3 Modes of Communication
advertisement

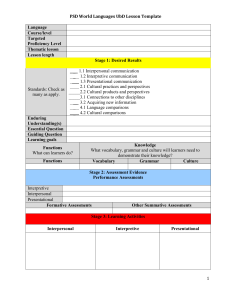
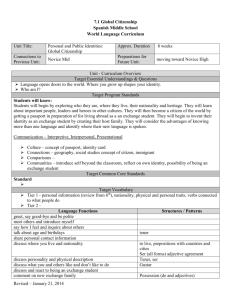
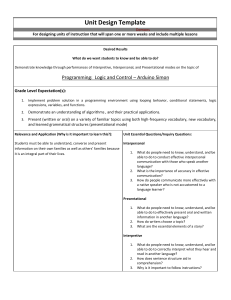
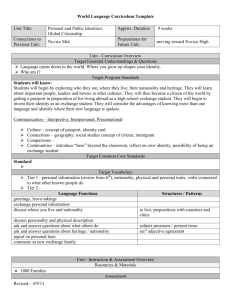
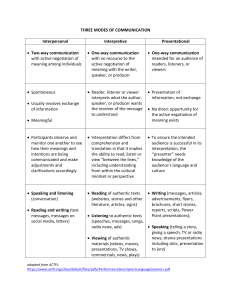
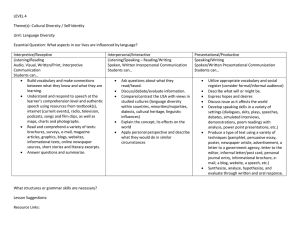
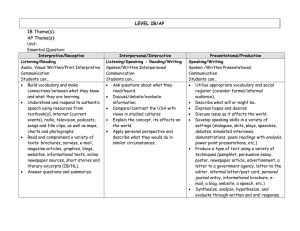
The Three Modes of Communication The Three Modes: Modes of Communication recognized by New York and national standards: Interpretive Interpersonal Presentational Interpretive “one way” reading or listening Interpretation of authentic language sources, e.g. texts, movies, radio, conversation, speeches, etc. Multiple ways of comprehension Implies ability to read and listen for literal and inferential meaning Interpersonal “two way” interactive communication listening – speaking listening-writing reading -speaking reading - writing Listening-speaking Games Songs, Rhymes and Finger Plays Props and concrete materials Dialogues Role play Reading/listening-speaking-writing a. Preview the context/topic by activating background knowledge and contextual clues b. Use visuals to present the main ideas/context c. Help students to anticipate/comprehend new vocabulary by conducting a Total Physical Response (TPR) activity to acquire new words d. Help students to establish a purpose for listening/reading/viewing e. Use skimming (get the gist) and scanning (seek specific information) Possible Activities: matching visuals, following a map or diagram, drawing a sketch to show comprehension graphic fill-ins: completing a form, diagram, or other graphic material while exploring the text matching main ideas to parts of the text selecting main ideas from a list of possibilities checking off specific ideas found in a text from a list of possibilities matching titles to sections of the text Presentational “one to many” communication Giving presentations, audio broadcasts, writing for publication, etc Focus on clear transmission of message Using the Modes in Assessment I. Interpretive Communication Students listen to or read an authentic text (e.g., newspaper article, radio broadcast, etc.) and answer information as well as interpretive questions to assess comprehension. Teacher provides students with feedback on comprehension/understanding. III. Presentational Communication Students engage in presentational communication by sharing their research/ideas/opinions. Sample presentational formats: speeches, drama, skits, radio broadcasts, posters, brochures, essays, websites, etc. II. Interpersonal Communication After receiving feedback regarding the Interpretive Phase, students are engaged in realistic interpersonal oral communication about a particular topic for a specific purpose. This phase could be either audio- or videotaped. Create an activity that reinforces interpersonal communication (the ability to describe) using this image. Create an interpersonal activity based on this text Create an interpersonal activity using this picture