File
advertisement

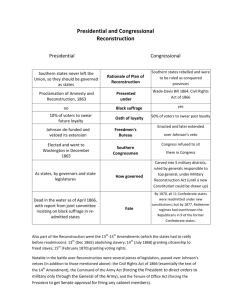
REVIEW QUESTION In their plans for Reconstruction, both President Abraham Lincoln and President Andrew Johnson sought to 1. punish the South for starting the Civil War 2. force the Southern States to pay reparations to the Federal Government 3. allow the Southern States to reenter the nation as quickly as possible 4. establish the Republican Party as the only political party in the South REVIEW QUESTION In their plans for Reconstruction, both President Abraham Lincoln and President Andrew Johnson sought to 1. punish the South for starting the Civil War 2. force the Southern States to pay reparations to the Federal Government 3. ALLOW THE SOUTHERN STATES TO REENTER THE NATION AS QUICKLY AS POSSIBLE 4. establish the Republican Party as the only political party in the South CONGRESSIONAL RECONSTRUCTION • “Andrew Johnson presented a weak plan for Reconstruction, liberally pardoning exConfederates and allowing reconstructed governments to be dominated by proslavery forces, which passed black codes to keep the freedmen subjugated” • Congress reconvened in December 1865 and immediately expressed displeasure with Johnson’s Reconstruction plan RADICAL REPUBLICANS Senator Charles Sumner Representative Thaddeus Stevens • Sumner and Stevens, set out to dismantle Johnson’s Reconstruction plan and to dictate Reconstruction on Congress’s terms • Called for – black voting rights – confiscation of Confederate estates, and military occupation of the South • NO LENIENCY! Congressional Election of 1866 • WIDENED THE DIVIDE BETWEEN PRESIDENT JOHNSON AND CONGRESS • President Johnson embarked on a “swing around the circle” tour where he gave speeches at various Midwestern cities to rally the public around his policy of lenient Union recognition for the southern states • His tour was a complete failure as he exchanged hottempered insults with the critics in the crowd. • Congressional Republicans took to “WAVING THE BLOODY SHIRT”- appealing to voters by reminding them of the sacrifices the Union made during the Civil War • When the congressional election was complete, the Republicans won more than the TWO-THIRDS MAJORITY in the House & the Senate that they needed to override any presidential vetoes “Swing around the circle” tour CIVIL RIGHTS ACT 1866 • Passed over Johnson's veto (block) • Weakened Black Codes • Negroes = rights with whites • Authorized use of federal troops for enforcement Freedmen’s Bureau Act 1866 • Passed over Johnson’s veto • Extended life of this federal agency • PROVIDE NEWLY FREE AFRICAN AMERICANS WITH FOOD/CLOTHING/SCHOOL ING/JOB RESOURCES • Protected Negroes Civil Rights • Use of military force if necessary th 14 Amendment 1866 • NEGROES ARE CITIZENS (ALL PERSONS BORN OR NATURALIZED IN THE US ARE CITIZENS BOTH OF THE US AND THE STATE THEY RESIDE • EQUAL PROTECTION OF THE LAWS • Declared the Confederate debt void • Disqualified most former Confederate leaders from holding office unless pardoned by Congress • EVERY SOUTHERN STATE REFUSED RATIFICATION (except Tennessee) Military Reconstruction Act 1867 • • • • Passed over Johnson’s veto SOUTH DIVIDED INTO 5 MILITARY DISTRICTS Military governor commanded federal troops TO REMOVE MILITARY RULE: – Conduct election open to Blacks and Whites for delegates to a Constitutional convention – New State Constitutions had to guarantee African American suffrage (vote) – Ratification of the 14th Amendment – 1869 – only 4 Southern states did not comply – Act did not go as far as giving freedmen land or education at federal expense. th 15 Amendment 1870 • Radical Republicans – still concerned that once the states were re-admitted to the Union, they would amend their constitutions &withdraw black suffrage – moved to safeguard their legislation by adding it to the federal Constitution with the 15th Amendment • 15TH AMENDMENT PROHIBITED THE STATES FROM DENYING ANYONE THE RIGHT TO VOTE “ON ACCOUNT OF RACE, COLOR, OR PREVIOUS CONDITION OF SERVITUDE.” th 15 Amendment 1870 • 15th Amendment did not guarantee the right to vote (SUFFRAGE) regardless of sex – outraged feminists like Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony – Equally disappointing to feminists was the fact that the 14th Amendment marked the first appearance of the word “male” in the Constitution – Efforts to include female suffrage in the 15th Amendment were defeated • Literacy tests and poll taxes were often used to keep blacks from voting. Intimidation and lynching were also common means to keep blacks from the polls