Taxonomy- Powerpoint
advertisement

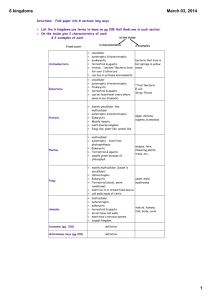
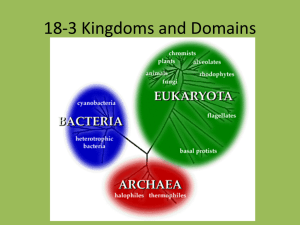
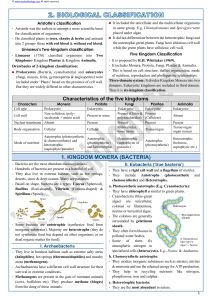
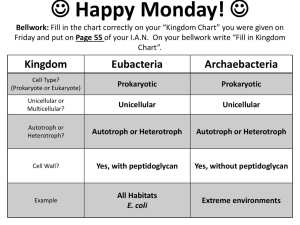
taxonomy How we classify organisms based upon structural similarities and differences Carolus Linnaeus • The “Father of Modern Taxonomy” • Established methods for classifying and naming organisms that are still used • BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE – Two name names Five kingdoms system • The most general classification – Monera – bacteria – Protist – Fungi – Plants – animals Kingdom Monera • Prokaryotic – No membrane-bound organelles – No nuclear membrane • Unicellular • Some are heterotrophic • cyanobacteria are autotrophic because they perform photosynthesis Protists • Eukaryotic – Membrane-bound organelles – Nuclear membrane • Mainly unicellular • Some are heterotrophic and some are autotrophic protozoa • These do not have cell walls • Examples include ameba and paramecium Algae • These protists have cell walls and chloroplasts • These protists are autotrophic • Some are multicellular like sea weed! Blue algae fungi • Fungi are eukaryotic • Fungi can be unicellular – Yeast and bread mold • Fungi can be multicellular – mushrooms • All fungi are heterotrophic • A fungus lives on its food source • They absorb the nutrients they need from the environment • Digestive enzymes are secreted into their food source for EXTRACELLULAR digestion • The end products of digestion (nutrients) are absorbed Plants • All plants are multicellular • All plants are eukaryotic • All plants are autotrophic • Plant cell walls are made of cellulose bryophytes • No true roots stems or leaves • No vascular tissue to circulate food or water • They are only a few centimeters in height • Must live in a moist area – mosses Tracheophytes • True roots, stems and leaves • They have vascular tissue to circulate food and water • They can grow to great heights • They can live in many different environments Animals • All animals are eukaryotic • All animals are multicellular • All animals are heterotrophic Classification Kingdom – most general Phylum – related classes Class – related orders Order – related families Family – related genus Genus – related species Species – most specific Species name • Based on a system of binomial nomenclature • The Latin version of the genus and species of an organism – Members of a species must be able to successfully reproduce and have fertile offspring Human versus chimpanzee • Human – – – – – – – Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primates Hominid Homo Homo sapien • Chimpanzee – – – – – – – Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primates Pongid Pan Pan troglodyte