Mutations
advertisement

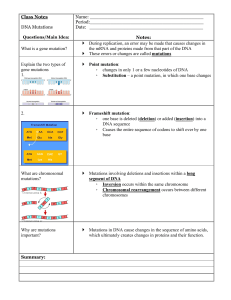
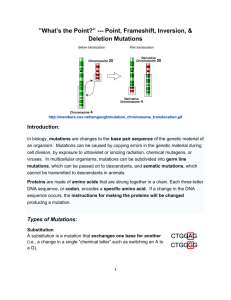
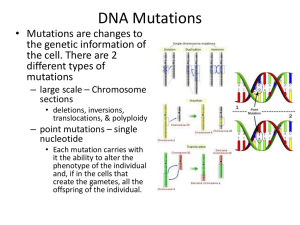
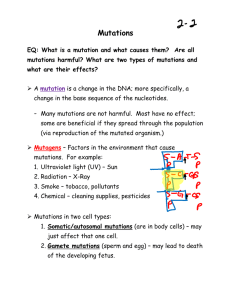
Mutations are changes to the base pair sequence of the genetic material of an organism. Mutations can be caused by copying errors in the genetic material during cell division, by exposure to ultraviolet or ionizing radiation, chemical mutagens, or viruses. Germ line mutations – can be passed on to descendants Somatic mutations – cannot be transmitted to descendants Point mutation – where only one base in the gene is copied incorrectly during DNA replication. This would be an error of the DNA-building enzyme, DNA polymerase. Point mutation example: (A) Substitution – exchanges one base for another example: change in a single “chemical letter” such as switching an A to a G C T G G A G C T G G G G Frameshift – Since protein-coding DNA is divided into codons three bases long, insertions and deletions can alter a gene so that its message is no longer correctly read or translated. The fat cat sat hef atc ats at Frameshift mutations example: (A) Insertion – extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in DNA C T G G A G C T G G T G G A G Frameshift mutations example: (B) Deletion – a section of DNA is lost, or deleted C T G G A G C T A G