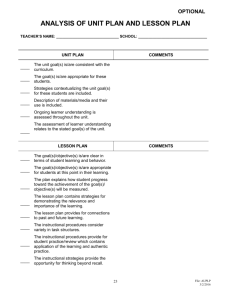
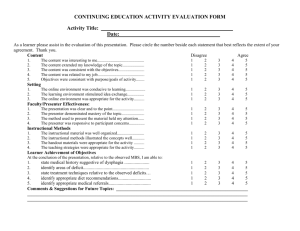
Learner Analysis
advertisement

City College of San Francisco Fitlinxx Kiosk Training Diane Reppun San Francisco State University ITEC 801 Brian Beatty - Excellent work, Diane. One of the best in the class… FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 1 Abstract This design project examines how best to train City College of San Francisco (CCSF) students to use a piece of software that is vital to successfully get credit for a Credit/Non-Credit class. Because the actual software is only available on a proprietary stand-alone system (Fitlinxx Kiosk), and there are only 3 kiosks in the CCSF Fitness Center, the Physical Education Department cannot use the kiosks for training as they are in use by students whenever the center is open. This project explores the use of a simulation that can be accessed by students and used to both train new users and improve the performance of existing students that may not be using the software to its full capabilities. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 2 Contents Project Goal and Description .......................................................................................................... 6 Performance Analysis ..................................................................................................................... 6 Motivation ................................................................................................................................... 7 Academic Workload ................................................................................................................... 7 Injury/Illness ............................................................................................................................... 7 Lack of Instruction ...................................................................................................................... 8 Lack of Training on the Fitlinxx Kiosk ...................................................................................... 8 Training Needs Assessment ............................................................................................................ 9 Learner Analysis ........................................................................................................................... 10 Prior Skills/knowledge Mastered .............................................................................................. 10 Attitude ..................................................................................................................................... 11 Motivation ................................................................................................................................. 11 General Learning Preferences ................................................................................................... 12 Educational and Ability Levels ................................................................................................. 12 Group Characteristics................................................................................................................ 12 Context Analysis ........................................................................................................................... 12 Performance Context ................................................................................................................ 12 Training context ........................................................................................................................ 13 FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 3 Instructional Goals ........................................................................................................................ 14 Sample Data Gathering Instrument ............................................................................................... 14 Goal Analysis ................................................................................................................................ 14 Task Analysis Methods ................................................................................................................. 15 Instructional Objectives ................................................................................................................ 16 Business Objectives .................................................................................................................. 16 Instructional Objectives ............................................................................................................ 17 Learner Objectives .................................................................................................................... 17 Instructional Sequencing Strategy ................................................................................................ 17 Instructional Strategy .................................................................................................................... 18 Pre-instructional activities ........................................................................................................ 19 Content Presentation ................................................................................................................. 19 Learner Participation ................................................................................................................. 20 Assessment ................................................................................................................................ 20 Follow-through Activities ......................................................................................................... 20 Instructional Activities .................................................................................................................. 21 Pre-Instructional Activities ....................................................................................................... 21 Content Presentation ................................................................................................................. 21 Learner Participation ................................................................................................................. 22 Assessment ................................................................................................................................ 22 FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 4 Follow-through activities .......................................................................................................... 22 Instructional Media and Delivery Methods .................................................................................. 23 Assessing Learning ....................................................................................................................... 23 Entry Behaviors ........................................................................................................................ 24 Pretest ........................................................................................................................................ 24 Practice Tests ............................................................................................................................ 24 Posttest ...................................................................................................................................... 25 Formative Evaluation .................................................................................................................... 25 Role of SME in Formative Evaluation...................................................................................... 26 One-to-one Evaluation .................................................................................................................. 26 Criteria ...................................................................................................................................... 26 Selecting Learners ..................................................................................................................... 27 Data Collection and Procedures ................................................................................................ 27 Assessments and Questionnaires .............................................................................................. 28 Learning Time ........................................................................................................................... 28 Data Interpretation .................................................................................................................... 28 Outcomes .................................................................................................................................. 29 Small – Group Evaluation ............................................................................................................. 29 Criteria, Data and Procedures ................................................................................................... 29 Selecting Learners ..................................................................................................................... 29 FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 5 Assessments and Questionnaires .............................................................................................. 30 Data Summary and Analysis ..................................................................................................... 30 Field Trial...................................................................................................................................... 30 Development Strategy................................................................................................................... 30 Implementation Strategy ............................................................................................................... 31 Summative Evaluation .................................................................................................................. 32 Expert Judgment ........................................................................................................................... 32 Congruence Analysis ................................................................................................................ 32 Content Analysis ....................................................................................................................... 32 Design Analysis ........................................................................................................................ 33 Utility and Feasibility Analysis ................................................................................................ 33 Field Trial...................................................................................................................................... 33 Outcomes Analysis ................................................................................................................... 33 Conclusions ................................................................................................................................... 34 References ..................................................................................................................................... 35 FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 6 Project Goal and Description Students that enroll in City College of San Francisco’s (CCSF) Physical Education course, ‘Fitness Center Super Circuit’ (PE 200C), are required to document, via a special computer based system designed by Fitlinxx, Inc., 25 (twenty-five) workouts throughout the semester in order to get credit for the course (no letter grades). The Fitness Center is open 6 days a week for approximately 12 hours each day, and students may use the Center at any time. A workout is not based on a minimum amount of time, or a set amount of exercises performed. Students are told “a workout is whatever you make it”, essentially, as long as they log any activity or exercise via the Fitlinxx system, 25 (twenty-five) times during the semester, they can obtain credit for the class. However, on average, one third of all students do not log the minimum workouts to earn credit for the course. Because exercise has been shown to assist substantially in the control of many risk factors that may lead to the development of coronary heart disease, this course may be the preventive intervention of choice to discourage poor cardiovascular health (Boone, 1983). The goal of this analysis is to determine if a knowledge deficit is responsible for so many student’s not earning credit for the class, and if so, if the training gap can be met by developing online and/or mobile training modules to increase the percentage of students that earn credit. Performance Analysis With approximately one third of the students failing to earn credit, it would be expected that there are multiple reasons to explore regarding the causes for failure. Some of the reasons to explore would be: FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 7 Motivation Individuals motives form the basis upon which exercise promotion can be successful (Ingledew, Markland, & Ferguson, 2009). 1. Physical. Are the students motivated to sign up but not sufficiently motivated to schedule the time and make the effort to work out? 2. Educational. As a credit/no credit class, there is no academic penalty for not completing the class. 3. Emotional/Social. Students may feel embarrassed or socially awkward when they come into the Fitness Center if they do not feel they have the physical capabilities of other students. Academic Workload The students may believe at the beginning of the semester that they have sufficient time to work out approximately twice a week, but find that their other workload is too demanding. As this is a credit/no credit course, it is not detrimental to their scholastic grade to eliminate it from their schedule. In a study of credit vs. letter grade transitions, it was found that the transition from the restricted to expanded evaluation systems appeared to raise the academic standards for the students, particularly undergraduates (Suddick, & Kelly, 1981) Injury/Illness Students may become injured or sick and after missing a sufficient number of weeks, catching up with full workouts may seem unobtainable. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 8 Lack of Instruction Students are only required to view one 40 minute video/DVD as an orientation to the Fitness Center. This video covers the entire use of the Fitness Center, to include the Fitlinxx system and the equipment in the room. After the first semester, students receive no additional information or training if they are repeating the course. Lack of Training on the Fitlinxx Kiosk Many students are unaware that there are situations where the software is not recording their workout. The student must then perform a manual entry to record the workout for credit. Students can also record outside exercise that they participate in, and this can count as a valid workout. As an instructor in the Fitness Center, approximately 8 hours per week, for over 5 school years, I have observed that many students do not know how to use the Fitlinxx system correctly, and most are not able to enter workouts that have not been recorded correctly by the equipment in the room. The basic entry method is a Fitlinxx Kiosk, which acts as a touch screen to enter data. Ability to enter workouts manually using the Fitlinxx system significantly reduces the amount of workouts that are not counted towards credit. For example; if a student comes into the Fitness Center, logs into the Fitlinxx system, works out on a machine that is not recording their activity, then logs out of the Fitlinxx system; they will not be recorded as doing a workout that day. Therefore; lack of knowledge of how to use the Fitlinxx system can significantly reduce the number of workouts a student earns toward their minimum requirement. Additionally, some students will ask instructors to check the system for workout information, but when they find that a workout did not count, they must be trained one-on-one to FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 9 input the information in the Fitlinxx system; therefore, it is clear that for many students, the video instruction is not sufficient for them to perform the necessary tasks. While it is not publicized, it is possible to enter enough workouts via the Fitlinxx system to get credit for the course, even if the student does not work out or engage in any physical activity in the Fitness Center. Because many students are unable to use the Fitlinxx system adequately, they don’t even know that they could get credit for the class by using the software to full advantage. To confirm this, and/or get more input on the training needs of students in the Fitness Center, a survey will be conducted that specifically addresses the use of the Fitlinxx system. The desired status is for all students to obtain credit; the actual status is that approximately one third do not get credit each and every semester. If improper use of the software is one cause of the gap, then a more thorough training tool to increase a student’s ability to use the Fitlinxx system would be beneficial towards meeting the desired status. See also Appendix A for the performance analysis questionnaire. For the many other causes of student’s failure, more research and analysis will have to be performed before solutions are formulated to address the issues. Training Needs Assessment To develop training for students to better use Fitlinxx, the Training Needs Assessment must focus on what learners need to know to effectively use the Fitlinxx system. This requires a Subject Matter Expert (SME) in Fitlinxx software. It is important to differentiate between what is necessary for the learner to know to successfully earn credit in the course, versus those tasks which are interesting and useful, but not critical to master in order to earn credit; therefore, the SME must also work with an instructor who knows what the department uses to determine if a FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 10 student has met the minimum requirements. It would also be helpful if the students were able to provide insight into what areas they are least familiar with and what tasks are most difficult for them to perform using only the existing video/DVD training. To this end, a survey of current students would help to determine the current level of understanding of the software and if they currently have the skills necessary to use the software to the extent necessary to ensure credit completion. Based on respondent’s lack of understanding in any area critical to ensuring compliance with the goal of earning credit in the course, creation of a simulation training tool would be warranted. Students would learn to perform the following tasks, in priority order: 1. Determining if a cardiovascular exercise performed in the Center was recorded in the Fitlinxx software. 2. Add a non-recorded cardiovascular exercise performed in the Center to the Fitlinxx system. 3. Add a cardiovascular workout performed outside the Center to the Fitlinxx system. 4. Check to see if a workout has been recorded by the Fitlinxx system. Learner Analysis The learners at City College of San Francisco are one of the most diverse groups of students of higher education that could be found in the United States. The age range would be from teens to eighties or even nineties; both sexes; all ethnic groups; multiple language proficiencies from non-English speaking to fluent in multiple languages including English. See Appendix B for City College Fact Sheet. Prior Skills/knowledge Mastered FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 11 This area would also be extremely diverse. While almost none would be familiar with the Fitlinxx system, as it is not a widely used system throughout the US, and is extremely rare in high schools, the level of familiarity with the Fitlinxx Kiosk based, touch screen computer programs could be high among young adults and tech savvy adults. For many, this might be the first time that they have encountered a touch screen system, or even used a software system that requires logging in and performing tasks. However, every student at City College has access to the computer learning labs and student help centers. Any system that would be developed would have to be able to cater to the beginning computer user, but also offer short cuts for the experienced users that might become bored with basic operations. Attitude As this is a university setting, all the learners are voluntarily signing up for the class. While a Physical Education requirement may exist for transfer to other schools, there are many different classes that can meet that requirement, so the assumption would be that these learners have a willingness to participate in the class and that having signed up, they would be well disposed to learning how to use the software that allows them to record and monitor their progress. Motivation There will be many different reasons students would be motivated to learn the Fitlinxx system. Primarily to ensure successful completion of the course, but other intrinsic motivational factors could exist; for example, Fitlinxx is a very good system for tracking your progress and evaluating whether you have met goals that you set for yourself. In order to do this, you must know how to use the Fitlinxx software. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 12 General Learning Preferences Again, the number and diversity of learning preferences would be great, given the heterogeneous make-up of the learners. It would be preferable to develop the training system to incorporate as many different learning styles and options as possible. It might even be worthwhile to consider having the training program duplicated to the extent possible, in other languages. Educational and Ability Levels The majority of learners will have completed a high school level education; however, a small number of adult education learners may not have completed that level. Some adult learners may also have advanced degrees. Group Characteristics As stated earlier, this is an extremely heterogeneous group of individuals. The learning tool must take into account different levels of prior education, different age groups, different English language levels and different levels of technological experience. Context Analysis This section looks at the way that the training will be conducted and what the environment will be like when the learner uses the skills learned in the training. Performance Context 1. Physical aspects. The Fitlinxx system is located inside the Fitness Center, where a total of 3 (three) Kiosks run the software and allow students to log in and perform all the tasks. There are sometimes multiple students lined up to use the Kiosk’s and pressure on the students to finish their entries quickly so that others are not delayed. Knowledge of FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 13 how long it takes to perform each task, via simulation training, would enable students to know when to finish what they are doing and return to the Kiosk when it is in less demand. 2. Social aspects. Each learner must establish his or her own skills to use the Fitlinxx system. While some students come to the center together or in small groups, this is not the norm, and most students at one time or another will need to come to the center on their own to complete the required number of workouts. Most students already performing their workout are not interested in assisting other users who are using the Kiosk. Training context 1. Physical aspects. Due to the limited availability of Fitlinxx Kiosks in the Fitness Center, and given that it is constantly being used by students who are starting or finishing a workout, the Fitlinxx Kiosks would not be an appropriate tool to use in training. For this reason, computer based software that simulates the Fitlinxx software would be needed. The ability to run the software on both computers and mobile devices would be optimal as many students have mobile devices that they can use while actually in the Fitness Center, thus allowing them the ability to practice what they have learned via the app. However, other students would need to be able to use the training tool at home or in campus computer centers; therefore, it should also be internet accessible. The transition from clicking with a mouse to touching a choice on the touch screen would be minimal and easily demonstrated in the Fitness Center. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 14 2. Social aspects. As this is not performed in a group, online learning would be appropriate as the learning environment would closely match the performance environment. Instructional Goals The instructional goal for this project is to create a teaching module that will accomplish the following: 1. Learners will know when and how to enter a cardiovascular workout on the Fitlinxx system, to ensure credit for workouts completed. 2. Learners will know how to review information on the Fitlinxx system to know if they are obtaining appropriate credit for workouts completed. Sample Data Gathering Instrument Appendix C will be used to gather information. This survey will be given out to students that come to the Fitness Center for a period of two weeks in March, 2012. In addition, the survey will be sent to all students with valid CCSF email addresses who are enrolled in PE 200C during the same time period. Output will require both quantitative and qualitative analysis. Goal Analysis The first step in instructional analysis is to identify the domain(s) of learning the learner will be using to accomplish the goal. The determined goal, while it involves some minor psychomotor skill interacting with the kiosk, is largely an intellectual skill. It primarily involves applying rules and making discriminations and also requires some well-structured problem solving skills. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 15 In the decision making process, there are rules, but the learner primarily has to problem solve, for example; “Should I try and enter my ID number or is this a manual entry machine?,” or “Did the exercise machine accept my ID number, or was there some problem?” In Bloom’s taxonomy, they must get to the level of application, but no analysis or synthesis is required. In Gagne’s types of learning, the learner will be applying rules with only some problem solving, but will not be required to apply cognitive strategies to the task (Dick, Carey, & Carey, 2009). Task Analysis Methods The appropriate analysis method is a procedural approach for the decision making process required for students to decide if they need to log a manual workout or not, and the step by step tasks involved in logging that workout. For the procedural analysis, the following questions were asked; "What are the mental and/or physical steps that the learner must go through in order to complete this task, and what order should they be performed?" While there are some decision components to the tasks, they are primarily tasks that the learner must complete, in a logical order, to accomplish the goal; therefore, a flow chart method of breaking down the instruction will be used. A subject matter expert in the Fitlinxx software was able to perform the initial steps by answering the following questions (Smith & Ragan, 1999): 1. Collecting information about the task and the content implied by the goal in order to be familiar with the terminology involved. 2. Rewrite the goal in the form of a representative test question. 3. Analyze the task and walk through my thought process as I complete the task and write down the steps I would use to complete the tasks. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 16 4. Review the steps recorded in step 3 and question each step in the process of completing the task. This will help me to find the unobservable cognitive knowledge that underlies my behavior. 5. Identify the shortest, simplest way to complete the path, noting factors that require this simpler path. 6. Make notes of factors that may require more steps or more complex steps. 7. Choose the steps and circumstances that best match the intentions of the goal. 8. Make a list of the steps and decision points appropriate for the goal. 9. Confirm the analysis with other experts. The analysis resulted in the task analysis diagram in Appendix D. Instructional Objectives A sub-set of the possible solutions to the problem of student failure in PE 200C will be addressed by this course. The objectives for this course are: Business Objectives 1. Completion rates for the Fitness Center Super Circuit (PE 200C) will increase to over 80%. 2. Instructors will experience a reduction in the number of students that request one- on-one training on the Fitlinxx system. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 17 Instructional Objectives 1. Given a scenario of an exercise completed in the Fitness Center, the learner will be able to determine if manually entering the workout on the Fitlinxx Kiosk is required. 2. Given the On-line Fitlinxx simulation software, the learner will be able to enter an exercise performed on a machine in the Fitness Center. 3. Given a description of a workout previously entered by a user, the learner will be able to check to see if that workout has been entered in the Fitlinxx system. Learner Objectives 1. You will be able to determine if you need to enter a cardiovascular workout on the Fitlinxx Kiosk by answering a few simple questions and using the online Fitlinxx simulation software, you will learn how to enter a manual workout on a piece of equipment you use in the Fitness Center or an activity you participated in outside the Fitness Center. 2. Using the online Fitlinxx simulation software, you will learn how to view workout information. 3. When you use the Fitness Center Fitlinxx Kiosk you will be able to do all the actions you learnt how to do using the Fitlinxx simulation software. Instructional Sequencing Strategy In order to determine the instructional sequence, first you must identify the elements to be sequenced, and second, select the organizing principle (Pattern, Chao & Reigeluth, 1986). In FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 18 answer to the first question, this project was evaluated from the perspective of the learner’s response. The learner will be required to memorize some verbal information for basic identification of when to enter a workout, which can be represented as physical elements for them to recognize. Next, the instruction will follow a step-by-step intellectual task entering information, then checking their work. Each element will be presented in sequence via the simulation software. For the second question, Posner and Strike (1976) presented a scheme that identifies two basic groups of principles for organizing elements: those that are empirically based and those that are logically based. From those two basic groups, five categories were created. After evaluating the five categories, the Learner–related principles will be applied to this instructional sequencing in order to capitalize on learning strategies that are expected to promote the correct use of the Fitlinxx software. The learner responses, and structuring the instruction in a way that considers how learners learn, will enhance the instructional strategy and activities. Simulating the Fitlinxx software will allow the learner to experience the tasks with information provided at each step that guides them through why they are selecting an option, and lead them to the next step. Additionally, if the learner finds that they already know how to perform a specific action, they can skip that section of the learning, just as they would skip the task in the Fitness Center if they do not need to use it or if they have previously learned the task. Instructional Strategy It is thought that most competent learners are able to organize information over short periods of time (Pattern, Chao & Reigeluth, 1986), and the basic information in this course will not require a long time for a student to learn and master. Therefore, the instructional strategy will be to introduce the entire course in one web-based tool that allows the learner to pick what FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 19 subjects and area they want to focus on, after being given a short pre-test that will help them determine if they are as familiar with the software as they think they are. Learners may overestimate their understanding of a module, so the pre-test will point out any of these misconceptions. At that point the learner will be able to pick and choose the exercises, quizzes, questions and practice that they want to use, and how long they want to use it. Given that this course will involve both verbal and intellectual activities, care must be taken to ensure that distinctions are made between the learning components for each type of learning outcome (Dick, Carey, & Carey, 2009). Pre-instructional activities Verbal – Show learners the various ways they will see the verbal information and give examples to promote recall. Intellectual – State the learner objectives and give a pretest that will promote motivation and link the learner to prerequisite knowledge in memory. Content Presentation Verbal – Elaboration strategy will be used to increase the likelihood that learners will store information logically and be able to use it even if the conditions in the Fitness Center change the way the information is presented. Intellectual – It will be important to make the Fitlinxx simulation software as realistic as possible which promotes the logical sequence to entering and reviewing information that already exists on the Fitlinxx Kiosk. Scenarios will be provided that reinforce the learners transfer of the information to real world scenarios that may occur in the Fitness Center. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 20 Learner Participation Verbal - Various quizzes and matching activities will be used to support the verbal information that the learner must master. This will also be supported by photographic examples of the types of queues they must be able to recognize in the Fitness Center, which will allow them to establish and organizational structure of the information. Intellectual – As in the content presentation, the simulation of the actual software the learner will use promotes the congruence of the practice to the conditions that they will encounter in the Fitness Center. As this is a very well defined problem, the amount and use of practice scenarios will enhance the learning without the concerns for unfamiliar context situations, and will be able to be transferred to the performance context. Assessment Verbal – As the basic method for content presentation is itself quizzes and matching activities, where the learner will receive immediate feedback, it is not anticipated that a separate verbal assessment will be needed. Intellectual – The culminating assessment will be the completion of scenario based examples, which the learner will complete from beginning to end, using the simulation software. Separate scenarios will be created that test all the learner objectives, but may also be combined to ensure the learner understands that tasks can be conducted individually, or as part of a whole process. Follow-through Activities Verbal and Intellectual – It is anticipated that the learner will use the skills learned in the course very soon after completing it; or may in fact access the course while using the FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 21 Fitness Center (if it can be made available on mobile devices). Additionally, the learner will have the ability to re-take the course at any time, focusing on specific areas that they may have not been able to perform in the Fitness Center; thus, enabling them to self-correct their performance. Instructional Activities The instructional activities for this course will involve accessing a tutorial with quizzes, questions, and online drill-and-practice. The students will review the content material online which simulates the actual software that they will be using to accomplish the objectives. Using considerations from the instructional strategies, the following instructional activities were included: Pre-Instructional Activities First, state learner objectives so the learner knows what is expected of them, and what they can accomplish. Second, the only required module of the course will be a pre-test to help the learners determine where they need to concentrate, and what modules they should attempt first. The pre-test will contain scenarios that show how you can fail course if not using Fitlinxx Kiosk correctly, at the same time as testing their knowledge to motivate learners. Learners will receive immediate feedback of pre-test in order to determine which modules they should work on in the course. Content Presentation Learners will be shown examples of various ways they may be prompted to manually enter a workout in order to give them the prompts they will encounter in the Fitness Center. The simulation software is then used in a step by step process to enter a workout or to review workout information, depending on which module they choose. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 22 At the end of each module more scenarios will allow users to select the correct response then walk user through correct entry. Learner Participation In order to stimulate learner participation, the learner will be allowed to re-take the pre-test but will be walked through correct answer for any incorrect responses. The will also be given matching activities to prompt memory and recall of context situations. The fact that the learner can select the module(s) the learner needs, versus making the learner go through all modules regardless of the results of the pre-test, will motivate the learner to participate and feel that their time is not wasted on information they already know. Optional quizzes throughout the modules will reinforce the learners understanding of their performance and the scenarios will lead the learner through complete cycles and objectives. Assessment Scenarios, pre-test, and quizzes will provide the assessment, but students will receive immediate feedback on these assessments so they know where to immediately focus their attention. The final assessment will be in the Fitness Center where students will be required to enter real information and check their entries on the Fitlinxx Kiosk. Follow-through activities Because the Fitlinxx Kiosk shows data entered immediately, the learner will be able to assess how successful they are immediately. If they are unsuccessful, they will be encouraged to return to the online course simulation and re-take the modules they need. Essentially, the purpose FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 23 for taking the course is to engage in the follow-through activity of using the Fitness Center. Appendix A is a table of the instructional strategies linked with instructional activities. Instructional Media and Delivery Methods This course will be produced in Flash or some equivalent technology that allows the simulation of the Fitlinxx Kiosk Software. Unfortunately, Fitlinxx does not install its software on anything but administratively protected computers, which does not allow any other program to be installed such as Captivate or Camtasia. Additionally, the actual use of the software, while more realistic, would not allow the user to attempt as many options as can be allowed using a simulation because the user would be entering data that would be recorded as actual workouts. The Fitlinxx Kiosk software does not allow users to delete workout information they enter. The course will be made available online and open to all students at City College of San Francisco. Students will be encouraged to take this course on their own prior to attending their first Fitness Center session, and encouraged to re-take all or part of it if they are having problems using the Fitlinxx Kiosk software. As a Flash course, the learner will be able to select sub-sets of information that they need to review or learn, but at many points in the simulation, they will be given quizzes and opportunities to test their understanding of portions of the course. These will be for self-evaluation, not for external testing purposes. A partially completed example can be seen at http://sfsuovc.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Fitlinxx-Diane-ReppuDec-6-Final.swf Assessing Learning The objectives that were developed provide a basis for criterion based assessment. The learner will be able to determine if they need to enter a cardiovascular workout on the Fitlinxx Kiosk, and then enter that information using the Fitlinxx Kiosk Simulation software. The learner FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 24 will also use the Fitlinxx Simulation software to learn how to view workout information. Finally, the learner will be expected to apply those skills using the Fitness Center Fitlinxx Kiosk. Dick, Carey, and Carey (2009) describe four types of assessments: entry behaviors, pretests, practice tests, and posttests. Entry Behaviors The task analysis has already determined that there are two entry level skills for the learner to be able to learn the tasks required to complete the instruction. However, learners may still attempt the course without having to ‘test’ on these two criteria. The learners will be informed that attempting the course without appropriate English skills may reduce their satisfaction with the instruction and that completing the final objective to the course, to use the skills learnt in the Fitness Center, will not be possible without the other entry requirement of having a Fitlinxx Login ID. Pretest The pretest for this course will be a significant element for learners to evaluate what modules they want to concentrate on during their self-determined training time. As stated earlier in the pre-instructional activities section of this paper, a pre-test will be the first module for all learners. The pre-test will contain scenarios that show how learners can fail the course if they don’t use the Fitlinxx Kiosk correctly. Learners will receive immediate feedback from the pre-test in order to determine which modules they should work on in the course. Appendix F is an example of the pre-test scenario questions. Practice Tests FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 25 Throughout the course, learners will be given quizzes, as tests, to help them determine if they have learnt the information from that module. They will be short and specific to the module the learner is attempting. Successful completion of all the tests in a module will give the learner confidence to translate the skill they have learnt to the performance context, the Fitness Center. Posttest With the exception of the summative evaluation process, no post-test is proposed for this course. The learners will be encouraged to repeat the course if they do not find that the skills they learnt are allowing them to successfully enter workouts and review workouts on the Fitlinxx Kiosk. Formative Evaluation The process of obtaining data to revise instruction is essential for a training course such as this because the learner will be essentially alone while completing the instruction. Without significant input from test subjects, and subsequent revisions, the course could be confusing and de-motivating to learners and the may not be willing to continue the course. Additionally, the information must be correct in simulating the performance tool so that the learner is not taught the ‘wrong’ way to accomplish a task. For those reasons, both one-on-one and SME analysis will be the focus of the formative evaluation. It is expected that the most significant input will be from these two evaluations; however, following this, the other stages of formative evaluation, recommended by Dick, Carey and Carey (small group and field study), should refine the revisions necessary to complete the course. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 26 One way to help anchor the formative process is to use the instructional strategy table developed during the Instructional Roadmap, this will help to develop the questions needed in the one-to-one, small group and field trial (Dick, Carey, & Carey, 2009). Role of SME in Formative Evaluation For this course, it is important that at least one other SME evaluate the software to ensure that the correct information is being provided and that the simulation performs expected. A novice user may not be able to ‘click’ through the modules and check things quickly or notice if something does not work the way it does on the Fitlinxx Kiosk. The SME can annotate any discrepancies in their understanding of the actual program, which can then be used to compare the simulation again to the Fitlinxx software, so that corrections can be made to the simulation. One-to-one Evaluation This is an evaluation process where individual prospective users are asked to use the proposed learning module. Comments, suggestions and challenges are recorded by an evaluator in a one-to-one training environment. Criteria Is the course clear to the learner? What is the impact on the learner? Is this course a feasible option to provide the instruction? FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 27 Selecting Learners For this course, with such a diverse group of possible learners, more than three types of learners referenced in Dick, Carey and Carey (2005), should be selected. Some of the groups that must be represented are non-English speaking, from various cultures; older, non-technical learners; younger non-technical learners; technically proficient learners; and experienced users. Table 1 shows the matrix of information to be recorded and used with learner subjects. One to One Evaluation Criteria Matrix Age Range Self-expressed technical Fitlinxx Kiosk level Experience Beginner None 20 to 40 Intermediate < 1 semester 40 to 60 Advanced 1 to 3 semesters < 20 ESL? Y/N Y or N > 60 > 3 semester Table 1 Data Collection and Procedures In order to facilitate collection of information, each user will be observed by an evaluator and asked to describe their thoughts and reactions to each phase of the instruction. The evaluator will be told to “let the learner try and figure things out” and to wait for the learner to attempt to solve any problems before stepping in to help. If the learner cannot continue, the evaluator will give them just enough information to get them back on track. This should elicit information on the clarity of instruction. Multiple one-to-one sessions with various users should provide an FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 28 overall evaluation for use in modification of the course. The observer(s) will record the testing sessions with an over the shoulder recording technique to record both the audio and video of their interactions with the simulation. The developer will then watch the recording, identify the areas where each tester had problems, and make modifications as necessary to that section of the course. Assessments and Questionnaires As the course contains multiple quizzes and questions, the evaluator should be sure to note how each learner did on these mini-assessments, as it can be an objective measure of how they understand the instruction. Learning Time The video facilitates the ability to record the amount of time the user is interacting with the program versus commenting on the content. This should provide a basic idea of the time it will take various learners to complete the course if all modules are attempted. This information will be added to the product so that learners will be able to determine if they want to attempt a module during the current session, or come back and attempt the module at a later time. Data Interpretation After all the one-to-one evaluations have been completed, a matrix will be created to find those responses that are consistent among learners. While it is important to not generalize from one learner, it is also important to look at each area of concern, and evaluate it in terms of improving the course. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 29 Outcomes At this point, the information from the one-to-one evaluation will be used to make adjustments to the course before the next phase of formative testing takes place. If there are changes to the user interface, that significantly change the interaction with the learners, additional one to one testing will be conducted before moving on to the next phase of formative evaluation. Small – Group Evaluation As the learning modules become more stable as a result of the one to one evaluation, small groups of learners are asked to evaluate the modules without individual observation. Criteria, Data and Procedures As a small group of users attempts the course, the users will be asked to enter their results from the pre-test, list what modules they are attempting, and note their results of each quiz or question they are asked in the course. This will provide the data to validate the course and the changes that were made as a result of the one-to-one evaluation. Selecting Learners Similar to one-to-one selection, a group of approximately ten to fifteen people will be recruited to complete the training, on their own, and enter the information required. This will produce a somewhat biased group, because they will be learners who are willing to keep track of their progress, and will probably not include learners from the significantly non-English speaking group. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 30 Assessments and Questionnaires The procedure states that the testing learners will annotate their results on quizzes and questions that are part of the course. Additionally, they will be asked to complete a questionnaire on their impression of the usability, their attitude toward the course and delivery etc. (Appendix C). Data Summary and Analysis Quantitative analysis of the self-reported scores alone with analysis of the questionnaires will be used to make refinements to the course. Field Trial As this is an individual course, available on-line, to be taken when students decide they want to learn more about the Fitlinxx software, additional learners would be added to construct the ‘field trial’. The number of learners being asked to test the software will be increased and instead of using analysis of their scores on the internal tests, the same questionnaire (see Appendix B) will be used and evaluated to look for trends and areas where the designer will need to make refinements. There is no separate performance context for the course. The context of performing the skills learned in the course, are used in the Fitness Center, not in a larger group environment. Development Strategy This course will be developed using Flash or similar technology so that a good simulation can be created. The development steps are: FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 31 1. Hire instructional designer to create simulation software. 2. Conduct formative evaluation process. 3. Revise simulation software based on formative evaluation. 4. Make software available on City College web site and post links from Physical Education program to training site. It is anticipated that approximately 80 hours will be necessary for initial development; followed by an additional 20 hours of updates dependent on the results of the formative evaluation process. Once the formative evaluation steps are complete, and there is a version 1.0 completed, posting of the software on the City College web hosting service will be one step, but additional access to the simulation could be provided via stand-alone systems made available in the Fitness Center and in other student accessible computer labs. An affordable option now exists to use touch screens to even further simulate the Fitlinxx Kiosk experience, so these resources should be included in development. Some additional development time could be dedicated to making the stand alone option function in the Fitness Center. Implementation Strategy Implementing the simulation software involves making the software available to all students at City College of San Francisco via the web site. The more important implementation task is to publicize the existence of the software and incorporating it into the orientation information that students are required to take before being accepted into the class. Additionally, existing students need to be targeted as prospective users of the software, and to do this, the Fitlinxx Kiosk can be incorporated into the process as there is a message area that each student sees every time they log into the center. Instructors should be asked to encourage any student FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 32 that is having difficulty to use the software, and if possible, a stand-alone station that allows the student to access the simulation while in the Fitness Center. Summative Evaluation Summative evaluation is the design of evaluation materials and the collection of data to validate the instruction (Dick, Carey, & Carey, 2009). For this summative evaluation process there will be two phases; expert judgment and field trial. Expert Judgment The main question to be answered during the summative evaluation phase is; Does the training course have the potential for meeting the needs of City College of San Francisco P.E. 200? Congruence Analysis CCSF needs a cost effective way to increase the completion rate of students in P.E. 200. This online course will be compared to the existing video orientation that all students must take to enroll in the course. While the orientation contains more general information, it also contains some of the information on how to use the Fitlinxx Kiosk, and a comparison can be made regarding whether the organizational goal of increasing completion rates is better met by the orientation or the online course. Content Analysis Just as in the formative analysis, an SME would be used to evaluate the content of the online course. As the actual software is available for comparison, the SME will be easily able to FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 33 compare the two and provide a complete evaluation of the content of the software for the organization. Design Analysis Analyzing the instructional strategy used in the instruction may require a review of the design materials that include reviewing the components and their potential for gaining and maintaining learners potential. A checklist can be used to compare the video orientation and the online training course. Utility and Feasibility Analysis As the comparison orientation video is also an online available option, there is little or no difference between this and the new online software training course; however, there is slightly different technology used for the new online software and an evaluation can be conducted to ensure that the new software is feasible to be deployed on different platforms available to learners. Also, interviewing the supervisor of the Fitness Center should be conducted to create an evaluation that meets the needs, resources, and constraints of the course. Field Trial The training course will be implemented as intended and multiple users from different groups as representative of the population as possible from Table 1 will be used. Outcomes Analysis FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 34 Impact on Learners – The evaluation will determine if the learners are better able to perform the tasks that are required to successfully enter workouts. The total number entered can be compared to the average for users not in the field trial. Impact on Organization – By comparing the number of workouts entered for all learners involved in the field trial, with all other students during the same period of time, it would be possible to see if there is an increase in the average workouts completed. Management Analysis – The evaluation will answer questions regarding the feasibility of the instruction and the implementation plan of using online learning. If there are learners that cannot access the instruction, or are unable to get access to the technology necessary to complete the course, then adjustments will be made to make the technology more available. This could have a significant fiscal impact on the implementation of the course. Conclusions City College of San Francisco’s Fitness Center is a state of the art exercise room with computerized training software designed to help students keep track of their workouts. While the software is not difficult to use, the lack of training opportunities due to the proprietary nature of the software and hardware caused a significant gap in the student’s ability to use the software. The simulation software envisioned by this analysis will help to reduce the failure rate of students and increase their satisfaction with the course. FITLINXX KIOSK TRAINING 35 References Boone, J. L. (1983). A New Curriculum for Fitness Education. Public Health Reports (1974) Vol. 98, No. 5 (Sep. - Oct., 1983), pp. 507-516. Dick, W., Carey, L., & Carey, J. O. (2009). The Systematic Design of Instruction. 7th edition. Boston : Pearson/Allyn and Bacon Ingledew, D., Markland, D., & Ferguson, E. (2009). Three levels of exercise motivation. Applied Psychology: Health & Well-Being,1(3), 336-355. Posner, G.J., & Strike, K.A. (1976). A categorization scheme for principles of sequencing content. Review of Educational Research, 46(4), 665-590. Scandura, J. M., Lee, W., Lee F. (1967). Rule Generality and Consistency in Mathematics Learning, American Educational Research Journal , Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 303-319 Smith, P.L. & Ragan, T. J. (1999). Instructional Design. 2nd edition. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Merrill. Suddick, D., & Kelly, R. (1981). Effects of transition from pass/no credit to traditional letter grade system. The Journal of Experimental Education, 50(2), 88-90. Van Patten, J., Chao, C., & Reigeluth, C.M., (1986). A review of Strategies for sequencing and synthesizing instruction. Review of Educational Research, 56(4), 437-471. Appendix A Yes No Answer and Comments Performance Analysis Question 1. Can the performance problem be identified? X Several problems are quite evident if you spend some hours in the Fitness Center but possibly more could be identified with a questionnaire. 2. Is the problem related to important organizational or business unit goals? X Student success in any class is a high priority for any school. 3. Are there established operational goals for this outcome? X All students should be able to obtain a minimum score and get credit in the class; only sickness or injury should make this difficult Approximately 1/3 of all students who take the course do not get credit. Students that do not understand how to use the Fitness Center Kiosk (Fitlinxx) are not able to record their sessions, which is the cause for not getting credit in the class. 4. Is the operational goal being met? 5. Is there an operational need? (gap) X X 6. Have job performance standards been set for achieving the operational goal? X 7. Are job performance standards being met? X Currently, there does not seem to be any direction being given to instructors or program managers to achieve better results. See 4 8. Is there a job performance need? (gap) X Several performance gaps exist, each would have different solutions. 9. Are there external factors outside of the control of local management that are contributing to the performance gap? (regulations, hiring constraints, labor contract, etc.) X Access to paid course developers is not possible due to California budget constraints. 10. Are there internal factors within the control of the local management that are contributing to the performance gap? 11. Are there reasonable solutions for the performance needs? X X The program manager does not have time to develop more instructional modules, and only has access to video for class development. As an instructor, and student in SFSU ITEC program, I can develop other methods to teach students how to use Fitlinxx. Derived from Table 2.1 in Systematic Design of Instruction, Dick, Carey, and Carey Appendix B CCSF Fact Sheet Appendix C SURVEY – HOW CONFIDENT ARE YOU USING THE FITLINXX KIOSK? 1. How many semesters have you been enrolled in PE 200C? Circle one letter. a. First semester b. More than 1 semester but less than 4 semesters c. More than 4 semesters 2. Do you feel you know as much as you need to know about using the Fitlinxx Kiosk? Circle: Y N 3. How often do you manually log a cardiovascular workout? Circle one letter. a. . Every time I workout b. Occasionally, when I use a non-recording piece of equipment c. Never d. I don’t know how to manually log a cardiovascular workout. 4. How did you learn how to use the Kiosk? a. Orientation Video/Online Video. b. An instructor showed me. c. A friend/colleague/other student showed me. d I don’t know how to use the Kiosk. e. Other: Please specify __________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ SURVEY – HOW CONFIDENT ARE YOU USING THE FITLINXX KIOSK? (Continued) 5. Do you think there is enough training available on the Kiosk functions? Circle: Y N If you circled no, please explain why. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Appendix D Appendix E Instructional Roadmap Instructional Strategy Instructional Activity Pre-Instructional Show learners the various ways they Verbal will see the verbal information and - State Learner Objectives. - Pre-Test to help the learners give examples to promote recall. determine where they need to concentrate. - Intellectual: State the learner Intellectual Scenarios that show how you can fail course if not using objectives and give a pretest that Fitlinxx Kiosk correctly. - will promote motivation and link the learner to prerequisite knowledge in memory. E-1 Immediate feedback of pre-test. Instructional Roadmap Instructional Strategy Instructional Activity Content Elaboration strategy will be used to Verbal - Examples of various ways you increase the likelihood that learners may be prompted to manually will store information logically and enter a workout. - be able to use it even if the Simulation software used in conditions in the Fitness Center step by step process to enter a change the way the information is workout. presented. - Simulation software used in step by step process to review workout information. It will be important to make the Intellectual Fitlinxx simulation software as - Scenarios will allow users to select the correct response then realistic as possible which promotes walk user through correct entry. the logical sequence to entering and reviewing information that already exists on the Fitlinxx Kiosk. Scenarios will be provided that reinforce the learners transfer of the information to real world scenarios that may occur in the Fitness Center. E-2 Instructional Roadmap Instructional Strategy Instructional Activity Learner Participation Various quizzes and matching Verbal - Re-take pre-test, and walk activities will be used to support the learner through correct answer verbal information that the learner for any incorrect responses - must master. This will also be Matching activities to prompt supported by photographic examples memory and recall of context of the types of queues they must be situations. able to recognize in the Fitness Center, which will allow them to establish and organizational structure of the information. E-3 Instructional Roadmap Instructional Strategy As in the content presentation, the Instructional Activity Intellectual - Selection of modules the learner simulation of the actual software the needs, vs. making the learner go learner will use promotes the through all modules regardless congruence of the practice to the of the results of the pre-test will conditions that they will encounter motivate the learner. - in the Fitness Center. As this is a Optional quizzes throughout the very well defined problem, the modules will reinforce the amount and use of practice scenarios learners understanding of their will enhance the learning without performance - the concerns for unfamiliar context Scenarios to lead learner situations, and will be able to be through complete transferred to the performance cycle/objectives. context. E-4 Instructional Roadmap Instructional Strategy Instructional Activity Assessment Verbal - As the basic method for content Scenarios, pre-test, and quizzes presentation is itself quizzes and will provide the assessment, but matching activities, where the students will receive immediate learner will receive immediate feedback on these assessments feedback, it is not anticipated that a so they know where to separate verbal assessment will be immediately focus their needed. attention. - The culminating assessment will be Intellectual The final assessment will be in the Fitness Center where the completion of scenario based students will be required to examples, which the learner will enter real information and complete from beginning to end, using the simulation software. check their entries on the Separate scenarios will be created Fitlinxx Kiosk. that test all the learner objectives, but may also be combined to ensure the learner understands that tasks can be conducted individually, or as part of a whole process. E-5 Instructional Roadmap Instructional Strategy Instructional Activity Follow- Up Activities It is anticipated that the learner will Verbal & use the skills learned in the course Intellectual - Because the Fitlinxx Kiosk shows data entered, the learner very soon after completing it; or will be able to assess their work may in fact access the course while immediately. If they are using the Fitness Center (if it can be unsuccessful, they will be made available on mobile devices). encouraged to return to Additionally, the learner will have simulation. the ability to re-take the course at any time, focusing on specific areas that they may have not been able to perform in the Fitness Center; thus, enabling them to self-correct their performance. E-6 Appendix F Sample Pre-Test Questions Read the following scenario and answer the questions below: 1. You go to the Fitness Center and start your workout using the Fitlinxx Kiosk, you proceed to a treadmill. The treadmill has a label on the top that reads “Enter, ID, Enter”. You follow the instructions, but you do not get prompted to input your ID; instead you are prompted to enter the type of workout you want to do and other information. The treadmill starts and your complete a 20 minute jog on the treadmill. Circle one Q1. Do you have to manually enter your treadmill time on the Fitlinxx Kiosk? Y N Q2. If you log in and press Finish Workout, should you see any activity logged? Y N Q3. If you also did some strength work, using your ID, will you have a N Y Workout that will count toward your minimum number? 2. You go to the Fitness Center, you start a workout on the kiosk, but you are unable to start any activity because you remember you have a test to study for. You also remember that you did a workout yesterday out of the Fitness Center. You manually log that workout before you leave, then press Finish Workout. Q1. Will this workout count towards your minimum number? Y N Y N Q2. If you don’t enter a manual workout before you leave, will logging in, then pressing Finish Workout, count towards your minimum number? Overall Score: 95 / 96 possible Final Presentation (12 points) 3 points: Presentation of information is very 3 organized. Presentation is pts exceptionally clear, easy to follow, and meets time expectations. 2 points: Presentation of information is somewhat organized. Presentation is clear and easy to follow. 1 point: Presentation of information is poorly organized. Presentation is unclear, hard to follow, or violates time expectations. 0 points: Presentation of information is disorganized. Presentation is confusing or very hard to follow. 2 points: Media props (slides, documents, etc.) are used effectively. 1 point: Media props (slides, documents, etc.) are used ineffectively. 2 points: Presentation describes the design project or instructional material, but doesn’t represent the design in any significant way. 1 point: 0 points: Presentation poorly describes the Presentation does not describe the design project and instructional design project and instructional material. material. Comments: 3 points: Notably well-designed media 3 props (slides, documents, etc.) are pts used effectively to support presentation content. 0 points: No media props (slides, documents, etc.). Comments: Presentation (12) 3 points: Presentation represents and describes the instructional design project; including demonstrating 3 representative instructional pts material or activities. Comments: 3 points: Demonstrated instructional material has exceptional 3 production value – notably pts aesthetically pleasing and easy to use. Comments: 2 points: Good production value – aesthetically pleasing and easy to use. 1 point: Low production value – amateurish “look and feel.” 0 points: Poor production value. No consistent “look and feel.” Instructional Design Report (84 points) Performance Analysis (3) 3 points: Design document explains the performance anaysis process 3 AND clearly defines the pts performance gap: desired status, current status, and the performance deficit. 2 points: 1 point: Design document vaguely defines the Design document poorly defines performance gap or vaguely describes the performance gap. the performance analysis process. 0 points: Design document does not define the performance gap or describe the performance analysis process. Comments: 3 points: Design document clearly 3 describes an effective needs pts assessment process. Needs Assessment (6) 2 points: 1 point: 0 points: Design document vaguely describes Design document poorly describes the Design document does not define the the needs assessment process. needs assessment process. needs assessment process. Comments: 3 pts 3 points: 2 points: Design document clearly defines Design document defines but does and prioritizes the training needs. not prioritize the training needs. 1 point: Design document vaguely defines the training needs. 0 points: Design document does not define the training needs. Comments: Learner Analysis (3) 3 points: Design document contains a thorough explanation of multiple learner characteristics that are 3 pts relevant to this instructional situation. Comments: 1 point: Design document contains a weak Design document contains some explanation of learner explanation of learner characteristics characteristics that are relevant to that are relevant to this instructional this instructional situation. situation. 2 points: 0 points: Design document does not contain any explanation of learner characteristics that are relevant to this instructional situation. Analysis Instrument (3) 3 points: Design document includes at least one effective instrument used for 3 front end analysis (Performance, pts Needs, Conrtext, or Learner). 2 points: Design document includes at least one instrument used for front end analysis (Performance, Needs, Conrtext, or Learner), but the instrument may not be effective. 1 point: Design document describes at least one instrument used for front end analysis (Performance, Needs, Conrtext, or Learner). 0 points: Design document does not include a description or sample analysis instrument. Comments: 3 points: The context analysis clearly 3 describes the performance pts context. 2 points: The context analysis describes the performance context. 1 point: 0 points: The context analysis poorly describes the performance context. The context analysis does not describe the performance context. 2 points: The context analysis describes the instructional context, but does not adequately analyze the differences between the instructional and performance contexts. 1 point: The context analysis poorly describes the instructional context. Comments: Context Analysis (6) 3 points: The context analysis clearly describes the instructional context, 3 including analyzing the relevant pts differences between the performance and instructional contexts. 0 points: The context analysis does not describe the instructional context. Comments: 3 points: Design document analyzes tasks from a topic/content analysis 3 and/or a procedural analysis, as pts appropriate, including a visual diagram. (What) Task Analysis (6) 2 points: Design document analyzes tasks from a topic analysis and/or a procedural analysis, as appropriate, but the analysis is incomplete. 1 point: Design document analyzes data from a topic analysis and/or a procedural analysis, as appropriate, but treats the analysis very simply. 0 points: Design document does not analyze data from a topic analysis and/or a procedural analysis, as appropriate. Comments: 3 points: The design document clearly 3 describes and explains the task pts analysis process followed. (How and why) Comments: 3 points: The design document weakly describes or explains the task analysis process followed. (How and why) 1 point: The design document insufficiently describes the task analysis process followed. (How OR why) 0 points: The design document does not describe the task analysis process followed. (How or why). Instructional Objectives (3) 3 points: Design document contains clear, measurable instructional 3 objectives addressing three levels pts of audience: business, designer, and learner. 2 points: Design document contains vague but measurable instructional objectives. 1 point: Design document contains insufficiently described instructional objectives. 2 points: Design document contains vague explanation of instructional sequencing strategy(-ies). 1 point: Design document contains insufficiently described instructional sequencing strategy. 2 points: Design document contains vague explanation of instructional strategy and activities. (What OR Why) 1 point: Design document contains insufficiently described instructional strategy and activities. (What AND Why) 2 points: The document provides a clear but incomplete description of the development process, tasks, and resources required. 1 point: The document provides a vague description of the development process, tasks, and resources required. 0 points: Design document contains no instructional objectives. Comments: Instructional Sequencing Strategies (3) 3 points: Design document contains clear explanation of instructional sequencing strategy(-ies). 3 pts 0 points: Design document contains no meaningful discussion of instructional sequencing strategy. Comments: Instructional Strategy and Activities (3) 3 pts 3 points: Design document contains clear explanation of instructional strategy and activities. (What AND Why) 0 points: Design document contains no meaningful discussion of instructional strategy and activities. Comments: Development Strategy (3) 3 points: The document provides a clear description of the development process, tasks, and resources 3 required. (How production would pts occur.) (Preliminary budget, timeline, people resources required) Comments: 0 points: The document does not provide meaningful description of the development process, tasks, and resources required. Implementation (6) 3 points: Document provides implementation recommendations 3 that specifically and sufficiently pts address the specific context. (includes ties to other systems and subsystems) 2 points: Document provides implementation recommendations that are do not specifically address context. 1 point: Document provides implementation recommendations that ignore issues relevant to the specific context. 0 points: Document does not provide any implementation recommendations. 2 points: Document provides implementation recommendations that are inadequate or inappropriate. 1 point: Document provides implementation recommendations that are notably vague or hard to follow. 0 points: Document does not provide any implementation recommendations. 2 points: 1 point: Design document includes formative evaluation strategies that are not likely to produce effective results. Comments: 3 points: Document provides a specific list 3 of implementation pts recommendations that are clear and easy to follow. Comments: 3 points: Design document includes effective formative evaluation 3 pts strategies. (How-to) Design document includes formative evaluation strategies that may not be effective measures. 0 points: Design document does not include formative evaluation strategies. Comments: Evaluation (15) 3 points: The description and rationale of formative evaluation strategies is 3 pts clear and complete. 2 points: The description and rationale of formative evaluation strategies is vague or incomplete. 1 point: The description and rationale of formative evaluation strategies is very poor. 0 points: Design document does not include formative evaluation strategies. Comments: Evaluation (contined) (15) 3 points: 2 points: 1 point: 0 points: Design document includes effective Design document includes Design document includes 3 Design document does not include summative evaluation strategies. summative evaluation strategies that summative evaluation strategies that pts (How-to) summative evaluation strategies. are vague. may not be effective measures. Note: Summative evaluation strategies may address either “Kirkpatrick’s Levels” or Dick and Carey’s “Evaluating Alternatives” conceptual approach (or both). Comments: 3 points: The description and rationale of summative evaluation strategies is 3 pts clear and complete. 2 points: The description and rationale of summative evaluation strategies is vague or incomplete. 1 point: The description and rationale of summative evaluation strategies is very poor. 0 points: Design document does not include summative evaluation strategies. Comments: 3 points: Design document includes and explains at least one sample 3 instrument used for formative or pts summative evaluation. 2 points: 1 point: Design document explains (but Design document includes but does not include) at least one does not adequately explain at least one sample instrument used for sample instrument used for formative or summative evaluation. formative or summative evaluation. 0 points: Design document does not include at least one sample instrument used for formative or summative evaluation. Comments: 3 points: Document describes learning assessment instrument(s) and 3 pts includes a sample learning assessment (in the appendix). Assessing Learning (6) 2 points: Document describes learning assessment instrument(s) with sample items. 1 point: Document vaguely describes assessment instrument(s) or activities without giving sample items. 0 points: Document does not include learning assessment instrument information. Comments: 3 points: Instruments are closely tied to learning objectives and are likely to accurately represent student 3 pts performance levels. Comments: 2 points: Instruments are tied somewhat closely to learning objectives and will partially represent student performance levels. 1 point: Instruments are vaguely tied to learning objectives and will not accurately represent student performance levels. 0 points: Instruments are not tied to learning objectives at all. 3 points: Information is very organized 3 with well-constructed paragraphs. pts Document is clear, easy to follow. 2 points: 1 point: Information is organized with some Paragraphs are not well-constructed. well-constructed paragraphs. Document has flow problems. Document is somewhat clear. 0 points: Information appears to be disorganized. Document is not easy to follow. Comments: Some headings orphaned – otherwise excellent! 3 points: Paper follows APA Style Guidelines 3 where appropriate (headings, pts numbering, spacing, etc.) 2 points: Paper follows some APA Style Guidelines where appropriate. 1 point: Paper follows few APA Style Guidelines where appropriate. 2 points: Noticeable spelling and grammar mistakes (up to 5). 1 point: Frequent spelling and grammar mistakes (6-10). 0 points: Paper does not follow APA Style Guidelines where appropriate. Comments: Report Structure (18) 3 points: No spelling or grammar mistakes. 3 pts 0 points: Many spelling and grammar mistakes (11 or more). Comments: 3 points: Document includes all five of the following sections: Analysis, 3 Design, Development, pts Implementation, and Evaluation. (Though section names may vary.) Report Structure (continued) (18) 2 points: Document includes four of the following sections: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. (Though section names may vary.) 1 point: Document includes three of the following sections: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. (Though section names may vary.) 0 points: Document includes two or less of the following sections: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. (Though section names may vary.) Comments: 3 points: Document concludes with an 3 appropriate summary and/or pts conclusions section. Comments: 2 points: Document concludes with a weak or inadequate summary and/or conclusions section. 1 point: Document concludes with an inappropriate summary and/or conclusions section. 0 points: Document does not conclude with an appropriate summary and/or conclusions section. 3 points: Citations and references are used 3 appropriately and in standard pts APA format. Comments: 2 points: Citations and references are used but are incomplete or incorrect in some fashion. 1 point: Citations and references are used inappropriately or grossly inadequately. 0 points: Citations and references are not used.