SNC 1D1 Activity - Periodic Table Trends F2012
advertisement

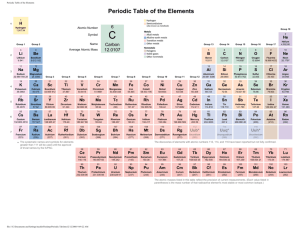
SNC 1D1 ACTIVITY – Exploring the Modern Periodic Table (Ref pp. 207-211) The Modern Periodic Law states that if elements are arranged according to their increasing atomic number (i.e. number of protons), a pattern can be seen in which similar properties occur regularly. The Atomic Radius of an Atom is the distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost edge of the atom. Instructions – 1. a) Using the Periodic Table provided and the graph paper provided, plot a graph of atomic radius (y-axis)vs. atomic number (x-axis) for the first twenty elements. b) What general trends can be observed in the graph? 2. Using the periodic table provided, answer the following questions: a) In what state are most elements at room temperature? b) Name 2 elements that are liquid at room temperature. c) Name 2 elements that are gaseous at room temperature. d) Which element has the highest melting point? e) Which element has the lowest melting point? f) Which element has the greatest density? g) Which element has the lowest density? h) Elements 1, 3, 11 and 19 are in the first column (Alkali metals) of the periodic table. How is the electron arrangement in these elements similar? i) How many electrons do you think there are in the outer orbit of the elements Rb and Cs? j) Elements 9 and 17 are in the second last column (Halogens) of the periodic table. How is the electron arrangement in these elements similar? k) How many electrons do you think there are in the outer orbit of the elements Br and I? l) Refer back to the Bohr-Rutherford diagrams for elements 3 to 10. Describe the general pattern that you observe across a row of the periodic table. m) Briefly describe how the following properties generally change as you go from left to right in the periodic table. a) Atomic number b) Melting temperature c) Atomic radius n) Briefly describe how the following properties generally change as you go down the columns of the periodic table. a) Density b) Melting temperature c) Atomic radius 3. Elements in the same column tend to form similar compounds. For example, the compounds that hydrogen forms with elements in the first column are LiH, NaH, KH and RbH. The compounds that hydrogen forms with elements in the second column are BEH2, MgH2, CaH2, and so on. Hydrogen forms the following compounds with other elements: CH4, NH3, H2O, and HF. What are the formulae of the compounds formed by the combination of hydrogen with the following? a) Silicon (Si) b) Phosphorus (P) c) Sulphur (S). 4. a) Read p. 208 and define the term valence electron. b) Answer Questions #1-5, 7-10 from p. 211 of the ONScience9 textbook.