity o Lewis Dot Structures In-Class Practice Worksheet 1 Bonding Notes (pages 65-66); o Valence Shell Electron excluding “shape” Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) on page 66 Models Lab N/A 1st Quarter Retest on ALL Topics 10/29 and 10/30 QUIZ 10/31 and 11/5 Review Worksheet (pages 71-72) Vision Writing Assignment Vocabulary ionic bond covalent bond polar covalent bond electronegativity polyatomic ion molecule Polyatomic Ions Quiz 2 Complete Models Lab Review Chemical Bonding Test chemical formula molecular formula structural formula Lewis structure monatomic diatomic intramolecular force HW Assignments Worksheet 1 (pages 65-66); excluding “shape” on page 66 Vision Writing Assignment Study for Retest Study for Polyatomic Ions Quiz 2 (page vii) Bonding Review Worksheet (pages 71-72) Readings for Nomenclature VSEPR linear bent tetrahedral trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal By the end of this Topic, you should be able to demonstrate proficiency in the following areas: Essential Understandings The concepts developed in this standard include the following: Lewis dot diagrams are used to represent valence electrons in an element. Structural formulas show the arrangements of atoms and bonds in a molecule and are represented by Lewis dot structures. Bonds form between atoms to achieve stability. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between ions. Elements with low ionization energy form positive ions (cations) easily. Elements with high ionization energy form negative ions (anions) easily. Polar bonds form between elements with very different electronegativities. Non-polar bonds form between elements with similar electronegativities. Polar molecules result when electrons are distributed unequally. Knowledge, and Skills In order to meet this standard, it is expected that students will predict, draw, and name molecular shapes (bent, linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, and trigonal pyramidal). draw Lewis dot diagrams to represent valence electrons in elements and draw Lewis dot structures to show covalent bonding. use valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model to draw and name molecular shapes (bent, linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, and trigonal pyramidal). recognize polar molecules and non-polar molecules.