Chemical Reactions
advertisement

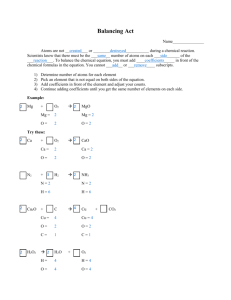
Chemical Reactions Chapter 11 Do Now- In your own words Write an explanation for what Is happening in this picture. Objective- 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions HW – Pg 329 # 9-12 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions • Word Equations 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions • Word Equations Reactants → Products 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions • Word Equations Reactants → Products iron + oxygen → iron(III) oxide Symbols Used in Chemical Reactions + → ↔ (s) (l) (g) (aq) Heat Pt ∆ Symbols Used in Chemical Reactions + → ↔ (s) (l) (g) (aq) Heat Pt Separates two reactant and two products “Yields” Separates reactants from products Reaction is reversible solid liquid gas aqueous solution ∆ heat was supplied to reaction Element (Pt) used as catalyst • Chemical Equations Reactants → Products iron + oxygen → iron(III) oxide Fe + O2 → Fe2O3 + + + → • Chemical Equations Reactants → Products iron + oxygen → iron(III) oxide Fe + O2 → Fe2O3 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide Mg + O2 → MgO Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide Mg + O2 → MgO 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO • Do Now - Write the ionic or molecular formula for Lithium Oxide Aluminum Sulfide Silicon Oxide • Objective – Balance Chemical Equations • Homework – finish Pg. 329 # 9 – 12 and handout • Do Now - Write the ionic or molecular formula for Lithium Oxide Li2O Aluminum Sulfide Al2S3 Silicon Oxide SiO2 Balancing Chemical Equations Take the time to write the steps you used to balance this problem. If you can write the steps used you can use them to balance any chemical equation. Fe + O2 → Fe2O3 1. Determine correct formulas for all reactants and products. 2. Write a skeleton equation. 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side and the product side. 4. Balance the number of atoms of each element by adding coefficients. (The subscripts can’t be changed now) 5. Check that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. 6. Check to see that all coefficients are in lowest whole number ratio possible. Iron + Fe + oxygen → iron oxide O2 → Fe2O3 1. Determine correct formulas for all reactants and products. 2. Write a skeleton equation. 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side and the product side. 4. Balance the number of atoms of each element by adding coefficients. (The subscripts can’t be changed now) 5. Check that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. 6. Check to see that all coefficients are in lowest whole number ratio possible. Iron + Fe Fe O + oxygen → iron oxide O2 → Fe2O3 Fe O 1. Determine correct formulas for all reactants and products. 2. Write a skeleton equation. 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side and the product side. 4. Balance the number of atoms of each element by adding coefficients. (The subscripts can’t be changed now) 5. Check that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. 6. Check to see that all coefficients are in lowest whole number ratio possible. Iron + Fe Fe 1 O 2 + oxygen → iron oxide O2 → Fe2O3 Fe 2 O 3 1. Determine correct formulas for all reactants and products. 2. Write a skeleton equation. 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side and the product side. 4. Balance the number of atoms of each element by adding coefficients. (The subscripts can’t be changed now) 5. Check that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. 6. Check to see that all coefficients are in lowest whole number ratio possible. Iron + Fe + oxygen → iron oxide O2 Fe 1 O 2 Fe Fe 1 O 2 → Fe2O3 Fe 2 O 3 + O2 → Fe2O3 Fe 2 O 3 1. Determine correct formulas for all reactants and products. 2. Write a skeleton equation. 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side and the product side. Iron + Fe + oxygen → iron oxide O2 Fe 1 O 2 4. Balance the number of atoms of each element by adding coefficients. (The subscripts can’t be changed now) Fe 5. Check that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. 6. Check to see that all coefficients are in lowest whole number ratio possible. Fe Fe 2 O 3 + O2 Fe 1 O 2 Fe O → Fe2O3 → Fe2O3 Fe 2 O 3 + O2 → Fe2O3 Fe O 1. Determine correct formulas for all reactants and products. 2. Write a skeleton equation. 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side and the product side. Iron + Fe oxygen → iron oxide + O2 Fe 1 O 2 4. Balance the number of atoms of each element by adding coefficients. (The subscripts can’t be changed now) Fe 5. Check that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. 6. Check to see that all coefficients are in lowest whole number ratio possible. 4Fe Fe 2 O 3 + O2 Fe 1 O 2 Fe 4 O 6 → Fe2O3 → Fe2O3 Fe 2 O 3 + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 Fe 4 O 6 1. Determine correct formulas for all reactants and products. 2. Write a skeleton equation. 3. Determine the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side and the product side. Iron + Fe oxygen → iron oxide + O2 Fe 1 O 2 4. Balance the number of atoms of each element by adding coefficients. (The subscripts can’t be changed now) Fe 5. Check that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. 6. Check to see that all coefficients are in lowest whole number ratio possible. 4Fe Fe 2 O 3 + O2 Fe 1 O 2 → Fe2O3 Fe 2 O 3 + 3O2 Fe 4 O 6 4Fe → Fe2O3 → 2Fe2O3 Fe 4 O 6 + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3