Types of Bonds and Polarity

Friday December 4, 2015
TO DO RIGHT NOW:
1. P110- copy words of the day
2. P114-glue in reading “Chemical bonding”
3. P115- title “Types of Bonds”
3. p116- title “Using EN to determine bond type”
HOMEWORK
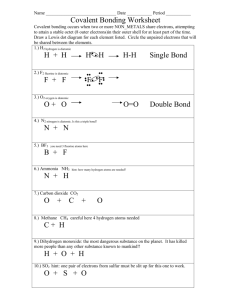
Due Monday- Polarity and EN worksheet
REMINDERS
• Check your grades.
• Tutorials today until 3:00 only
Unit 6
Chemical Bonding Article
Yellow Chemical Bonding paper
A chemical bond is:
An attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that holds the atoms together (the hook up!!!)
Why do atoms bond? (outer flap)
Most elements (besides noble gases) are very unstable
When they bond they become more stable
(like a noble gas)
Everybody has their 8!!!
They had to share to help each other out.
How do atoms bond?
atoms bond by gaining, losing, or sharing e-
Most Group A elements (s and p - block) want to attain an octet (8 valence e-)
Octet Rule – most elements want to have 8 valence electrons to achieve stability
Types of bonding (open flaps)
1.
Ionic Bonds
Transfer e from a metal to a nonmetal
Smallest ratio is called a formula unit
Example (metal) CaCl
2
(nonmetal)
Ionic Bond (draw & label this!)
e e e -
Metal nonmetal e -
Higher electronegativity
More attractive!
+ +
Notice the pair of electrons is all the over on the right.
2.
Covalent sharing of e- between 2 nonmetals
Smallest ratio of a covalent compound is called a molecule
Examples: H
2
H
2
O & C
6
H
12
O
6
2 types of covalent bonds:
(draw pics too)
Nonpolar covalent
Equal sharing of e -
=
+ +
Polar covalent
Unequal sharing of e -
Notice right is pulling harder
+ +
Example: HCl Example: H
2
Polar Covalent Bond
electrons shared unequally
Chlorine has higher electronegativity
(EN) so it pulls harder
HCl
Hydrochloric acid
3.
Metallic Bonding
All involved atoms are metals (duh!)
Electrons are shared in a “sea of free flowing or mobile electrons” by all atoms
This flow is responsible for ductility, malleability, luster and ability to conduct heat and electricity
Example: copper wire
The “sea” of electrons
2 ways to determine bond type
(fold up your bottom flap)
1.
Location on the periodic table metal + nonmetal = Ionic nonmetal + nonmetal = Covalent metal + metal = Metallic
2. taking the difference in the electronegativity (subtract!!!)
4.0 ionic 1.7 polar cov
Sulfur and Hydrogen
2.5 – 2.1 = 0.4
Nitrogen and Cesium
3.0 – 0.7 = 2.3
Chlorine and Bromine
3.0 – 2.8 = 0.2
0.3 nonpolar cov
Polar covalent
Ionic
Nonpolar covalent
Why do atoms bond clip https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NgD
9yHSJ29I
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Djs
D7Hcd9U