STUDY GUIDE Chapter 18 Test
advertisement

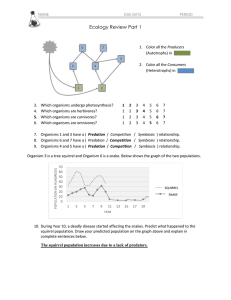
Name: ______________________________________ Period: ____ Date: _________ #: __________ STUDY GUIDE Chapter 18 Test 18.1: Everything is Connected Ecology: the study of the relationships of organisms with one another and with their environment. Biotic: Living factors. Includes anything alive in the environment. Abiotic: Nonliving factors. Abiotic factors include water, soil, light, and temperature. Organization in the Environment Organism: 1 single living thing. Population: a group of individuals of the same species that live together. Communities: all the different types of species that live and interact in an area. Ecosystems: include the different types of organisms within the community and the abiotic environment. Biosphere: the part of the Earth where life exists. The biosphere extends from the deepest parts of the ocean to high up in the air. 18.2: Living Things Need Energy Organisms can be divided into 3 groups based on how they obtain energy: 1. 2. Producers: use sunlight directly to make food. They do this through the process of photosynthesis. Consumers: eat other organisms to get energy. a. b. c. d. 3. Herbivore: eat plants Carnivore: eat animals Omnivore: eat both plants and animals Scavenger: eat dead animals Decomposers: break down dead organisms. They are nature’s recyclers, fungus and bacteria. Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramids Food Chain: a diagram that shows how energy in food flows from one organism to another. Food Web: a diagram that shows the food relationships between organisms in an ecosystem. Energy Pyramid: Triangular diagram that shows an ecosystem’s loss of energy, which results as energy passes through the ecosystem’s food chain. Limiting Factor: A resource that is so scarce, it limits the size of a population. For example, if there is enough water for 5 lions, then 5 lions or less will live there. The limiting factor is water. Carrying Capacity: the largest population that an environment can support. For example, if there is enough water for 5 lions, then 5 lions or less will live there. The carrying capacity is 5 lions. Competition: When 2 or more individuals or populations try to use the same resource. For example, two lions compete for the same mate. Predator: Animal that does the hunting. For example: Owl Predators have adaptations which help them to catch their food. Prey: Animal that gets eaten. For example: Mouse Prey have adaptations which help them to escape predators. Symbiosis: A close, long-term association between two or more species. At least one species benefits from this relationship. There are 3 types of symbiosis. 1. Mutualism: both species benefit 2. Commensalism: one species benefits and the other is not affected. 3. Parasitism: one species benefits and the other is harmed.