Protist and Fungi Notes ppt
advertisement

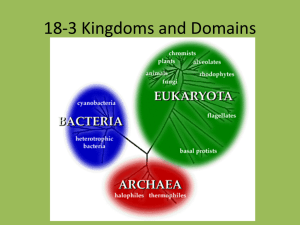
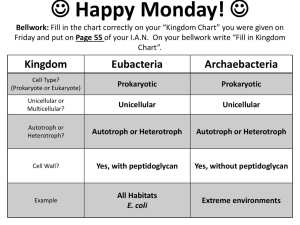
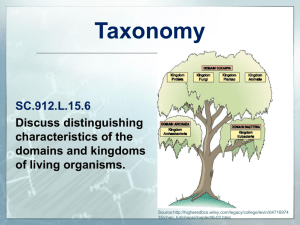
WELCOME, BIO-NINJAS Today you will need: Writing Utensil, Bellwork Sheet, Journal and Kingdoms Chart. Have your Homework out and ready. Bellwork: Use your notes/chart from yesterday to complete the bellwork. • Write the following question and a complete answer: • What are at least two similarities and two differences between Archaebacteria and Eubacteria? (there are multiple correct answers) Quiz Time • You will have 7 minutes to complete the quiz • Number 6 is a bonus question • When you finish open your notes and start a new page called “Protists and Fungi” Homework Tonight • Use the video to answer questions on the sheet you picked up. • Due Tomorrow! Expect a quiz! Youtube: “Protists by Bozeman Science” Video is only about 5 minutes long Quick Recap Walking pneumonia: the Gonorrhea is a result of a bacterial lung infection from Mycoplasma pneumoniae. sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a bacterium Halophiles:These are salt-loving bacteria that grow in places like the Great Salt Lake of Utah Archaebacteria Archaea Eubacteria Bacteria Protista Fungi Eukarya Plantae Anamalia The Six Kindoms And from these Domains evolved the six Kingdoms. Prepare page 62 for Notes Standard B8.C: Compare characteristics of taxonomic groups including archaea, bacteria, fungi, protists, plants and animals Essential Question: How would I know if I’m looking at a protist or fungi? Domain Eukaryota KINGDOM PROTISTA • Protists are simple eukaryotic microorganisms. • can be unicellular or multicellular but contain no specialized tissue. • Examples: algae, amoebae, protozoans, euglena, and slime molds. • Protists live in aquatic environments, love pond water • Can be photosynthetic autotrophs or heterotrophs. • Amoebae eat by phagocytosis. They surround and take other cells into their membranes. • Sexual or Asexual reproduction • Some are parasites and can cause diseases. • 3 ways protists move: 1. Flagellum = tail whip 2. Cilia = tiny hairs 3. Pseudopod = “fake foot” Flagellum Pseudopod(s) Cilia Kingdom Cell Type? (Prokaryote or Eukaryote) Unicellular or Multicelluar? Autotroph or Heterotroph? Cell Wall? Example Fungi Protista Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Some do and some don’t Algae, euglena Protists Video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0 -6dzU4gOJo Highlight and trade notes while the video plays Domain Eukaryota Kingdom fungi • Fungi are eukaryotic • Examples: yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. • Mostly multicellular, but some, like yeast are unicellular. • Fungal cells have cell walls that contain chitin. • Fungi are heterotrophs/decomposers. • Reproduction can be both asexual and sexual at different stages in their life cycles and often involves the production and dispersal of spores. • Harmful: Some fungi can cause disease in plants or animals. • Helpful: penicillin (antibiotic) is a type of mold that kills bacteria. • Helpful: Yeast is used to bake bread while other fungi are used to produce cheese and yogurt. The Faces of Fungi… Mycorrhizae Kingdom Fungi Cell Type? (Prokaryote or Eukaryote) Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicelluar? Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph? Heterotroph Cell Wall? Yes, chitin Example Yeast, mold, mushroom Protista Fun-guy video facts (See what I did there?) • Fungi (introduction) – You should have 3 facts • Cordyceps – You should have 1 fact • Truffles – You should have 6 facts Fill in the chart using the information from your notes. “Enhance” your chart using the following colors: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote: • • Color eukaryotic boxes blue Color prokaryotic boxes yellow. Unicellular vs Multicellular: • • • Color unicellular boxes purple Color multicellular boxes orange Color the both boxes half purple and half orange. Autotroph or Heterotroph: • • • Color heterotrophic boxes red Color autotrophic boxes green Color the both boxes half red and half green. Cell Wall: • • • Color the yes boxes grey Color the no boxes light blue Color the both boxes half grey and half light blue.