Chapter 4 - Problem Solving
advertisement

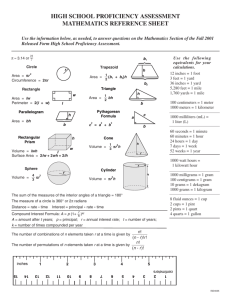
Chapter 4 Problem Solving in Chemistry Charles Page High School Dr. Stephen L. Cotton 1 Section 4.1 What Do I Do Now? OBJECTIVES: –List several useful problem-solving skills. 2 Section 4.1 What Do I Do Now? OBJECTIVES: –Describe the three-step problemsolving approach. 3 Word Problems The laboratory does not give you numbers already plugged into a formula You have to decide how to get the answer. Like word problems in math. The chemistry book gives you word problems (just like real life!) 4 Problem solving 5 1. ANALYZE a) Identify the unknown Both in words and what units it will be measured in. Write it down! May need to read the question several times. b) Identify what is given (the “known”) Write it down! Unnecessary information may also be given Problem solving c) Plan a solution The “heart” of problem solving Break it down into steps. Look up needed information: Tables Formulas Constants, or conversion factors *Choose an equation 6 Problem solving 2. CALCULATE doing the arithmetic; use of calculator? 3. EVALUATE Round off to proper # of sig. figs. Proper units? Need Scientific Notation? Check your work! Reread the question, did you answer it? Is it reasonable? Estimate an approximate answer 7 Example of Problem Solving Remember to: –Analyze –Calculate –Evaluate Sample problem 4-1, page 86 Sample problem 4-2, page 87 8 Section 4.2 Simple Conversion Problems OBJECTIVES: –Construct conversion factors from equivalent measurements. 9 Section 4.2 Simple Conversion Problems OBJECTIVES: –Apply the techniques of dimensional analysis to a variety of conversion problems. 10 Conversion factors A “ratio” of equivalent measurements Start with two things that are the same: one meter is one hundred centimeters write it as an equation 1 m = 100 cm can divide by each side to come up with two ways of writing the number 1 11 Conversion factors 1m 100 cm 12 = 100 cm 100 cm Conversion factors 1m 100 cm 13 = 1 Conversion factors 1m 100 cm 1m 1m 14 = = 1 100 cm 1m Conversion factors 1m 100 cm 1 15 = = 1 100 cm 1m Conversion factors A unique way of writing the number 1 In the same system they are defined quantities so they have unlimited significant figures Equivalence statements always have this relationship big # small unit = small # big unit 1000 mm = 1 m 16 Write the possible conversion factors for the following: Between kilograms and grams between feet and inches using 1.096 qt. = 1.00 L 17 What are they good for? We can multiply by one creatively to change the units . 13 inches is how many yards? 36 inches = 1 yard. 1 yard =1 36 inches 13 inches x 1 yard = 36 inches 18 What are they good for? We can multiply by a conversion factor to change the units . Problem: 13 inches is how many yards? Known: 36 inches = 1 yard. 1 yard =1 36 inches 13 inches x 1 yard = 0.36 yards 36 inches 19 Conversion factors Called conversion factors because they allow us to convert units. really just multiplying by one, in a creative way. 20 Dimensional Analysis A way to analyze and solve problems, by using units (or dimensions) of the measurement Dimension = unit (such as g, L, mL) Analyze = solve Using the units to solve the problems. If the units of your answer are right, chances are you did the math right! 21 Dimensional Analysis A ruler is 12.0 inches long. How long is it in cm? ( 1 inch = 2.54 cm) in meters? A race is 10.0 km long. How far is this in miles? – 1 mile = 1760 yds – 1 meter = 1.094 yds Pikes peak is 14,110 ft. above sea level. What is this in meters? 22 Dimensional Analysis Problem: Jules Verne wrote a book 20,000 leagues under the sea. How far is this in feet? Sample 4-5, page 93 23 Another measuring system has different units of measure: 6 ft = 1 fathom 100 fathoms = 1 cable length 10 cable lengths = 1 nautical mile 3 nautical miles = 1 league Converting Between Units We often need to express a measurement in different units from the one given or measured. Use dimensional analysis! Remember to: –Analyze –Calculate –Evaluate 24 Converting Between Units Sample 4-6, page 94 Sample 4-7, page 94 25 Section 4.3 More Complex Problems OBJECTIVES: –Solve problems by breaking the solution into steps. 26 Section 4.3 More Complex Problems OBJECTIVES: –Convert complex units, using dimensional analysis. 27 Multistep Problems Many complex tasks in daily life are handled by breaking them down into manageable parts Consider cleaning a car: –vacuum the inside –wash the exterior –dry the exterior –apply a coat of wax 28 Multistep Problems When converting between units, it is often necessary to use more than one conversion factor. Sample 4-8, page 97 Sample 4-9, page 98 29 Converting Complex Units By complex, we mean units that may be expressed as a ratio: –speed is: miles/hour –gas mileage is: miles/gallon –density is: g/cm3 Sample 4-10, page 99 Sample of ft2 to yd2 and mm3 to cm3 30