Worksheet2 Unit 2 Materials technology
advertisement

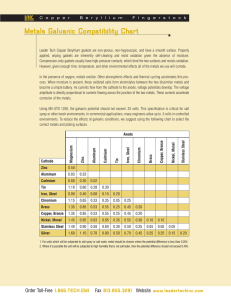
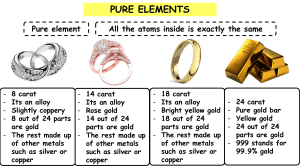
WORKSHEET2 UNIT 2 MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY •Which materials are widely used in engineering? •What is meant by recycling? •How does recycling affect engineering design? Look at page 14 Do 1.1. Complete 2.a Look at the meaning of the following words: magnetism = force of attraction galvanized = coated with zinc (Zn) to prevent rusting recyclable = can be recycled chromium = (Cr) and nickel (Ni) = metals added to steel to make stainless steel traces = small quantities scarcity = limited availability /rarity insulation = both electrical insulation and thermal insulation wire = single strand of metal scrap = waste material intended for recycling alloy = a mixture of metals sometimes containing a non-metal, for example carbon (C) in steel brass = an alloy of copper (Cu), zinc and, often lead (Pb) /led/ bronze = an alloy of copper and tin (Sn) melting down = using heat to change the state of a substance from solid to liquid energy-intensive = using a lot of energy electrolysis = passing an electrical current through a liquid or solid in order to separate chemical compounds ore = mineral from which metal is extracted hardwood = timber from pine trees softwood = timber from pine trees ironmongery = collective term for small metal items commonly used in buildings, for example door handles, hingers, screws, nails. Do exercise 2a Do exercise 2c Homework 3a, 3b, 3c, 3d WHAT IS MEANT BY CATEGORIZING MATERIALS? Putting materials into different categories/ types. Example: Metals - steal + copper Do 4 NOTE brakes are designed to slow down vehicles or moving parts. often they work through friction, by applying pressure to pads which are pressed against the sides of the disc, the inside of the drum, or directly against a wheel rim. Alternatives use systems that use electro magnetic force, systems that exploit the braking effects of engines or flywheels (via clutches and gearboxes), aerodynamic braking systems ( for example spoilers on aircraft, parachutes on dragsters), and reverse thrusters on jet engines. Brake discs are often made of ferrous metals (iron-base_ for example steel), or sometimes ceramic materials. Examples of materials used to make pads include: compounds of advanced materials (cars), ferrous metals (trains), rubber (bicycles), ceramics (performance cars) Do task 5a. Note: Green refers to ecological issues Red refers to heat (red hot means very hot) A hot topic is a current important topic Read the text and answer the questions in 5b Answers: 1. Because they use friction, which wastes energy as heat 2. They recover heat and use it to power the car 3. The ability to generate high levels of friction, and to resist the effects of friction and consequent heat 4. 4. Heat from the engine being absorbed by the chassis, which can damage sensitive parts such as electronic components and plastic parts