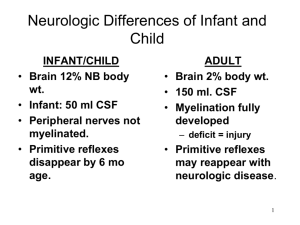
Neuro Powerpoint

Neurologic Trauma
8-10 Questions
Monti Smith, MSN, RN
Increased Intracranial Pressure
• The cranial vault contains:
– Brain tissue
– Blood
– Cerebrospinal fluid
– These three things give your brain a state of equilibrium
• Monro-Kellie Hypothesis - ↑ in any of the cranial vault components causes a change in the volume of the others by displacing or shifting CSF, ↑ CSF absorption or ↓ blood volume
Pathophysiology of ICP
• Normal ICP is 10 – 15 mm Hg
• Most commonly associated with head injury
• Secondary effect in conditions such as:
– Brain tumor
– Subarachnoid hemorrhage
– Encephalopathies
• ↑ ICP affects cerebral perfusion, produces distortion, and shifts brain tissue
Pathophysiology cont.
• Reduced cerebral blood flow results in ischemia
• Complete ischemia for > 3-5 mins. results in irreversible damage
• Early stages of ischemia - vasomotor centers are stimulated resulting in a slow bounding pulse & respiratory irregularities
Pathophysiology cont.
• CO
2
concentration regulates cerebral blood flow – rise causes dilation whereas a fall vasoconstricts
• Cerebral edema occurs when there is
↑ in water content of the brain tissue
Pathophysiology – Cerebral
Response to ↑ ICP
• Autoregulation – the brain’s ability to change the diameter of its blood vessels automatically for maintenance of constant cerebral blood flow
• Cushing’s response – the brain’s attempt to restore blood flow by increasing arterial pressure to overcome increased intracranial pressure
Decompensation Phase
• Exhibit changes in mental status & V/S –
Cushing’s triad:
– Bradycardia
– Widening pulse pressure/hypertension
– Respiratory changes
• Herniation of brain stem + occlusion of cerebral blood flow = cerebral ischemia & infarction = leading to brain death
If there is a Q on the test:
• What you would look for in the question, do they have these three things:
– Far apart BP
– Pulse in the 50’s
– Temp would be high
Clinical Manifestations of ↑ICP
• Change in level of responsivenessconsciousness
– The most important indicator of the pt’s condition
• Any sudden change in condition has neurologic significance:
– Restlessness without cause
– Confusion
– ↑ drowsiness
Complications of ↑ICP
• Brain stem herniation
– Not much you can do for this
• Diabetes insipidus
– Treat with fluid, check on lyte’s
• Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
– Restrict fluids
Management of ↑ICP
• ↑ICP is a true emergency a treat promptly
• Goal – ↓ cerebral edema, lowering volume of CSF, or ↓ blood volume while maintaining cerebral perfusion
• Administer osmotic diuretics to dehydrate brain & reduce cerebral edema
– Mannitol
– Glycerol
Nursing Diagnoses
• Ineffective airway clearance
– Diminished cough and gag reflexes
• Ineffective breathing patterns
• Ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion
• Deficient fluid volume
• Risk for infection
– b/c of hole they put in head to monitor pressure
What Can The Nurse Do?
• Maintain airway & monitor breathing
• Maintain proper positioning
• Maintain proper fluid balance
• Monitor for s/s of infection
• Monitor for potential complications
– Stool softeners to prevent straining during a poo
– Keep an emotional/stress free environment
Management of ↑ICP
• Foley catheter to monitor urinary output
• Serum osmolality levels to assess hydration
• Corticosteriods to help reduce edema
• Maintain cerebral perfusion by using fluid volume
& inotropic agents
• Reduce CSF & blood volume by draining CSF
• Control fever to ↓ rate at which cerebral edema forms
Head Injuries
• Trauma to scalp, skull, or brain
– Primary: initial damage to the brain (like you get hit in the head with a hammer)
– Secondary: evolves over hours & days after the injury (like Liam Neeson’s wife)
• An injured brain is different than other injured body parts because of its location!
– There is no where for the swelling and all that to go, so the pressure just increases and is super bad news
• Scalp injuries – causes lots of bleeding, but usually minor
Types of Force
• Acceleration injury
– Head in motion
– Like in a car wreck
• Deceleration injury
– Head suddenly stopped
– Like if you’re sitting stopped in your car and someone hits you
Skull Fractures
• Break in the continuity of the skull caused by a forceful trauma
• Fracture may be open or closed
– Open is if you have any tear in the dura
– Closed is when the dura is still intact
• Types of Fractures
– Simple – a clean break, straight little line
– Comminuted – a splintered break or there are multiple fracture lines
– Depressed – bone fragments that are depressed or imbedded into the brain tissue
– Basilar – fracture at the base of the skull
Clinical Manifestations
• Dependent on severity and distribution of brain injury
• Persistent, localized pain suggest fracture
• X-ray needed for diagnosis
• Basilar skull fracture frequently produces hemorrhage and CSF leakage
• Bloody CSF suggests brain laceration or contusion
Assessment & Diagnostics
• Physical Exam & Neuro status
• CT scan
• MRI
• Cerebral angiography
Medical Management
• Close observation if nonsurgical
– HOB is usually 30 degrees
• Surgery for depressed fractures
– IV antibiotics for these guys
• Monitor for CSF leakage
– Might leak out ears (otorrhea) and nose
(rhinorrhea)
– Get some sterile gauze and place it with some tape under their nose. Tell the pt not to be blowing their nose
Traumatic Brain Injury
• Occurs as a result of an external physical force that may produce a diminished or altered state of consciousness
• The brain responds to forces by forward movement within the cranial vault
• Motor vehicle crashes are the most common cause
• The cognitive impairment that they suffer from that is usually irreversible
Battle Sign
• Like a bruise or whatever behind their ear.
This is a good indicator that they hada basilar skull fracture. This is a good assessment.
Primary Brain Injury
• Results from physical stress within the brain tissue caused by open or closed trauma
• Open head injury – occurs with skull fracture or penetration of the skull
– The brain has been exposed to the outside/environmental contaminants. Not too good…
Damage that occurs to the vessels, sinuses, cranial nerves, anything like that
• Closed head injury – result of blunt trauma and is more serious
– You’re hit really hard and your brain gets squished.
You can’t really go in and repair anything.
Types of Brain Injuries
• Concussion – minor, client may or may not lose consciousness, causes no structural damage
– These guys should go to the hospital to make sure it’s not something more serious, but generally these people will be sent home and be given instructions to stay awake or woken often if they do sleep. Make sure they’re not confused, vomiting, c/o weakness or HA, etc. This is important b/c these are signs of internal damage. Usually take a few days to get over
• Contusion – major, client loses consciousness, brain is bruised
– This pt may lose consciousness for a few mins, usually have a decrease in BP, respirations, can lose control of their bowel/bladder. Usually when they go unconscious you can usually easily rouse them, but they’re very hyperactive when they get up (like all jumpy and what-not). Usually take several months to get over. Client may be left with HA, vertigo, seizures after the contusion.
Epidural Hematoma
• Results from arterial bleeding into the space between the dura and inner surface of the skull.
• Often these are caused by fractures of the temporal bones.
The break can cause a tear to the artery right there and it will form quickly
Epidural Hematomas
• Initial s/s:
– They go unconscious then they have a brief period of lucidity followed by a decreased
LOC
– This is a medical emergency! This person can have respiratory arrest w/I minutes!
– For this person they go in and drill holes to decrease the ICP. If there’s a clot they go in and remove it. If there is a bleed they’ll go and try to stop it. Might put in a drain to prevent reacumulation of the blood
Medical Management
• MEDICAL EMERGENCY!!!!!
• Burr holes through skull
• Possible craniotomy
• Drain
Subdural Hematoma
• Results from venous bleeding into the space beneath the dura and above the arachnoid
• Most common cause is trauma. Can be caused by bleeding disorderes or ruptured aneurysms.
Most are venous
(caused by ruptures of small vessels). Arterial ones are more rapid.
Types of Subdurals
• Acute – occur with major head trauma, s/s develop over 24-48 hours.
– S/S changes in LOC
• Subacute – occur with less severe contusions, s/s develop 48 hours-2 weeks
– S/S changes in LOC
• Chronic – occur with minor head injuries, s/s develop 3 weeks-3 months, most frequently seen in the elderly (we get older and our brain shrinks in our skull that stays the same size).
Harder to diagnose. Symptoms can mimic dementia or Alzheimer's
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
• Accumulation of blood within the brain tissue caused by tearing of small arteries and veins in the white matter
• Direct trauma (fractures and things, bullet wounds, stab injuries). You’ll see it a lot if someone has a tumor that bleeds all around it. High BP can cause this, anticoagulation therapy people who fall and hit their heads, bleeding disorders
Medical Management of Brain
Injuries
• Physical & neurological exam
• CT & MRI scans
• Ventilatory support
• Seizure prevention
• Fluid & electrolyte maintenance
• Nutritional support
• Management of pain & anxiety
What Is The Nurse’s
Responsibilities?
• Ongoing neurological assessment
– LOC
– VS
– Motor function
– Pupil size
Cerebrovascular Disorders
(6-8 Questions)
Monti Smith, MSN, RN
Stroke
• Definition – A disruption in the normal blood supply to the brain
• Medical emergency. Needs to be treated immediately, the longer it lasts the worse the symptoms are
• 3 rd most common cause of death in the
United States
• Primary cause of adult disability in the
United States
Types of Strokes
• Ischemic
– Thrombotic
– Embolic
– Transient Ischemic Attack
• Hemorrhagic
Thrombotic Stroke
• Results from thrombosis or narrowing of a blood vessel
• Most common cause of strokes
• Associated with DM & HTN
• Can be preceded by a TIA
• Usually don’t lose consciousness in the first 24 hours
Embolic Stroke
• Embolus dislodges & occludes a cerebral artery resulting in infarction & edema
• Second most common cause of stroke
• Mostly originates from the endocardial layer of the heart
• Lodges wherever the vessel narrows or where it bifurcates
• If we don’t treat the underlying cause of these kinds of strokes or else it is almost certainly going to happen again
Hemorrhagic Stroke
• Caused by bleeding into the brain tissue, ventricles, or subarachnoid space
• Causes can vary
– HTN, aneurysms, bleeding tumors…
– You don’t want these kinds of strokes. If you survive the acute phase you’re going to have major problems
• Deficits are severe & recovery is long
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
• Temporary loss of neurologic function caused by ischemia
• Can last from 15 minutes to 24 hours
• Serve as a warning sign of further cerebrovascular disease
• Complete recovery between attacks
Clinical Manifestations
• Motor deficits
– Hemiparesis
– Hemiplegia
– Ataxia
• Communication
– Dysarthria
– Dysphagia
– Aphasia
• Expressive Aphasia – their brain is thinking correctly but the words are coming out wrong. They know what they want to say but can’t get it out
• Receptive Aphasia – they get confused by what you say. On the way from the ear to the brain the msg gets messed up. It never gets
Clinical Manifestations cont.
• Cognitive Impairment
– Memory loss
– ↓ attention span
– Poor reasoning
– Altered judgment
• Psychological Effects
– Loss of self-control
– Depression
– Emotional lability
Clinical Manifestations cont.
• Perceptual Disturbances
– Homonymous hemianopsia
• Loss of half of your visual field
– Loss of peripheral vision
– Diplopia
– Difficulty judging distances
– Apraxia
• Inability to perform a previously learned action
Assessment & Diagnostic Findings
• History, assessment, neuro exam
• CT without contrast
• EKG
• Carotid doppler
• May also see
– Cerebral angiogram
– Transcranial doppler
– Transesophageal echocardiography
• Put scope down throat to look at the back of your heart. A regular echo can’t see the back of the heart.
– MRI
Medical Management for Acute
Stroke
• Thrombolytic Therapy within 3 hours of s/s
– Noncontrast CT of head
• Looking for blood. If they have blood it means it might be a hemorrhagic stroke and you don’t want to give them things that are going to increase their risk of bleeding
– Blood tests for coagulation studies
– Screening for hx of GI bleeding in past 3 months or major surgery in last 14 days
Surgical Management
• Carotid endarterectomy
– Go in and clean out the carotid arteries of plaque and stuff
• Carotid stenting
– Don’t see this alone as much. May do the cleaning and stenting at the same time
• Aneurysm clipping, coiling
• Resection of arteriovenous malformation
(AVM)
Medical Management
• Prevention is the most important!
• What are some modifiable risk factors?
– HTN
– Afib
– ↑ Lipids
– DM
– Smoking
– Carotid stenosis
– Obesity
– Excessive alcohol consumption
Medical Management
• Coumadin for atrial fibrillation
• Plavix, ASA, Ticlid for TIA’s and strokes from suspected embolic or thrombotic causes
• Statins
– For cholesterol
• Antihypertensives
Acute Nursing Interventions
• Support respiratory system
• Frequent neuro exam
• Monitor cardiovascular system
• Monitor musculoskeletal system
• Monitor for skin breakdown
• Monitor for constipation
• Promote normal bladder function
• Right after they’ve had the stroke be super nice to them
• Then in rehab we are harder on them. Boot camp kind of thing.
Acute Nursing Interventions cont.
• Assess & monitor nutritional status
• Be supportive with communication efforts
• Initially arrange client’s environment within their perceptual field
– Use their good eye, so to speak
• Give client & family clear & understandable explanations regarding situation and procedures
Nursing Diagnoses for Patients with Stroke
• Impaired physical mobility R/T hemiparesis, loss of balance and coordination, spasticity, and brain injury
• Acute pain (shoulder) R/T hemiplegia and disuse
• Self-care deficits R/T stroke sequelae
• Disturbed sensory perception R/T altered sensory reception, transmission
• Impaired swallowing
Nursing Diagnoses
• Incontinence R/T flaccid bladder, detrusor instability, confusion, or difficulty communicating
• Disturbed thought processes R/T brain damage, confusion, or inability to follow instructions
• Impaired verbal communication R/T brain damage
Nursing Diagnoses
• Risk for impaired skin integrity R/T hemiparesis/hemiplegia, or ↓ mobility
• Interrupted family processes R/T catastrophic illness and caregiving burdens
• Sexual dysfunction R/T neurologic deficits or fear of failure
Goals for Patient & Family
• Improvement of mobility
• Avoidance of shoulder pain
• Achievement of self-care
• Attainment of bladder control
• Improvement of thought processes
• Achievement of some form of communication
• Maintenance of skin integrity
• Restoration of family functioning
• Absence of complications
Achieve Self-Care
• Encourage to assist in personal hygiene as soon as able to sit up
• Start with affected side
• Dressing - better balance in seated position
• Improves morale if fully dressed
• Use clothing size larger than normal
• Place on affected side - dress first
Attain Bladder Control
• Offer urinal/Bedpan on schedule
• Upright posture & standing position for males
Achieve Communication
• Speech-language therapist to assess needs
• Be sensitive to reactions & needs
• Always treat patient like an adult
• Lend strong moral support
• Consistent schedule, routines, & repetition
• Surround with familiar objects
• Have attention, speak slowly, one at a time
Maintain Skin Integrity
• Emphasis on bony areas & dependent parts
• Specialty bed during acute phase
• Regular turning & positioning schedule
• Keep skin clean & dry
• Gentle massage of healthy skin
• Adequate nutrition
Improve Family Coping
• Family plays important role in recovery
• Involve them in patient’s care
• Need to avoid doing for patient what patient can do for himself
• Inform them rehab is long & progress may be slow
Sexual Dysfunction
• Profoundly altered by disability
• Often experience loss of self esteem & value
• Encourage to keep active, adhere to exercise program, continue to remain self sufficient
• May benefit from sexual counseling
Home Care Planning
• May require speech therapist & occupational therapist
• Emotionally:
– tires easily
– will become irritable & upset at small things
– likely to show less interest in things
– depression is common
Home Modification
• OT assess home environment & recommends modifications
• Shower - sitting on stool
• Long-handled bath brush
• Portable shower hose
• Handrails
Communication
• Speech-language pathologist assess ability to communicate
• Nursing - includes listening, asking to follow simple directions, & observing cope with dysfunction
Continued Management
• Promoting positive self-esteem
– Give as much psychological security as possible
– Patience & understanding while learning to speak
– Treat patient as adult - use kind, unhurried manner
– Accept patient’s behavior & feelings
– Avoid completing thoughts & sentences for patient
– Environment should be relaxed & permissive
– Encourage to socialize with family/friends
Critical Thinking
• The nurse planning care for a client who suffered a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) with residual dysphagia would write on the care plan to avoid doing which of the following during meals?
– (A) Feed the client slowly
– (B) Give the client thin liquids
– (C) Give foods with the consistency of oatmeal
– (D) Place food on the unaffected side of the mouth
Brain Tumors
• Definition: A localized intracranial lesion that occupies space within the skull.
• Tumors usually grow as a spherical mass but can grow diffusely, infiltrating tissue.
Brain Tumors
• Primary
– Originate within the CNS
– Cause unknown – possibly genetics, defective immune system, heredity, viruses, head injury
• Secondary/Metastatic
– Develop from structures outside the brain
– Lesions occur commonly from lung, breast, lower GI, pancreas, kidney, skin
Gliomas
• Most common brain neoplasm – about
60% of all brain tumors
• Spread by infiltrating into surrounding neural tissue
• Total removal causes considerable damage to vital structures
• Astrocytomas – most common type
Pituitary Tumor
• Most common is Adenoma
– 10 – 25% of all brain tumors
– Symptoms are caused by pressure on adjacent structures or hormonal changes
– Pituitary gland AKA hypophysis
Menigioma
• Encapsulated, globular, and well demarcated
• Causes compression and displacement of surrounding brain tissue
• Tends to recur
Acoustic Neuroma
• AKA cerebellar pontine angle tumors because of anatomic location.
– On the 8
th
cranial nerve
• More prevalent in females
• Common symptoms: hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness
Clinical Manifestations of Brain
Tumors
• Symptoms of increased ICP
– Headache
– Vomiting
– Papilledema
– Personality changes
– Focal deficits
• Motor
• Sensory
• Cranial nerve dysfunctions
Diagnostic Findings
• CT Scan, MRI, PET Scan
• Stereotactic biopsy – diagnoses deep-seated brain tumors
• Cerebral Angiography – for visualization of cerebral blood vessels
– Because sometimes tumors are very vascular and they don’t want to cut it out before they get rid of the vessels cause you might bleed to death
• EEG – Detects abnormal brain waves and temporal lobe seizures
• Cytologic studies of CSF – detect malignant cells
Treatment Modalities
• Transsphenoidal microsurgical removal
– Up your nose. Take the tumor out of your nose!
Eww
• Radiosurgery with a Gamma Knife – delivers high dose of radiation – no surgical incision
• Stereotactic – Laser or radiation delivery –
Implantation of radioisotopes
• External-beam radiation
• Brachytherapy – surgical implantation of radiation sources
Nursing Management
• Monitor patient for aspiration (surgical)
• Monitor for ↑ICP
• Frequent reorientation may be required
• Monitor patients with seizure history
• Assess motor function
• Assess speech
• Pupillary size and reaction may be affected by cranial nerve involvement
Cerebral Metastases
• Metastatic brain lesions constitute 10% of all intracranial tumors
• Cerebral Metastases is most common
• Signs and Symptoms include:
• Headache
• Paralysis
• Seizures
• Aphasia
• Focal Weakness
• Altered Mentation
• Personality Changes
Medical Management
• Palliative treatment
• Surgery
– Treatment of choice for brain tumors
• Radiation therapy
• Chemotherapy
• Corticosteroids – headaches (to decrease chance of
HA)
• Osmotic agents – decrease IOP (i.e. manitol)
• Anticonvulsants
• Analgesics
• You probably won’t see chemotherapy IV because chemotherapy can’t cross the BBB
Seizures & Headaches
(8-10 Questions)
Monti Smith, MSN, RN
Seizure Disorders
• Definition – An abnormal, sudden, excessive discharge of electrical activity within the brain
• Causes vary and are classified as:
– Primary/Idiopathic – no identifiable cause
– Secondary – hypoxemia, fever, head injury, hypertension, CNS infections, metabolic/toxic conditions, brain tumor, drug withdrawal, allergies
Seizures
• Six types of generalized seizures
– Tonic-clonic
• Generalized seizures, also called Grand Mauls or whatever.
2-5 minutes, person goes rigid, LOC, incontinence. After they come around they’re confused and all that mess
– Absence
• They just stare off, usually last seconds
– Myoclonic
• Brief jerking or stiffening of the extremities. Usually last for a few seconds.
– Atonic/Akinetic
• Lost of muscle tone, may fall down.
– Clonic
– Tonic
Seizures
• Partial or Focal
• Two main classes
– Complex
• Psychomotor
• Temporal lobe seizures
– Simple
Seizures
• Unclassified/Idiopathic
– Account for about half of all seizure activity
– Occur for no known reason
– Do not fit generalized or partial classification
Seizures
• Patient may have memory loss during seizure activity & a short time thereafter
• Brain damage may occur when seizures are severe or prolonged
• Risk for hypoxia, vomiting, pulmonary aspiration, persistent metabolic abnormalities
• Goal of treatment is control of the seizure and determination and control of the cause long-term
– If we can figure out what’s causing it and treat that then we have a good chance of getting rid of these guys
Management
• Management meets individual patient needs not just manage and prevent seizures
• Drug therapy – goal is to achieve seizure control with minimal side effects
• Drug therapy controls rather than cures
Status Epilepticus
• Definition – Acute prolonged seizure activity
– Either last 30 mins or seizure after seizure after seizure after seizure after seizure and so on
– The brain isn’t getting any oxygen during this time
• Considered a major medical emergency
• Produces cumulative effects
• Repeated episodes of cerebral anoxia & swelling may lead to irreversible & fatal brain damage
• Goal of management is to stop the seizures as quickly as possible, ensure adequate cerebral oxygenation , and maintain a seizure-free state
Seizure Treatment
• Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
– Controls medically intractable simple or complex partial seizures
– Appropriate for persons not candidates for surgical intervention
– Appropriate for persons not controlled by less invasive treatment options
– Surgically implanted in the left chest wall
– Activated to deliver intermittent VNS
Headache
• One of the most common complaints
• More of a symptom than disease
• Stress response
• Vasodilation
• Skeletal muscle tension
Types of Headaches
• Primary – no organic cause
– Migraine
– Tension
– Cluster
– Cranial arteritis
• Secondary – associated with a cause
– Brain tumor
– Aneurysm
Migraines
• Recurring vascular-type headache characterized by unilateral or bilateral throbbing pain
• Cause not clearly demonstrated
– Occurs more commonly in women
– Strong familial tendency
– Typical time of onset is puberty
– Highest incidence ages 20 – 35
Types of Migraines
• Migraine with aura
– Visual disturbances
– Parasthesias
– Motor dysfunctions
• Migraine without aura
Clinical Manifestations
• Usually begins on awakening but can occur any time
• Migraine is divided in 4 phases
– Prodrome
– Aura
– The headache
– Recovery
Clinical Manifestations
• Prodrome Phase
– Experienced by 60%
– Symptoms occur hours to days before headache
• Depression
• Irritability
• Feeling cold
• Food cravings
• Anorexia
• Activity level changes
Clinical Manifestations
• Aura Phase
– Occurs in about 20%
– Lasts less than an hour
– Focal neurologic symptoms
– Visual disturbances
– Numbness and tingling in lips, face, or hands
– Mild confusion
– Slight weakness of an extremity
– Drowsiness or dizziness
Clinical Manifestations
• Headache Phase
– Vasodilation and serotonin level declines
– Throbbing headache, severe and incapacitating
– Photophobia
– Nausea/Vomiting
– Duration 4 – 72 hours
Clinical Manifestations
• Recovery Phase
– Pain gradually subsides
– Muscle contraction in the neck and scalp are common
– Muscle ache and local tenderness
– Exhaustion
– Mood changes
– Physical exertion exacerbates pain
– Extended sleep may occur
Medical Management
• Therapy is abortive or preventive
• Abortive (symptomatic)
– Best for frequent attack sufferers
– Aim at relief or limiting headache at onset or while in progress
• Preventive
– Frequent attacks at regular or predictable intervals
– Would take these on a daily basis
Medical Management
• Serotonin receptor agonists
• Most specific anti-migraine agents available
• Cause vasoconstriction
• Reduce inflammation
• May reduce pain transmission
• Examples
– Ergotamine
– Sumatriptan
– Dihydroergotamine
Medications
• Ergot Alkaloids
– Ergotamine
– Dihydroergotamine
• Triptans
– sumatriptan (Imitrex)
Prophylactic Treatment
• Antiepileptics
– Topamax, Depakote, Valproic Acid
• Antidepressants
– Amitriptyline, nortriptyline
• Antihypertensives
– Propranolol, Verapamil, Lisinopril,
Candesartan
• Botulinum toxin A (Botox)
Alternative Treatment
• Biofeedback
• Behavioral therapy
• Herbs
– Feverfew
– Petasites hybridus (herb Butterbur)
• Acupressure/acupuncture
• Massage/chiropractic
• Exercise
Migraine Triggers
• Menstrual cycles • Fatigue
• Overuse of certain meds
• Nitrites
• Bright lights
• Foods with tyramine
• Sleep deprivation
• Depression
• Milk products
• Processed foods
• Aged cheese
• Wine & Chocolate
• Monosodium
Glutamate
Nursing Management
• Goals
– Administer medications to treat acute event
– Prevent recurrent episodes
• Patient education regarding precipitating factors
• Possible lifestyle or habit changes
• Pharmacologic measures
Relieving Pain
• Early phase requires abortive medication therapy ASAP
• Ongoing phase includes
– Comfort measures
– Quiet room/area
– Dark environment
– Elevate HOB 30 degrees
– Antiemetics as needed
Cluster Headache
• Severe form of vascular headache
• Most frequent in males ages 20 – 40 years
• Unilateral coming in clusters of 1 – 8 daily
• Watering of the eye and nasal congestion
• Attacks last 15 mins. to 3 hrs.
• May have crescendo – decrescendo pattern
• Described as penetrating and steady
Clinical Manifestations
• Excruciating pain (boring or piercing in nature)
• Orbital or supraorbital pain
• Eye tearing
• Tenderness of the temporal artery
• Facial flushing
• Elevated skin temperature on the ipsilateral side
• Very restless behavior
Precipitators
• Alcohol
• Nitrites
• Vasodilators
• Histamines
Medical Therapy
• Medication therapy
– Triptans
– Tricyclic antidepressants & vasoconstrictors
– 100% oxygen @ 7 – 9 l/min for approx.
15 mins.
– Exercise
• Prophylactic therapy
– Calcium channel blockers (verapamil)
– Corticosteroids (prednisone, solumedrol)
Cranial Arteritis
• Inflammation of cranial arteries
• Severe headache localized in region of temporal arteries
• Inflammation may be generalized
(vascular disease)
• Inflammation may be focal (cranial arteries)
• Older population – greatest incidence >70
Clinical Manifestations
• Fatigue
• Malaise
• Weight loss
• Fever
• Inflammation – heat, redness, swelling, tenderness, or pain over affected artery
• Visible nodular temporal artery may occur
• Visual problems from ischemia
Treatment
• Corticosteroids to prevent loss of vision due to vascular occlusion or rupture of involved artery
• Patient teach: Abruptly stopping medication can lead to relapse
• Analgesics for comfort
Tension Headache
• Contraction of the muscles in the neck and scalp
• Most frequent cause is stress
• Steady, constant feeling of pressure
• Described as band-like or a weight on top of the head
• Chronic rather than severe
• Probably most common type of headache
Nursing Considerations
• Reassurance that the cause is not a brain tumor
• Employ stress reduction techniques
– Biofeedback
– Exercise
– Meditation
• Symptomatic relief of symptoms
– Local heat
– Massage
– Analgesics, antidepressants, muscle relaxants
Neurologic Infections,
Autoimmune Disorders, and
Neuropathies
15-20 Questions
Monti Smith, MSN, RN
Neurologic Infections
• Meningitis
• Brain Abscess
– Infectious material in the brain
• Encephalitis
Meningitis
• Inflammation of the meningeal tissues
• Classified as:
– Bacterial – gains access through bloodstream, wounds of the skull, & fractures to the skull or sinuses
• Can be deadly!
– Viral – cause is viral or secondary to lymphoma, leukemia, or HIV
• Commonly seen in colleges, military bases, etc. More common in the winter (b/c that’s when you typically get more infections)
Clinical Manifestations
• Headache
• Fever
• Nuchal rigidity
• Positive Kernig’s sign
– When the pt is lying with their knee up to their stomach. The leg can’t be completely extended.
• Positive Brudzinski’s sign
– When you flex their neck, their knees and hips flex as well
• Photophobia
Autoimmune Disorders
• Multiple Sclerosis
• Myasthenia Gravis
• Guillain-Barré Syndrome
Multiple Sclerosis
• A progressive, degenerative disorder characterized by demyelination of nerve fibers of the brain & spinal cord
• Cause is unknown, but thought to be related to genetics, infection, & immunity
• Affects mostly women between 20-40
• Characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation
• Seen more in cold climates
Types of Multiple Sclerosis
• Relapsing-remitting
– Most common
– These pts will tend to experience series of attacks or exacerbations followed by complete or partial remission
• Primary progressive
– Disease shows progression from onset with occasional plateaus and temporary minor improvements
– As soon as a pt finds out they have MS it is progressing
• Secondary progressive
– Chronic progressive form. No real periods of remission
– Small breaks with some relief
• Progressive-relapsing
– Worst one. Most commonly found in men
– Characterized by gradual decline, no real periods of remission
Early Symptoms
(Common early S/S)
• Tingling (lasts a few days usually)
• Numbness (lasts a few days usually also)
• Loss of balance
• Blurred or double vision (very common. A lot of times people will go to the eye dr for this and the eye dr guy sends them in to be checked for MS)
• Weakness in one or more limbs
Clinical Manifestations Motor
• Fatigue and stiffness of extremities
– Spacticity
• Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes
• Positive Babinski’s reflex
• Visual difficulties
– Could be blurred vision, double vision, decreased visual acuity, nystagmus (googly eyes)
• Intention tremor
– I don’t usually have a tremor all the time, but when I go to perform an activity (like picking up a cup) I get the tremor
• Unsteady gait
• Dysmetria
– Inability to direct or limit movement. Like I want to go one way but I can’t
Clinical Manifestations Sensory
• Facial pain
• Numbness
• Tingling
• Burning
• Bladder function changes
– Can be urgency, frequency, having to pee a lot at night
• Bowel function problems
• Problems with sexuality
– Impotence, decreased vaginal secretions, etc.
Clinical Manifestations
Cognitive
• Inattentiveness
• Impaired judgment
• Decreased concentration
• Decreased short-term memory
• Decreased ability to perform calculations
Assessment & Diagnostic Findings
• MRI
– They are looking for Demylenating plaques
(called MS plaques) in the brain, neck, and spine.
A lot of the times you can tell from the symptoms where the problem might be. Vision problems = head. Tingling = neck. Leg problems = spine.
• CSF analysis
• Evoked potential studies
• Neuropsychological testing
– How bad are your cognitive impairments?
• Sexual history
Medical Management
• No cure
• Goals of treatment: delay progression of disease, manage chronic symptoms, & treat acute exacerbations
• Management strategies target various motor
& sensory symptoms & effects of immobility
– Some people may only take one thing a week to prevent progression while not in an exacerbating stage. Others have to be on super tons of stuff all the time. It just depends on the person
Pharmacologic Treatment
• Disease-modifying
– Betaseron, Avonex, Rebif, Copaxone,
Novantrone, Methylprednisolone
• Symptom management (spasticity)
– Baclofen
– Valium
– Zanaflex
– Dantrium
Pharmacologic Treatment Cont.
• Symptom management (urinary problems)
– Urecholine
– Prostigmin
– Ditropan
• Symptom management (CNS stimulants)
(to try and fight the symptoms of fatigue)
– Cylert
– Ritalin
– Provigil
– Amantadine
Nursing Interventions
• Promote physical mobility
– Walking, stretching, swimming, stationary bikes. Do things that aren’t strenuous because the quick stuff can make their spasticity worse
(which is bad). Plan rest and activity accordingly
– MS pt’s do poorly if their body temp goes up. The higher the temp, the worse their symptoms.
• Prevent injury
– MS causes a lot of problems with incoordination and their gate. They may have to use assistive device
• Enhance bowel & bladder control
– May require training
• Enhance communication
– Like for someone in a progressive form, might have problems with their communication. She hasn’t really seen this
• Improve sensory & cognitive function
• Teach about medications
• Educate family
Myasthenia Gravis
• Definition – An autoimmune disease that involves a decrease in the number and effectiveness of acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction
– Antibodies are found in 80-90% of people with myasthenia gravis (MG)
– 80% of pt’s diagnosed with MG end up having thymus gland problems (could be hyperplasia or a tumor which is called a thymoma)
• Thymus gland is believed to be where these antibodies are produced
• Etiology – Although unclear, research strongly suggests cause is antibodies to acetylcholine receptors
• When someone has MS their immune system makes antibodies that damage or block many of the muscles’ acetylcholine receptors. The effected muscles don’t work as well as they would normally if they had all the acetylcholine receptors…
Incidence of MG
• Not hereditary
• May have 5% familial incidence
• Onset before age 10 or after age 60 is rare
• Peak age between 20-30 years
• Women affected 3 times more often than men if onset before age 40
Clinical Manifestations
• Extreme skeletal muscle weakness
– Usually of the bigger muscles. May have trouble getting up from sitting.
Waxing/waning of this. Worsen with use and improves with rest. This is a hallmark sign of the disease! Muscles are usually stronger in the morning and weaker in the evening
• Fatigability
• Diplopia (double vision)
• Ptosis (drooping of the eyelid)
• Sleepy, mask like expression.
– Could have changes in expression or speech, difficulty with mastication
(chewing).
• Dysphonia (voice impairment)
• Extremity weakness
– Sometimes they can’t even keep their head up b/c their neck is super weak
• Respiratory weakness
• Bulbar = the combination of the chewing, swallowing, speech stuff.
This could be bulbar weakness or whatever to describe weakness in these three places
Diagnostic Findings in MG
• History & physical exam
• Tensilon test
– Tensilon facilitates the transmission of impulses at the myoneural junction leading to temporary improvement of symptoms.
It’s administered IV
– Their eye is droopy and you give them this and their eye isn’t droopy anymore. Then after a few mins the eye is droopy again.
– Tensilon inhibits the breakdown of acetylcholine. It can cause Vfib and cardiac arrest. Make sure you have atropine in case that happens and you need to give it!
• Acetylcholine receptor antibodies
– They take your blood and do a test. About 80-90% of pts with
MG will test positive for these guys
• Electromyography (EMG)
– Stick a needle in your muscle and they do tests and things to see how your muscles are working…
• CT scan, MRI
Medical Management
• Anticholinesterase medications
– Mestinon
• Immunomodulating drugs
– Prednisone
• Cytoxic medications
– Imuran, Cytoxan, Neoral
Medical Management
• Plasmapheresis
– Used to treat exacerbations. Done IV. Take the plasma and plasma components (kind of like dialysis). They separate the blood cells and the antibodies, then they put the blood back in. This simply reduces the number of circulating antibodies. In about 75% of pt’s this gives them great improvement, but it’s only temporary…
• IV immune globulin
– They don’t think it works that great, and it’s very expensive. So they don’t do this much
• Thymectomy
– They go in and remove your thymus gland. It’s in your chest, they have to go crack your ribs to remove it. Can give you partial or complete remission. Can take up to 3 years to have the full effects from the surgery (for all the antibodies to get out of your blood stream). Can combine this with plasmapheresis to help…
Crises in MG
• Myasthenic Crisis
– Acute exacerbation of muscle weakness caused by inadequate dose of anticholinergic medications, infection, stress, or surgery
• Not enough
• Cholinergic Crisis
– Cause by overmedication with cholinergic drugs
• Too much
• Symptoms are the same in both so you can tell the difference with a tensilon test.
Important to get a Hx
Nursing & Client Education
• Educate on importance of medication management
• Teach energy conservation strategies
– B/c pt fatigues easily
– We need to encourage things like handicap stickers
– Tell them to do stuff when their strength is at it’s best
(usually in the mornings)
• Instruct on strategies to prevent ocular manifestations
– Use eyedrops, wear patches at night to keep the eyelids closed, surgery, etc.
• Educate on ways to minimize risks of aspiration
– Plan meal times around medications!
• Remind client of the importance of maintaining health promotion practices
Nursing Diagnoses
• Ineffective breathing pattern
• Ineffective airway clearance
• Impaired physical mobility
• Impaired verbal communication
• Constipation and other bowel dysfunctions
• Self care deficit
• Altered nutrition
Guillain-Barr é Syndrome
• An acute inflammatory process characterized by varying degrees of motor weakness and paralysis
• An autoimmune attack on the peripheral nerve myelin
• Mortality generally results from complications of respiratory compromise
• Typically begins with muscle weakness and starts at the bottom of the body
• Cause is unknown, but could be a viral infection, trauma, surgery, or an immunization, but who knows…
Clinical Manifestations
• Ascending weakness (starts at the bottom and works it’s way up)
• Parasthesias, hypotonia, & areflexia (no reflexes) of extremities
• May see bulbar weakness such as paralysis of ocular muscles & inability to swallow
• Worst case scenario: respiratory failure
• Weakness may start and then peak on the
14 th day. Can be longer, can be shorter
Assessment & Diagnostic Findings
• History & physical
– Key is that it’s travelling up the body!
• Elevated protein in CSF
– They would find this during a lumbar puncture
• Abnormal EMG
– Reduced nerve conduction
Medical Management
• Airway maintenance (most important thing!!!! If they have ascending paralysis it could paralyze their diaphragm and if that happens then they can’t breathe)
• Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
• Plasmapheresis
• Provide range of motion for clients with decreased mobility
• Prevent pulmonary emboli
• Encourage independence with ADL’s
• Most people recover b/w 6 months to a year. But it can come back! That is a long recovery time.
Sometimes it plateaus 4 to 6 weeks, in some cases
1 year.
Nursing Diagnoses
• Ineffective breathing pattern
• Impaired physical mobility
• Impaired verbal communication
• Fear and anxiety related to paralysis
• Imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirements
Peripheral Neuropathies
• Disorder affecting the peripheral & sensory nerves characterized by bilateral & symmetric disturbance of function, usually beginning in the feet & hands
• Symptoms: loss of sensation, muscle atrophy, diminished reflexes, pain, & parasthesias
• Causes: systemic diseases, vitamin deficiency, drug toxicity, infections, trauma, heavy metals, and exogenous substances
Restless Legs Syndrome
• Characterized by leg parasthesias associated with an irresistible urge to move
• Common in iron deficiency, renal failure,
DM, rheumatic disorders, & pregnancy
• Complaints of intense burning or crawlingtype sensation
Management of RLS
• Sinemet
• Mirapex
• Requip
• Clonidine
• Clonazepam
• Some antiseizure meds
Cranial Nerve Disorders
• Trigeminal Neuralgia (Tic Douloureux)
– Very, very painful!!
• Affects the trigeminal or 5 th cranial nerve
• Cause unclear: Suspect
– Compression of 5 th nerve by a vein or artery
– Injury to the trigeminal nerve
– Herpes Virus (HHV6)
Managing Trigeminal Neuralgia
• Determined by amount of pain experienced.
Usually unilateral but can be on both sides
• Nonsurgical
– Carbamazepine
– Baclofen
– Amitriptyline
• Surgical
– Janetta procedure – arterial decompression
– Radiofrequency percutaneous electrocoagulation
Bell’s Palsy
• Definition – Acute paralysis of cranial nerve VII (facial)
• Age is not a factor
• Onset is acute
• Maximal paralysis within 48 hrs – 5 days
• Cause – unclear – possibly result of inflammatory process
Managing Bell’s Palsy
• Prednisone
• Analgesics for pain
• Avoid corneal abrasion by use of eye ointments and patch or tape
• Use straws to diminish drooling
• Warm moist heat
• Facial exercises
• 80% full recovery
Degenerative Neurologic
Disorders
Parkinson’s Disease
• Definition – A slowly progressing neurologic movement disorder eventually leading to disability
• Degenerative or idiopathic form is most common
• Cause is unknown
• Research suggests: genetics, atherosclerosis, excessive accumulation of oxygen free radicals, viral infections, head trauma, chronic antipsychotic medication use, environmental exposures
– More men than women, symptoms usually show up in the 50’s
Pathophysiology
• Associated with decreased levels of dopamine
• Loss of dopamine stores result in more excitatory neurotransmitters than inhibitory neurotransmitters – imbalances that affect voluntary movement
• Clinical symptoms appear with 60% neuron loss and 80% dopamine decrease
Clinical Manifestations
• Classic Symptoms (triad)
– Tremor (often the 1 st sign)
• Usually seen first at rest, and then aggravated by stress. Like a booger rolling tremor
– Rigidity
• Increase resistance to passive motion. You try to move them and they get stiff
– Bradykinesia
• Automatic movements are super slow. This accounts for their stooped posture, shuffled gait. They also have no arm swings when they walk
• Another important symptom
– Postural instability (propulsive gait, they lean too far forward when they walk, like their balance is off. Their head is too far forward and they lose their balance very easily)
• Other manifestations
– Shuffling gait
– Dysphonia
Other Manifestations
• Excessive & uncontrolled sweating
• Orthostatic hypotension
• Gastric & urinary retention, constipation
• Sexual dysfunction
• Psychiatric disorders
– Depression, dementia, memory deficits, personality changes. They have a lot of hallucinations (can be b/c of meds)
• Sleep disorders
– A lot of times related to their medications
Diagnostic Findings
• Diagnosed clinically from patient history, presence of 2 – 3 cardinal manifestations: tremor, muscle rigidity, bradykinesia
• Family notices changes such as: stooped posture, stiff arm, slight limp, tremor, handwriting differences
• Medical history, presenting symptoms, neurologic exam, & response to pharmacologic management are carefully evaluated
Medical Management
• Levodopa
• Anticholinergics
• Dopamine agonists
• Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
• Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors
• Antidepressants
Surgical Management
• Thalamotomy
– Improve tremor and rigidity
• Pallidotomy
– Improve tremor and rigidity, not for demented people, they go in and burn stuff
• Deep brain stimulator
– Like a pacemaker thing in your brain
– The first two are permanent, once it’s done it’s done. The DBS can be turned on or off or moved from place to place
Nursing Diagnoses
• Risk for falls
• Self-care deficit
• Chronic confusion
• Impaired physical mobility
• Impaired verbal communication
• Risk for imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements
Huntington’s Disease
• Chronic, progressive, hereditary disease of the nervous system that results in progressive involuntary choreiform (dance like) movement and dementia
• It is transmitted as an autosomal dominant genetic disorder, & each child of a parent with the disease has a 50% risk of inheriting the disorder (very genetic!! But you usually don’t know you have it until you have children)
Pathophysiology
• Premature death of cells in the striatum of the basal ganglia
• Researchers believe glutamine abnormally collects in the cell nucleus causing cell death
• Onset between the ages of 35-45
• Slowly progressive disease
• Patients usually become emaciated & exhausted
– Because they are dancing around all day long uncontrollably!
• Death after 10 – 20 yrs
Clinical Manifestations
• Abnormal involuntary movements (chorea)
• Increasing intellectual decline
• Emotional disturbance
• Constant writhing, twisting, uncontrollable movement of the body
• Facial tics & grimaces
• Slurred, hesitant, explosive, unintelligible speech
• Chewing/swallowing difficulty
• As this gets worse, all these things get worse!
Clinical Manifestations
• Disorganized gait – ambulation becomes impossible
• Incontinence of bowel and bladder
• Affected cognitive function
• Emotional changes
– Nervous
– Impatient
– Suicidal depression
– Irritable
– Uncontrollable fits
– Apathy/Euphoria
Assessment & Diagnostic Findings
• Clinical presentation
• Positive family history
• Genetic marker
Medical Management
• Pharmacological
– Antipsychotics, antidepressants
• Nursing
– Maintain safety
– Treat physical symptoms
– Provide physical & emotional support
– Provide nutritional support
Alzheimer’s Disease
• Chronic, progressive, & degenerative brain disorder that is accompanied by profound effects on memory, cognition, & ability for self-care
• One of the most feared disorders of modern times due to its catastrophic consequences for the patient & family
– Usually the pt doesn’t know they’ve lost their mind, it’s the people left to take care of them that suffer the most
10 Warning Signs
• 1. Memory loss
• 2. Difficulty performing familiar tasks
• 3. Problems with language
• 4. Disorientation to time and place
• 5. Poor or decreased judgment
• 6. Problems with abstract thinking
• 7. Misplacing things
• 8. Changes in mood or behavior
• 9. Changes in personality
• 10. Loss of initiative
Alzheimer’s Disease symptoms
Forgets entire experience
Normal age-related memory changes
Forgets part of an experience
Rarely remembers later Often remembers later
Gradually unable to follow written/spoken direction
Usually able to follow written/spoken direction
Gradually unable to use notes as reminders
Usually able to use notes as reminders
Gradually unable to care for self
Usually able to care for self
Stages of Alzheimer’s
• Stage 1
– Duration: 1 – 3 years
– Short-term memory loss
– Decreased attention span
– Subtle personality changes
• Only noticed by family members who were familiar with their personality before hand
– Mild cognitive deficits
– Difficulty with depth perception
Stages of Alzheimer’s
• Stage 2
– Duration: 2 – 10 years
– Obvious memory loss
– Confusion
– Wandering behavior
– “Sundowning”
• Sun goes down and they get crazier
– Irritability and agitation
– Decreased spatial orientation
– Impaired motor skills
– Impaired judgment
Stages of Alzheimer’s
• Stage 3
– Duration: 8 – 10 years
– Absent cognitive abilities
– Disoriented to time and place
– Severely altered communication skills
– Impaired or absent motor skills
– Bowel and bladder incontinence
– Inability to recognize family & friends
– Disturbed sleep patterns/increased sleep time
Diagnostic & Assessment Findings
• Exclude all other diagnoses
– Get blood work to make sure you’re not depressed, have had alcohol/drug abuse, drug toxicities, B12 and folate deficiency, thyroid problems, glucose problems, etc.
• CT/MRI
– Smaller brain (atrophy), enlarged ventricles
• MMSE
– Mini Mental Status Exam. Shows degree of cognitive impairment using a series of questions
• Neuropsychologic testing
– Diagnostic testing done by a neuropsychologist. Kind of the same thing as above, done to gain a baseline and to compare over time. Takes 4 or 5 hours to do
Medical Management
• Pharmacological
– Cholinesterase inhibitors – Aricept
– Memantine (Namenda)
– Antipsychotics – haldol, risperdal, zyprexa
– Antidepressants – prozac, zoloft
• Especially in the beginning when they’ve been diagnosed and their brain is still there. They might get sad when they know that they will go crazy
• Nursing
– Maintain safety
– Help maintain functional ability
– Help meet personal needs
– Maintain dignity
• There is nothing that is going ot make the alzheimers better, these are just used to slow down the progression of the disease
Nursing Management
• Support cognitive function
• Promote physical safety
– Esp. at night (sundowning)
• Promote independence in self-care
• Reduce anxiety & agitation
• Improve communication
• Provide socialization
– Small amt of people at a time, not the entire family, they’ll get confused
• Promote adequate nutrition
– Keep it simple!
• Promote balanced activity & rest
– Keep them busy during the day so they’ll be pooped at night and sleep, not wander around
• Educate on home & community based assistance
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Lou Gehrig’s Disease
• Definition – A disease of unknown cause in which there is a loss of motor neurons in the anterior horns of the spinal cord and the motor nuclei of the lower brain stem.
• More men than women are affected
• Onset usually in the 5 th or 6 th decade of life
• The body deteriorates, but your brain is completely aware of what’s going on…
ALS
• Characteristics
– Atrophy of hands, forearms, and legs
– Paralysis
– Death
• Typically occurs w/i 2 – 5 years of onset of symptoms. Usually die b/c of respiratory failure (paralyzation of the respiratory muscles, suffocate to death)
Nursing Diagnoses
• Risk for injury
• Self-care deficit
• Ineffective coping
• Chronic confusion
• Risk for impaired tissue integrity
• Total urinary and bowel incontinence
• Imbalanced nutrition: Less than body requirements
Clinical Manifestations
• Fatigue while talking
• Tongue atrophy
– Weakness of soft palate which impairs ability to laugh, cough, or blow their nose
• Dysphagia
– Difficulty swallowing
• Dysarthria
– Difficulty articulating your words
• Nasal quality of speech
• Fasciculations of the face
– Like a quivering action of the muscles, like a twitch.
Where the muscles contract
• Weakness of the hands and arms
• Spasticity
• Muscle atrophy extending to flaccid quadriplegia
• Eventual respiratory muscle involvement
– This is usually how they die
Assessment & Diagnostic Findings
• Based on S/S
• EMG
– Put needle in the muscle and they’re checking for the muscle activity
• Muscle biopsy
– The only test you can get that will definitively tell you if you have ALS or not. Go in and take a piece of your muscle and look at it
• MRI
Management
• No known cure
• Utilize an interdisciplinary approach to maintain optimum functioning
– Palliative care
• Riluzole – only drug approved for use in ALS
• Ongoing support and counseling are valuable
– Cause it’s rare and you’ll die quickly, hard to deal with emotionally
• Treatment for spasticity
• End of life issues
Nursing Diagnoses
• Risk for injury
• Imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirements
• Altered communication
• Risk for aspiration