PPT
advertisement
Securitization of IP
DR. Prabuddha Ganguli [PhD]
CEO
“VISION-IPR”
FLAT NO. 101/201, SUNVIEW HEIGHTS
SHER – E- PUNJAB SOCIETY , ANDHERI EAST , Mumbai 4001093
e-mail: ramugang@vsnl.com
Presentation at the WIPO-Italy International Symposium on
IPR and Competitiveness of SMEs in Textile and Clothing
Caserta, Italy, November 30-December 1, 2005
IPR Enabled Knowledge Incubation and
Realisable Value of IP to Potential Value of IP
Wealth Realisation
Product Lifecycle
Competitive sustenance
Market acceptability
IPR
Marketable Products/Processes
Management
Alignment with market
Idea into product/process
Ideas Actionable
Ideas demonstrable
Idea Feasibility
Freezing of options
Position in the protected
Technology grid
idea stage ..Technology
development
pganguli©2005
p.ganguli©2003
time
Value addition
to Organisation
& Market
Value of IP
• Dow Chemical Company lowered maintenance taxes
paid by aligning its intellectual assets with
business strategies reduced its annual costs for
obtaining and maintaining patents by $1.5 million.
By reducing its patent portfolio
from 12000 patents to 8500 patents from 1993 to 1999,
Dow saved $ 40 million in maintenance tax savings.
• IBM increased patent licensing royalty revenues 3,300%
from $30 million in 1990 to $1B today.
This recurring revenue stream is mostly
unrestricted cash that represents 1/9 of IBM’s
pretax profits and equates to $20B in product sales reve
pganguli©2005
Value of IP
• Philips Electronics, enhanced licensing
revenue by 45% and obtained 35%
more patents in 2000 as
compared to their performance in 1999.
• British Telecommunications generated ~
$14 million in new licensing revenue by
data mining its patent portfolio and
unlocking new sources of revenue
pganguli©2005
Traditional financing methods
•
Royalty recipients turn future receivables into cash
by selling the intellectual property outright.
-- the owner receives a lump sum
but loses all control over the assets.
•
Method of cashing in on royalty payments
has been to borrow against them.
This type of loan provides a fairly low amount
of proceeds
-- about 70% of the value of the receivables.
-- the term of these loan is < five years,
resulting in fairly high installment payments.
pganguli©2005
Loans using intellectual property rights as collateral
Venture companies lacking sufficient physical collateral,
such as land, buildings and other real estate,
and credit strength find it difficult to obtain loans
from financial institutions.
In these cases, Banks use loans secured by IPR,
such as patents and copyrights with market value.
Examples of intellectual property rights serving as collateral
•Patents that have been approved, patents that have been
filed (in principle, patents cannot be used as collateral before
they have been filed for approval) ;
Program copyrights (computer programs),
copyrights applying to content ; Other IPRs
pganguli©2005
Securitisations based on
royalties
2500
2000
1500
US $ million
1000
500
0
1992
1994
1996
2000
Source: www.dechert.com article by Malcolm S Dorris
pganguli©2005
IP Securitization by Industry
Industry
Issuance
$MM
% of total
issuance
Number of
transactions
Film
865
42
2
10
Music
446
22
14
70
Sport
315
15
1
5
Fast Food
290
14
1
5
Pharma
100
5
1
5
Apparel
24
1
1
5
Source: David Edwards in “From Ideas to Assets”, p. 605;
pganguli©2005
% number of
transactions
Securitization
Securitization is the pooling of revenue - generating assets,
and issuing securities backed by them.
The owner of the assets receives payment
based on the discounted present value
of the transferred assets,
and
the investors obtain a return on their investment
derived
pganguli©2005
from the assets' revenue stream.
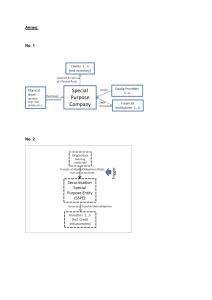
Securitization
Securitization means “a company, etc.
transfers specified assets that it owns
to a vehicle that is newly established
for the purpose of
holding assets (called “special purpose vehicle; SPV”)
and
raising funds backed up by
cash flows arising from transferred assets through the SPV.
It is financial means of raising funds by taking
only specific assets as reserves
instead of the entire asset base of the fund-raiser.
pganguli©2005
IP Securitization
Known Securitization Approaches
•issuance of publicly-offered corporate bonds
(typical securitization);
• issuance of privately-offered corporate bonds;
• privately-offered bonds that are practically
IP - backed loans
(e.g., privately-offered bonds underwritten
by a single institutional investor);
and non - recourse loans collateralized by IP (IPR)
pganguli©2005
IP Securitization
Known Securitization Approaches
•a scheme of securitizing rights in small portions
could also be added
since this scheme does not sufficiently secure
bankruptcy
remoteness of the assets at all and the investors
would
directly bear any risk concerning the assets,
it would be better to distinguish
this scheme from securitization.
pganguli©2005
IPR Securitization
•the characteristics of the assets to be securitized
•the transfer of assets to be securitized
i.e. transferability; true sales; effectiveness
against third parties; risk of cancellation of a
license contract ; evaluation of the IP concerned.
•credit enhancement
•issue of securities
•handling after the implementation of the securitization.
pganguli©2005
Securitization in USA
Asset-backed securities issued : 2.9 trillion $
Compare with straight corporate bonds issued 880 billion $
Diversification of Assets for securitization include
Lease credit claims and mortgages,
intellectual property (IP)
In January 1997, David Bowie, a U.K. rock star, issued
Bonds backed by the royalty claims for his music works,
and raised 55 million dollars in the U.S. financial markets.
This case is recognized as the first IP securitization.
pganguli©2005
Securitization of IP… Japan
Securitization of the ground-based broadcasting right
(a type of copyright) in 2002,
and
The first attempt of securitization of a patent right
was made in 2003.
pganguli©2005
IP Securitization
Use of System Supporting Business with Effective Use of Intellectual Property Rights
(SPC method)
pganguli©2005
Source:Dev.Bank of Japan)
DBJ cooperated with the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi, Ltd.,
in providing loans to GONZO K.K. to produce a new animated film.
In this project, GONZO transferred the intellectual property rights
to a special purpose company (SPC).
The SPC raised funds from DBJ and others, and
GONZO used the money it received from transferring the copyright
to produce a new work.
This new fund-raising method - distinct from
the “production committee method,” which involves equity – enables
the consolidated management and use of the copyright by the SPC
as well as the introduction of non-recourse loans and
outside investors, paving the way for the development of
content businesses that can compete on a global stage.
The key factors behind the success of this project were
GONZO's digital technology for animated productions and
the motivation to find a new form for the licensing business
run by GDH K.K.,
GONZO's parent company and an investor in the project.
pganguli©2005
Copyright securitized
Shochiku Co., Ltd., a film company,
granted TV Tokyo Corp.
the ground-based broadcasting right for 34 films
that had yet to be aired from among a total
of 48 of the popular serial films “It’s Tough Being a Man.”
The SPC, having obtained this content copyright
from Shochiku, raised funds from the Industrial Bank of Japan,
by offering the royalties for
the ground-based broadcasting right from TV Tokyo as backing.
pganguli©2005
Patents Securitized
Scalar Co., a venture company holding multiple patents
relating to optical technology and engaged
in the development of optical lenses,
had granted an exclusive license for four patent rights
that it owned to Pin Change, Co., Ltd.,
a venture company within Matsushita Electric Group.
Scalar transferred these patent rights to the SPC and then
SPC issued corporate bonds and raised funds backed up
by the royalties for the patent rights.
pganguli©2005
Examples… Securitization
Music industry : David Bowie's securitisation, others based
on receivables from music tapes.
Iron Lady's music receivables have been securitised.
Others:Scorpion, Ron Isley, etc
Fashion designers: In 1993, US fashion company Calvin Klein
raised US$58 million with the securitization
of royalties on perfume brands,
arising from the exclusive right
to use the Calvin Klein trade mark
on existing and future products.
Source: http://www.vinodkothari.com/index.htm
pganguli©2005
Chrysalis deal structured by Bank of Scotland{March 2001}
Source: http://www.vinodkothari.com/index.htm
GBP 60 million deal
The transaction uses a loan structure and
not a true sale structure.
The 15-year transaction includes a three-year revolving
period followed by a 12-year amortisation
period to a substantial residual amount
Funded by MUSIC Finance Corp and
the collateral was the Chyrsalis Group’s International
music catalogue and the revenues derived from the Catalogue
– the Net Publishers Share (NPS)
- via the US Commercial Paper market.
pganguli©2005
Chrysalis deal structured by Bank of Scotland
GBP 60 million ~ 40% of the estimated current value of the
catalogue and is non-recourse to the
rest of the Chrysalis Group.
Chrysalis is allowed to maintain control over
the administration and management of its
various music-publishing subsidiaries.
Effective interest rate after amortising all fees and costs
compared well to the Group’s then-prevailing
cost of borrowing.
pganguli©2005
Securitization… newer
approaches
• Monaco Records
– cash flows from Intellectual Property rights owned or
administered by the record label will go to repay
investors who can exercise their right to 'buy into'
profits when they reach a pre-determined level
– investors can realise their profit and a higher interest
rate in a much shorter time frame than with a traditional
Asset-Backed Bond issue, which will normally take
between 10 to 15 years to mature.
– the product will be offered to retail investors in the
capital market while earlier IP securitisation products
have been lapped up mostly by insurance companies on
private placement
pganguli©2005