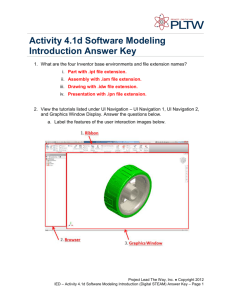
User Interface Design Components

User Interface Design
Components
Chapter 11 Handout
Objectives
To understand principles for navigation and design
To understand principles for input design
To understand principles for output design
To have the ability to design a user interface
Introduction
Interface design is the process of defining how the users will interact with the system and how that system accepts inputs and produces outputs
Three main mechanisms
– Navigation
– Input
– Output
Don’t forget about the GUI’s
Navigation Design
The goal is to make the system as simple to use—and so that the user hardly gives it any thought
Use the assumption that people will not read manuals
Use typical controls (like installation prompts)
– Use clear controls
Basic Navigation Principles
Prevent mistakes
– Use multiple menus
– Gray out commands
– Confirm important actions
Simplify recovery from mistakes
– Allowing the use of UNDO
Use consistent grammar order
File-save
Copy-paste
Navigation Controls
Languages
– Natural versus programming like SQL
– Use of Office Assistant
Menus
– Broad and shallow as opposed to narrow and deep
– One rule—no more than 8 items and 2-3 mouse clicks or keystrokes to execute action
– Grouping by interface objects (Customers, Orders) instead of by action (New, Update, Format)
Direct Manipulation
– Windows Explorer, PowerPoint
Messages
Error Messages
– First should explain the problem
– Second, describe how to correct it
– Third, provide button(s) for user response
Confirmation
Acknowledgement
Delay
Help
Polite versus impolite
Avoid humor and negative wording
Input Design
Facilitates the input of data into the system and ???
Basic principles
– Online or batch processing
Can you think of examples for both kinds?
– Capture data at the source
Avoid multiple entry of same info
Can utilize source data automation [examples???]
– Minimize keystrokes
Utilizing default values
Types of Input
Text
Numbers
Selection box
Input Validation
– Completeness check
– Format check
– Range check
– Check digit check
– Consistency check
– Database check
Output Design
Perhaps the most important part of system design because of its visibility and because of ????
Basic Principles
– Understand report usage
Types of report—all general or specific, real-time or batch—look at business value of the report
– Manage information load
Balance needed information as opposed to all information available
– Minimize bias
Ie utilizing alphabetical or numerical listing
Graphical displays of bar chart information
Types of Outputs
Types of Output
– Reports
Detailed
Summary
Turnaround document
Graphs
– Media
Paper
Electronic—web, CD, others??
Now what?
Well how do you go about actual creating the interface?
Do you just jump right in?
You could but….
User Interface Design Principles
First, user design is an art
You must make the interface
– pleasing to the eye
– simple to use
– Minimize the potential for errors
One of the biggest challenges is managing space
– That is, how do you include all the necessary information without overload the user (well see this in a little bit)
Six Main Principles
Layout
Content Awareness
Aesthetics
User Experience
Consistency
Minimal User effort
Layout
The interface should be a series of areas on the screen that are used consistency for different purposed
– Top area for commands and navigation
– A middle area for input or output
– Bottom area for status information
Content Awareness
Users should always be aware of where they are in the system and what information is being displayed
Including titles, and location menu
– Ie Home>>GBA 577>>Lecture Slides
Also applies to form/field labels
– Proper date formatting MM/DD/YYYY
Aesthetics
Interfaces should be functional and inviting to users through careful use of white space, colors, and fonts
Be careful of trade off concerning white space
Try to keep density of form low
Design of text should be kept to same size and type
– 10 point font is often preferred and no less than 8 point
– Serif font best for printed reports, sans serif better for computer screens, headings
Color and patterns should be used carefully and sparing (10% of men are colorblind)—but of course there are always exceptions
– Be careful of high contrast in colors
User Experience
Although ease of use and ease of learning often lead to similar design decisions, there is another tradeoff
– Trying to negotiate between experienced users and novices (ie difference between full and partial menus)
Ease of learning – how quickly users can learn new systems
Ease of use – how quickly users can use the system once they have learned it
Consistency
Enables users to predict what will happened before they perform the function
Trying to make programs simulate windows or macs
Trying to make web interfaces similar to other models (Amazon)
Try to use consistent terminology
– Customer versus client
– Use the same terms/field names for both forms and reports
Minimal User Effort
Making the interface easy to use, actions should be no more than 3 clicks away
User Interface Design Process
1.
Use Scenario Development
2.
Interface Structure Design
3.
Interface Standards Design
4.
Interface Design Prototyping
5.
Interface Evaluation
Use Scenario Development
An outline of the steps that the users perform to accomplish some part of their work
Think of the library project
– Some users may need to find specific information
– Others may need more general search results
One helpful tool is to think of processes and use modeling tools
Interface Structure Design
Defines the basic components of the interface and how they work together to provide functionality to the users.
This is similar to modeling in the user scenario—except that you draw out how each menu/screen is related to each other
Most similar to a Data Flow Diagram
(DFD)
Specific Interface Standards
Interface Metaphors
– Using a real world concept as a model for a computer system
Paper form or table
Online version of a check
Interface Objects
– Applying an understandable name to the fundamental building blocks of a system
Shopping cart example
Interface Actions
– Specifies the navigation and command style (menus), and grammar
Interface Icons
– Be careful as some icons are not intuitive
Interface Templates
– Designing the same appearance for each different page in the system
Interface Design Prototyping
A mock-up or simulation of a computer screen, form, or report.
– Storyboard
Hand-drawn pictures of what the screens will look like
– HTML Prototype
– Language Prototype
How do you select which technique?
Interface Evaluation
The objective is to understand how to improve the design of the system before it is completed.
There are four main common approaches
– Heuristic evaluation
– Walk-Through evaluation
– Interactive evaluation
– Formal usability testing
Heuristic Evaluation
Examines the interfaces by comparing it to a set of heuristics or principles of interface design.
– Checked separately by at least three members of the project team and then meet together to compare answers
Walk-Through Evaluation
A meeting conducted with users who will ultimately have to operate the system
This usually occurs in the interface design prototyping stage
Interface Evaluation
Users work individually with a member of the project team on a prototype of the model and discuss what their likes/dislikes
Provides additional information or missing functionality
Formal Usability Testing
Generally some type of scientific testing process that mostly can only be done with language prototypes
Can include surveys, video camera recording
It is very expensive and must include more than 5 users, but not really more than 10
Conclusion
At this point you should be able to
Understand the navigation, input, and output design principles and techniques
Understand the fundamental user interface design principles.
Understand the process of user interface design
Understand how to design the user interface structure
Understand how to design the user interface standards