Unit II Part 2 - Grosse Pointe Public School System
advertisement

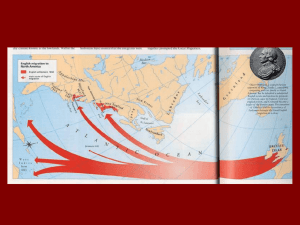
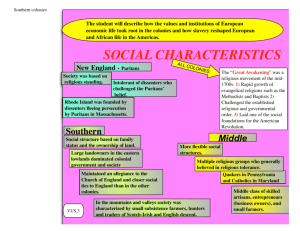
1607-1763 Unit II Part 2 The New England Colonies Remember James I gave out 2 charters in 1606 The First was to the London Co. which settled Jamestown The Second charter was given to the Plymouth Co (Later to be called the Council of NE) which was to make settlements in the northern region of “Virginia” Remember, at first it was ALL Virginia The Pilgrims v The Puritans Puritans were people who wanted to PURIFY the Anglican Church (the Church of England) In England they wanted separation of church and state Pilgrims were sometimes called Separatists because they had given up on purifying the Anglican Church and had separated from it. Pilgrims v Puritans There were only 35 Pilgrims who came over on the Mayflower in 1620. They were supposed to settle in the Southern region under the jurisdiction of the London Co. BUT the voyage was rough. December storms blew them way off course and they ended up in Cape Cod Bay in Mass. The Pilgrims: Background After the death of Elizabeth I, religious dissenters were increasingly persecuted Many found refuge in the Netherlands The Dutch were very tolerant. This is partly why they had such success in trade No one in the Netherlands was persecuted for religious reasons BUT there WERE problems for the transplanted Puritans and Pilgrims Problems in the Netherlands Since all religions were tolerated, the Pilgrims and Puritans were surrounded by infidels! Foreigners could find work in the Netherlands but the good-paying jobs were reserved for Dutch citizens English children were growing up Dutch! The Scrooby Group 35 Pilgrims who had traveled from Scrooby to the Netherlands got permission from the London Co. to settle in the Southern region They shared the ship, The Mayflower, with 67 others who the Pilgrims called Strangers The Pilgrims The December seas were rough and they were blown off course and ended up in the jurisdicion of the Plymouth Co. All aboard signed the Mayflower Compact before they got off the ship An agreement to abide by the laws that they would all make together…a recognition of their interdependence The Plymouth Plantation The Pilgrims DID get permission to stay in Plymouth Pilgrims were met by Squanto and Samoset who had had contact with John Smith earlier and spoke English Rough first winter. ½ died Were later aided by the natives: what to eat, how to hunt, etc. = Thanksgiving The Plymouth Plantation Governor Bradford Elected 30 times Wrote The History of the Plymouth Plantation Settlement grew slowly After 10 years the population of 300 shared one plow between them Was eventually swallowed up by the Puritans The Puritans “The great migration of the 17th century” refers to the migration of thousands of Puritans to the New World In 1630 Puritans on 17 ships with 1000 (families and their servants) sailed to the New World Settled in the Boston-Salem area Was called the Mass. Bay Co. The Mass. Bay Co. Their first governor: Winthrop Goal: to build A City on a Hill A model Christian community for all the world to see…a utopia Established a theocracy Industrious, prosperous By 1640 10,000 settlers Big interest in Education Puritan belief: Everyone should be able to read the Bible 1636 Harvard established to train ministers 1647 Mass. General School Act: communities taxed to support free public schools Critics were ousted 1635 Thomas Hooker wanted separation of Church and state Was ousted 1636 established Hartford Hartford and nearby communities drew up a constitution The Fundamental Orders of Conn.: first written constitution that really worked. Provided for 3 branches of government More Critics 1636 Roger Williams also wanted separation of Church and state AND suggested that the land they were occupying rightfully belonged to the Indians Was banished and founded Rhode Island Plantation Agreement at Providence (constitution) RI was first for religious freedom Ann Hutchinson Was also a critic but a woman and did not object to theocracy Said only members of the elect should hold civil office The Elect: those who had had a revelation of some sort and were sure of salvation Anne Hutchinson Belief was that the Age of Revelation had passed BUT Hutchinson claimed to have had a revelation! (A mere woman!) Was tried for heresy and banished (was pregnant) She was killed by Native Americans in NY in 1643 One of her followers founded New Hampshire New England Confederation Native Americans were a problem for all New England Confederation was an organization of different New England communities for defense against the Indians 1692 Salem Witch Trials Hanged: 19 people and two dogs Pressed: 1 Giles Corey Hysteria Girls and family slave Ergot? A mold growing on rye having hallucinogenic effects In Europe 500,000 killed between 15th and 17th centuries In the colonies: no more deaths but trials in Va. In 1706 and NC in 1712 The Dominion of New England King James II revoked charters of all colonies N. and E. of Penn and organized them into one Royal Colony: The Dominion of NE Royal Governor was Andros The Dominion ended with Wm and Mary 1689 The Toleration Act of 1689 Ended religious persecution Granted freedom of worship to all but Catholics and Unitarians Did NOT establish religious equality BUT Church attendance no longer required for voting The Half-Way Covenant The Puritans believed that the Age of Revelation had passed How to keep Church membership? The Half-way Covenant: Allowed the children of persons of good character to be baptized into the Church The Three Regions of the English Colonies New England: Mass. Conn., RI, NH Mid-Atlantic: NY, NJ, Penn, Delaware Southern: VA, NC, SC, Maryland, Georgia The Three TYPES of Colonies Charter: the governor is chosen by the people of the colony Proprietary: the governor is or is chosen by the proprietor Royal: the Governor is chosen by the King By the time of the Revolution… All colonies were Royal Colonies The English Civil War and Interregnum 1649-59 Cromwell’s followers = Roundheads Charles I’s followers = Cavaliers Cavaliers migrated to VA when it was clear that the King was losing the war The Other Colonies Maryland: the first Proprietary Colony Lord Baltimore (George Calvert) got a charter from Charles I Established Maryland as a bastion for Catholics 200-300 sailed on the Arc and the Dove Established a headright system to attract new settlers Maryland But then, Protestants came over The Maryland Toleration Act (to safeguard the rights of Catholics) was passed by the colonial legislature (1649) BUT was repealed by Protestant majority in 1655 causing a Civil War in Maryland! Grew tobacco like VA The Carolinas (Proprietary) 1660 Charles II gave a huge area to 8 favorites S. of VA Offered the Headright system Insured that nearly all white settlers owned property and had political power John Locke Drafted the Fundamental Constitutions… Unusual and unworkable: provided for a social hierarchy…a heredity nobility First settlers by 1680…Charleston.. Thriving fur trade and food to W. Indies. Also tobacco…prosperous The Carolinas Northern most region near Albemarle was poorer and more back-woodsy By 1712 separated into 2 Royal colonies: N and S Carolina Huguenots to S. Carolina when the Edict of Nantes was revoked The Middle Colonies NOTE: Dutch smugglers made it impossible for the English to enforce their trade regulations 1664 English captured Dutch New Amsterdam without a fight. And renamed it New York The Dutch did not consider the colony valuable enough to fight for New Jersey The Duke of York took a chunk of NY and gave it to two of his friends…Lord Berkley and Sir George Carteret Berkley sold his interest to some Quakers in 1674 Quakers Aka Society of Friends…established 1600 by George Fox and Margaret Fell Belief in sexual equality All are = in the eyes of God No ministers, no ritual Rejected idea of Original Sin and Predestination Were persecuted in Mass by Puritans 1702..NJ was made a Royal Colony Pennsylvania 1681 Wm Penn (Quaker) received Penn from King Charles II in leiu of a 16,000 debt that the crown owed to Penn’s father Wm Penn was the proprietor By 1685 9,000 settlers Many, though, objected to the idea of the absolute rule of the proprietor (though Penn was a good one) Pennsylvania continued 1701 The Charter of Liberties: a constitution written by a representative assembly limiting the power of the proprietor Penn did not fight it In 1703 Pennsylvania allowed 3 counties to form their own representative assembly = Delaware Georgia (late) 1732 Group of London Philanthropists, led by Oglethorpe, wanted to give English imprisoned debtors a fresh start Got permission from George II to found Georgia: Rules: no slavery and no alcohol Was unenforcable. Georgia 1752 trustees gave up and Georgia became a royal colony. George II supported the establishment of Georgia to act as a buffer between Spanish Florida and the lucrative tobacco-growing English colonies. Prior to the American Revolution All colonies had representative assemblies The right to vote depended upon property ownership (and , of course, you had to be a white, male, free, adult) The most democratic aspect of New England society was the town meeting