The Urinary System
advertisement

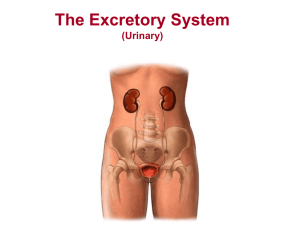
The Urinary System By: Jacob Miller & Bryce Schimon Period 5 Main Functions • Produces, stores and eliminates Urine • Regulates electrolyte balance • Controls blood volume • Maintains blood pressure Essential Parts •Kidneys •Ureters •Bladder •Urethra Functions of Essential Parts • Kidneys- helps maintain homeostasis • Ureters- runs parallel to vertebral column, carries urine from kidneys to bladder • Bladder- it lies within the pelvic cavity, behind the symphysis pubis and beneath the parietal peritoneum. It stores urine and forces it into the urethra • Urethra – lies between bladder to the outside of the body - conveys urine from the urinary bladder to the outside Structure of Urinary System • The Urinary system may also be called the Renal System because this group of inter-connected body parts contains many tissues and organs • The Urinary system contains two narrow tubes that transfer urine from the kidneys to the bladder which are called Ureters • The structure of the urinary system also includes collecting ducts, convoluted tubules and blood vessels The Kidneys Role • The kidneys are a bean shaped organ with a smooth surface and lie on either side of the vertebral column in a depression high on the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity • The Renal Sinus is a hollow chamber that allows the passing of blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels, and the ureter • The Kidneys role is to maintain homeostasis by regulating the composition ,volume and pH of the extracellular fluid. • They do this by removing metabolic waste from the blood and diluting them with water and electrolytes to form urine Pathway of Blood to Kidneys • Renal Arteries supply blood to the kidneys • Renal artery enters a kidney through the hilum and gives off several branches called interlobar arteries • The interlobar arteries branch, forming a series of incomplete arches called arcuate arteries which then give rise to interlobar arteries • Final braches lead to nephrons • Finally the renal vein then joins the inferior vena cava as it courses through the abdominal cavity. Nephrons • Nephrons consists of renal corpuscle and a renal tubule • Nephrons main function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances • Fluid flows through renal tubules on its way out the body • Renal Corpuscle – is composed of a tangled cluster of blood capillaries called glomerulus which is the 1st step in urine formation. • Glomerular capillaries filter fluid • Glomerular Capsule- is a thin walled, saclike structure that surrounds glomerulus . It receives the fluid that the glomerulus filters Urine Formation • Formation begins with filtration of plasma by glomerular capillaries, this is called glomerular filtration • Most of the fluid is reabsorbed into the blood stream • One capillary bed filters, the filtered fluid then moves into the renal tubule where majority of it becomes urine • Tubular Reabsorption moves substances from tubular fluid back into the blood • Tubular secretion moves substances from the blood within peritubular capillary into the renal tube • Kidney chooses what substances to keep • Extra fluid being eliminated is urine Composition of Urine • Composition of urine is different for everyone and based off of how much water they drink • Urine is about 95% water • Contains urea and uric acid • May contain amino acids and a variety of electrolytes Urea vs. Uric Acid •Urea • Urea is a by-product of amino acid catabolism • Urea enters the renal tubule by filtration • Uric Acid • Product of the metabolism of certain organic bases of nucleic acids • Active transports reabsorbs all the uric acid present in the glomerular but a small amount is secreted into the renal tubule and excreted in urine Process of Urine Elimination • Urine forms in the nephrons • Passes from collecting ducts through openings in the renal papillae and enters calyces of the kidney • It passes through the renal pelvis and a ureter conveys it to the urinary bladder • The urethra excretes urine to the outside Diseases • Kidney Disease • Urinary Tract Infection • Interstitial Cystitis • Kidney Stones • Bladder Cancer Work Cited • Zimmermann, By. "Urinary System: Facts, Functions & Diseases." LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 15 Jan. 2015. Web. 17 Apr. 2015. • "Urinary System." InnerBody. Web. 17 Apr. 2015. • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urinary_system • http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2001_saladin/folder_structure/ab/m2/s3/ • https://www.boundless.com/physiology/textbooks/boundless-anatomy-andphysiology-textbook/the-urinary-system-25/physiology-of-the-kidneys240/overview-of-urine-formation-steps-1171-2197/ • http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/kidney • http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/pubs/yourkidneys/ • http://www.google.com/search?safe=active&biw=1366&bih=674&noj=1&tbm= isch&sa=1&q=kidney+&oq=kidney+&gs_l=img.12 • http://www.google.com/search?safe=active&biw=1366&bih=674&noj=1&tbm=isch&sa= 1&q=bladder&oq=bladd&gs_l=img.1.0.0l10.1127.3374.0.5066.6.6.0.0.0.0.144.720.0j6.6.0 .msedr...0...1c.1.64.img..0.6.713.Q_hgzelqhH8#imgrc=ADFh4j4uuvfkCM The End