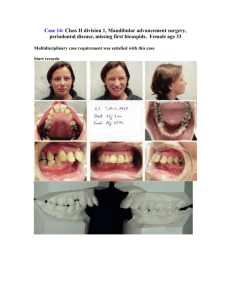
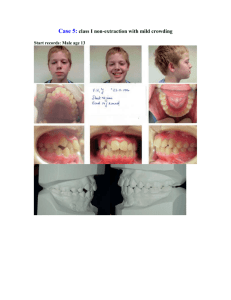
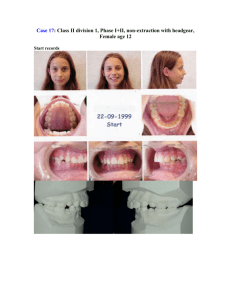
Medically Compromised Patient Case 2 Which of the following terms

Medically Compromised Patient Case 2
1.
Which of the following terms applies to the space between the maxillary central incisors? a.
Centric relation b.
Open bite c.
Diastema d.
Parafunctional e.
Fremitus
2.
The clinical observation noes in the mandibular sublingual region near the left canine and first premolar (arrow) that is hard when palpated is most likely a: a.
Torus b.
Polyp c.
Mucocele d.
Cyst e.
Ranula
3.
Which of the following best describes the papillary gingiva between the mandibular right central and lateral incisors? a.
Knife-edge b.
Cratered c.
Blunted d.
Rolled e.
Bulbous
4.
What is the clinical observation contributing to the appearance of the lingual surfaces of the mandibular anterior teeth? a.
Developmental anomalies b.
Periodontal splinting c.
Composite restorations d.
Dental calculus e.
Hypercementosis
5.
Which of the following blood pressure cuffs and area to which it is applied is correct for taking this patient’s blood pressure? a.
Child-size cuff applied to the left arm b.
Regular adult-size applied to left arm c.
Regular adult-size cuff applied to the right arm d.
Adult thigh-size cuff applied to the left leg e.
Adult thing-size cuff applied to the right leg
6.
What is the most likely interpretation of the oval-shaped radiolucency observed between the maxillary right and left central incisors (arrow)? a.
Infraorbital foramen b.
Incisive foramen c.
Incisive fossa d.
Canine fossa
e.
Nasal fossa
7.
What is the most likely interpretation of the round radiopacities observed near the teeth roots of the mandibular right and left canine and premolar regions (arrows)? a.
Osteosclerosis b.
Hypercementosis c.
Mandibular tori d.
Condensing osteitis e.
Fingerprint artifacts
8.
What is the most likely interpretation of the findings observed in the maxillary right posterior region (arrow)? a.
Retained root tips b.
Supernumerary teeth c.
Microdont molars d.
Implants e.
Retention pins
9.
The lack of image contrast and overall gray appearance of this patient’s radiographs may have resulted when the film packets were stored under each of the following conditions EXCEPT which one? a.
Strary radiation b.
High humidity c.
Excessive heat d.
Physical pressure e.
Long wavelength light
10.
The slight ground glass appearance to the mandibular posterior regions and the disappearance of the lamina dura and narrowing of the pulp chambers observed on this patient’s radiographs is most likely the result of: a.
Lack of professional dental hygiene care b.
Adverse effects of medications c.
Trauma from her habit of chewing on ice d.
Renal osteodystrophy e.
Significant calculus at the base of deep pockets
11.
Each of the following must be discussed with this patient’s nephrologist before quadrant scaling
EXCEPT which one? a.
Need for prophylactic premedication b.
Determination of blood clotting time c.
Adequacy of salivary flow d.
Assessment of vital signs e.
Pain management doses and contraindications
12.
Quadrant scaling appointments for this patient should be scheduled in the mornings, before her afternoon dialysis session. An appointment for extraction of the fractured teeth should be made on Saturday morning. a.
The first sentence is true, the second sentence is false
b.
The first sentence is false, the second sentence is true c.
Both sentences are true d.
Both sentences are false
13.
Which of the medications prescribed for this patient does NOT increase the risk of dry mouth and taste disturbances? a.
Vasotec b.
Cozaar c.
Lasix d.
Procrit e.
Prozac
14.
Which of the following would be the least helpful recommendation for assisting this patient with her goal of improved oral health? a.
Power toothbrush b.
Interproximal brush c.
Dental floss d.
Toothpick in holder e.
Floss threader
15.
The pale appearance of the gingiva and lessening demarcation of the mucogingival junction may be attributed to: a.
Anemia b.
Hypertension c.
ESRD d.
Dialysis e.
Periodontal disease
16.
Even with improved self-care, this patient’s medical conditions put her at an increased risk for each of the following EXCEPT which one? a.
Development of halitosis b.
Increase in dental calculus accumulation c.
Rampant decay d.
Demineralization of alveolar bone e.
Increased gingival bleeding
17.
Which of the following is the best choice to begin periodontal debridement in the mandibular right quadrant? a.
Sonic scaler b.
Ultrasonic scaler c.
Sickle scaler d.
Chisel scaler e.
Universal curet
18.
Which of the following ultrasonic instrument tip designs would be the best choice for initial periodontal debridement of the lingual surfaces of the mandibular anterior teeth? a.
Beavertail tip b.
Standard-diameter universal tip
c.
Standard-diameter triple bend tip d.
Slim-diameter straight tip e.
Slim-diameter curved tip
19.
Which of the following is NOT a likely adverse outcome of scaling this patient’s mandibular anterior teeth? a.
Tooth mobility b.
Root sensitivity c.
Gingival recession d.
Risk of tooth fractures e.
Longer appearance of the teeth
20.
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the mandibular anterior region probe reading changes seen at the 6-week reevaluation appointment? a.
Patient failed to stay motivated to follow oral self-care instructions given at initial appointment b.
Complex medical conditions that compromise this patient’s immune system have limited the healing process c.
Rapid reaccumulation of dental calculus after the initial scaling appointment has most likely prevented tissue shrinkage d.
Probing was done with greater than 10-20g of pressure causing the probe to penetrate the junctional epithelium e.
Heavy calculus limited access to the base of the pocket for accurate probe readings at the initial appointment
21.
Which of the following would be approved for use in treating this patient? a.
Air-powder polishing with sodium bicarbonate to remove stain b.
Controlled-release local delivery of tetracycline-containing fibers or doxycycline hyclate gel to periodontal pockets not responding to treatment c.
Sodium fluoride varnish application for prevention of caries and management of tooth sensitivity d.
Subgingival oral irrigation with saline solution for treatment of edematous gingival tissues e.
Aspirin or ibuprofen for postscaling pain management
22.
Which of the following mouth rinses would be best to add to this patient’s long-term daily ora self-care routine? a.
Listerine antiseptic b.
Perioguard c.
Biotene mouthrinse d.
Scope e.
Oral B Fluorinse
23.
The pulp vitality test may play a role in diagnosing the condition affecting which of the following teeth? a.
Maxillary right first molar and first premolar b.
Maxillary left and mandibular right second molars
ANSWERS
1.C
2.A
3.E
4.D
5.B
6.B
7.C
8.A
9.E c.
Maxillary right and left central incisors d.
Mandibular right and left central and lateral incisors e.
Mandibular right first molar and first premolar
24.
Which of the following should be communicated to this patient regarding her use of tarter control toothpaste? a.
Tarter control toothpaste will help prevent additional buildup of subgingival dental calculus b.
Tarter control toothpaste will help prevent additional buildup of supragingival dental calculus c.
Tarter control toothpaste will help remove the subgingival dental calculus formed on her teeth d.
Tarter control toothpaste will help remove the supragingival dental calculus formed on her teeth
25.
This patient has an increased risk for contracting hepatitis B. If the dental hygienist has not received the hepatitis B vaccine, he/she can legally refuse to treat this patient. a.
The first sentence is true, the second sentence is false b.
The first sentence is false, the second sentence is true c.
Both sentences are true d.
Both sentences are false
10.D
11.C
12.B
13.D
14.E
15.A
16.C
17.B
18.A
19.D
20.E
21.C
22.C
23.D
24.B
25.A