Exam 2 Overview
advertisement

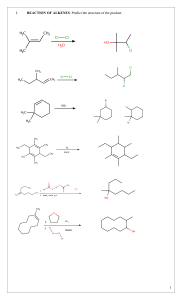
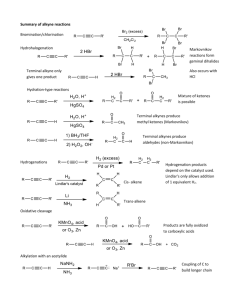
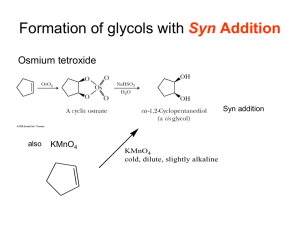
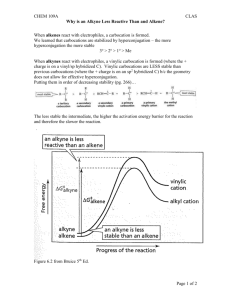
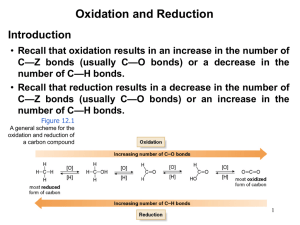
Chapter V 1) Alkene Structure/Nomenclature a. Geometry, hybridization, general molecular formula b. Longest carbon chain containing double bond c. Double bond gets numbering priority d. Consider cis/trans (hydrogen placement) and E/Z (highest priority placement) Chapter VI 1) Know the following information for each of the known reactions: a. Reagents b. Mechanism c. Intermediate d. Product e. Stereochemistry (racemic, syn-addition, anti-addition) f. Regioselectivity (markovnikov, anti-markovnikov) 2) Alkene Reactions a. Hydrohalogenation b. Acid-Catalyzed Hydration c. Halogenation d. Halohydrin Formation e. Oxymercuration f. Hydroboration g. Osmium Tetroxide h. Ozonolysis i. Catalytic Reduction: Hydrogenation 3) Other Information a. Know the difference between oxidation and reduction b. Oxidation is loss of hydrogens and gain of oxygen c. Reduction is gain of hydrogen and loss of oxygen d. Know heat of hydrogenation vs stability trend. Smaller absolute value of the heat of hydrogenation means more stable. (the negative indicates releasing energy) so releasing more energy indicates it was less stable to begin with. Chapter VII 1) Structure a. Geometry, hybridization, general molecular formula b. Low melting and boiling points (increases with molecular weight) 2) Nomenclature a. Longest carbon chain including alkyne b. Whichever comes first in molecule (alkyne or alkene) gets priority when numbering c. If alkyne and alkene are at same location in a molecule, alkene gets priority 3) Know the following information for each of the known reactions: a. Reagents b. Mechanism c. Intermediate d. Product e. Stereochemistry (racemic, syn-addition, anti-addition) f. Regioselectivity (markovnikov, anti-markovnikov) 4) Alkyne Reactions a. Hydrohalogenation b. Halogenation c. Oxymercuration d. Hydroboration e. Hydrogenation (to alkane) f. Hydrogenation (cis) g. Hydrogenation (trans) 5) Synthesis of Alkynes a. Know how to convert alkene to alkyne i. add Br2/CH2Cl2 , then eliminate them using 2 NaNH2/NH3 6) Synthesis using Alkynes a. Know how to add carbons to an alkyene i. Take off hydrogen using NaNH2/NH3 ii. Add R-X complex (usually a primary carbon) iii. Do the same thing to add carbons to the other side of the triple bond iv. use reactions to place functional groups on molecule Chapter VIII 1) Alkyl Halides a. C-X bond is polar b. Understand bond length and strength of different carbon-halide bonds 2) Radical Halogenation a. Be able to identify initiation, propagation, and termination steps b. Bromination is more selective than chlorination 3) Hammond’s Postulate a. Transition state is similar to reactants in exothermic reaction b. Transition state is similar to products in an endothermic reaction 4) Allylic Halogenation a. NBS is the source of the halogen b. Understand the stability of the allylic radical c. More than one product is possible due to resonance of allylic radical 5) HX and Peroxide added to alkene a. If using HBr: will get anti-Markovnikov product b. If using HCl or other halides: will get normal Markovnikov product Remember, this is a brief overview of what you need to know. Keep in mind this may not include everything you need to know. Make sure you do a lot of practice problems for each section. Write the mechanisms over and over again so they are engraved in your brain forever! :) GOOD LUCK EVERYONE!