Atmospheric and Oceanic Interactions
advertisement

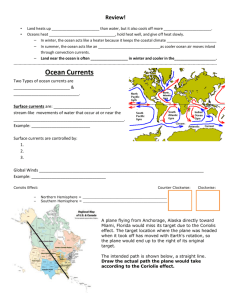
Atmospheric and Oceanic Interactions Air pressure the force of air on a surface Did You Know? Air pressure is caused by the weight of all the molecules that make up the air. - the combined force of air on just 1 square foot of surface, is about a ton! Did You Know? a high pressure system usually brings cooler temperatures and clear skies. a low pressure system usually brings warmer weather, storms and rain. Coriolis Effect the curving of moving objects, including wind, from a straight path due to Earth’s rotation Did You Know? The Coriolis effect causes wind and ocean surface currents to curve to the right north of the equator, and left south of the equator. Did You Know? There is an old urban myth that the Coriolis effect causes water going down drains or toilets to turn different directions above and below the equator? This myth is false! The Coriolis effect doesn’t influence such small bodies of water. Air Mass a large body of air that is similar in temperature, humidity, and air pressure throughout Did You Know? Air masses are categorized by temperature and moisture. Did You Know? When two different air masses meet, the boundary is called a “front” – there are 4 basic types. Convection Current the vertical circular motion of a fluid (such as air) in which hot material rises while cold material sinks Did You Know? Convection currents can happen in any material that flows, liquid or gas – Earth’s mantle Atmosphere Oceans And lava lamps!!! Did You Know? Convection currents happen because heating and cooling changes density Heating decreases density; less dense material floats. Cooling increases density; more dense material sinks. Land Breeze a wind that blows from the land to the sea at night Did You Know? The air over the ocean stays warm longer than the air over the land, after the Sun goes down? This causes convection currents that create land breezes blowing toward the ocean at night. Sea Breeze a wind that blows from the sea to the land during the day Did You Know? On a hot, sunny day the temperature of the sea hardly changes but the land heats up quickly. This causes the light breezes to blow toward land instead, making sea breezes. Psychrometer instrument used to measure the humidity of air Did You Know? Hotter air can hold more water, generally. Since your sweat can’t evaporate to cool you as quickly if humidity is high, it feels even HOTTER! Did You Know? The most humid state in the United States is Washington. The most humid regions of the world are coastal areas near the equator, like Thailand and India. Prevailing Winds wind that blows predominantly from a single direction Did You Know? If it wasn’t for the trade winds, America might not exist! in the 18th century, ships used them to cross the Atlantic Ocean. Anemometer instrument that records wind speed and direction Did You Know? The first anemometer was invented in 1450 by an Italian architect, Battista Alberti. He was called the “prophet” of the Renaissance. Deep Currents currents formed when cold air temperatures and high salinity (salt) of surface currents make water denser, causing it to sink to the bottom; thus resulting in movement Did You Know? The ocean has three temperature layers. 1. The surface, temperatures vary 030 deg C. 2. The thermocline, temperatures decrease with depth. 3. The deep layer is below 1000 m, the temperature is near 0– 5 deg C and there is no seasonal change. Did You Know? Changes in deep currents can slow the global currents enough to cause “mini-ice ages”. 1350-1850; scientists call it the “Little Ice Age” and it affected climate all over the world. Some scientists think it may be happening, again. Surface Currents water movement 3-10 ft below the surface nearshore and 33 ft in deep ocean areas Did You Know? Surface and deep water currents connect the currents in all of Earth’s oceans, in a giant “Global Conveyor Belt” This means that what happens in one ocean, affects all of the world’s oceans. Gulf Stream warm ocean current flowing Northeastwards off the Atlantic Coast of the U.S. from the Gulf of Mexico Did You Know? The warm waters of the Gulf Stream make it possible for some areas of Northern Europe have milder climates than places just as far north in Canada. Hurricane a large, rotating tropical storm with wind speeds of at least 74 mph Did You Know? Hurricanes lose strength when they go on land or into cold waters, so they usually form in oceans near the equator. They need warm waters to provide energy for the storm. Did You Know? Every second, a large hurricane can release the energy of 10 atomic bombs.