Physical versus Chemical Properties

Physical versus Chemical
Properties
Chapter 2 Section 2
Describing matter
Reviewing MATTER
• Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space
– Mass – the amount of matter in something
– Volume – the amount of space something occupies
• Which of the following is matter?
– A car?
– A box?
– You?
What is a property?
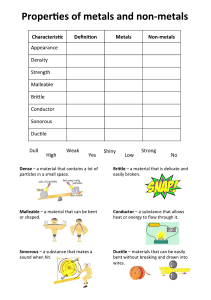
• Property: a characteristic of a substance that can be observed
Physical Property
Physical property: a property that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance.
Examples:
• luster
• malleability: the ability to be hammered into a thin sheet
• ductility: the ability to be stretched into a wire
• melting point
• boiling point
• density
• solubility
• specific heat
• Color
• Shape
• Size
• Density
• Melting Point
• Boiling Point
Physical Properties
Example of Physical Property
• The physical properties of sodium metal can be observed or measured. It is a soft, lustrous, silver-colored metal with a relatively low melting point and low density.
• Hardness, color, melting point and density are all physical properties.
Special Physical Properties
• Melting point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid at a given pressure water = 0 o C
• Boiling point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas at a given pressure water = 100 o C
•
Thermal
•
Density
•
Solubility
•
State
•
Ductility
•
Malleability
Chemical Properties
• Chemical property: a property that can only be observed by changing the identity of the substance
Chemical Properties
Examples of Chemical Properties
•
Reactivity with oxygen
•
Nonreactivity with oxygen
•
Flammability
•
Nonflammability
Chemical Properties
Comparison of Physical and Chemical Properties
Density
• Density is the amount of mass per unit of volume.
• Density can be used to identify a substance.
• The density of water is 1.0g/mL
Density Calculations
• Calculations:
D = m/V
• Ex: A cube has a mass of 2.8 g and occupies a volume of 3.67 ml. Would this object float or sink in water?
Mass = 2.8 g Volume = 3.67 mL
D = 2.8g/3.67 mL= 0.76 g/mL
– This object would float in water because its density is less than water (1.0 g/mL).
More Density Calculations
• Ex: A liquid has a mass of 25.6 g and a volume of 31.6 mL. Use the table below to identify the substance.
M=25.6 g V=31.6 mL
D = 25.6 g/31.6 mL
D= 0.81 g/mL
The substance is ethanol.
Substance
Mercury
Water
Ethanol
Density (g/mL)
13.6
1.00
0.81
Physical Change
Physical change is the change that affects one or more physical properties of a substance.
•
Imagine breaking a piece of chalk into two pieces. What are you changing? What is not being changed?
•
Physical changes do not change the identity of the matter involved
Physical Change
•
Freezing water for ice cubes
•
Sanding a piece of wood
•
Cutting your hair
•
Crushing an aluminum can
•
Bending a paper clip
•
Mixing oil and vinegar
Chemical Change
Chemical change happens when two or more substance are changed into one or more new substances with different properties.
•
Properties of a substance describe which chemical changes will or will not happen
•
Chemical change and properties are not the same, a change is the process in which it changes
Chemical Change
Examples of Chemical Changes
•
Soured milk
•
Effervescent tablets
•
Statue of Liberty
•
Baking a cake
Chemical Change
Clues that chemical change has occurred
•
Changes in color
•
Heat
•
Fizzing and foaming
•
Production of sound or light