Genetics: Inheritance
advertisement

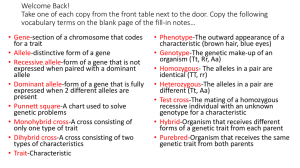
Genetics: Inheritance Meiosis: Summary Diploid Cells (2n): Cells with two sets of chromosomes, (aka “homologous chromosomes”) One set of chromosomes from each parent normal body cells Produced by mitosis Haploid Cells (n): Cells with one set of chromosomes Gametes or sex cells Produced by meiosis Meiosis: 2 rounds of cell division that produce cells with HALF the number of chromosomes Mitosis vs. Meiosis Some Definitions…. Genetics: The scientific study of heredity. Trait: A specific characteristic of an individual. (For example??) Gene: Sequence of DNA that codes for a protein (and, therefore, a trait) Passed down from parent to offspring Allele: Different possible forms of a gene (one from each parent) Homozygous: 2 of the same allele for the same gene Heterozygous: different alleles for the same gene Principle of Dominance Definition: Some alleles are dominant and others are recessive Which is the dominant allele for eye color, and which is the recessive? Which are the dominant alleles and which are the recessive? How do you know? Genotype vs. Phenotype Genotype: the genetic makeup (i.e. combination of alleles for each particular gene) Phenotype: the physical traits exhibited by an organism (observable) Can we PREDICT which trait(s) will be inherited?? Probability: Definition?? Punnett Squares Meiosis: How do we get genetic diversity? Crossing Over Segregation Fertilization Recessive Genetic Disorders What common trends might genetic disorders have? (Think about what DNA and genes CODE for!) Examples: Cystic Fibrosis, Tay Sachs Disease, Albinism If a genetic disorder is RECESSIVE, what does that mean? How might completely healthy parents have a child with a recessive genetic disorder?