08EPP Chapter 09
advertisement

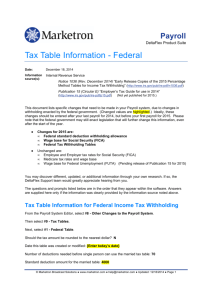
Chapter Introduction Section 1: The Economics of Taxation Section 2: Federal, State, and Local Revenue Systems Section 3: Current Tax Issues and Reforms Visual Summary You have just received your first paycheck and are looking forward to being paid $8 per hour for the 20 hours you worked. You look at your check and . . . “What? This check isn’t for $160! Where’s the rest of my money?” Make a list of the deductions that might be subtracted from your earnings. Read Chapter 9 to learn more about how governments raise revenue. All levels of government use tax revenue to provide essential goods and services. Section Preview In this section, you will learn that taxes are the most important way of raising revenue for the government. Content Vocabulary • sin tax • tax return • incidence of a tax • benefit principle • of taxation • • ability-to-pay • principle of taxation • proportional tax • • tax loophole • individual income tax • sales tax • average tax rate Medicare progressive tax marginal tax rate regressive tax Academic Vocabulary • validity • evolved What is the most important way for governments to raise revenue? A. Sell bonds B. Sell services C. Taxes 0% A A. A B. B 0% C 0% C. B C Economic Impact of Taxes Taxes affect the decisions we make in a variety of ways. Economic Impact of Taxes (cont.) • Taxes and other governmental revenues influence the economy by affecting – Resource allocation – Behavior adjustment • Sin tax Economic Impact of Taxes (cont.) – Productivity and growth – Determining incidence of a tax Shifting the Incidence of a Tax Which example demonstrates a tax encouraging an activity? A. Sin tax 0% D 0% A D. None of the above C C. Luxury goods tax A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B B. Interest paid on mortgages Criteria for Effective Taxes To be effective, taxes must be equitable, easy to understand, and efficient. Criteria for Effective Taxes (cont.) • Taxes must meet three criteria: – Equity—impartial and just: Makes sense to avoid tax loopholes – Simplicity—tax laws written so taxpayers and collectors can understand them • Individual income tax—complex tax • Sales tax—simpler Criteria for Effective Taxes (cont.) – Efficiency—easy to administer and successful in generating revenue • Individuals file a tax return before April 15th each year. Which of the taxes below was not worthwhile? A. Toll booth taxes B. Sales tax C. Luxury tax on small private aircraft D. Gasoline tax 0% A A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B C 0% D Two Principles of Taxation Taxes can be levied on the basis of benefits received or the ability to pay. Two Principles of Taxation (cont.) • United States taxes are based on two principles – Benefit principle of taxation • Limitations to the benefit principle of taxation • Those who receive government services are least likely to afford them. • Benefits are hard to measure and impact others. Two Principles of Taxation (cont.) – Ability-to-pay principle of taxation • We can’t always measure benefits derived from government spending. • Assumes individuals taxed more suffer less discomfort paying taxes Which method of taxes better suits you or your family? A. Benefit principle of taxation B. Ability-to-pay principle of taxation A. A B. B 0% A 0% B Three Types of Taxes All taxes can be broken down into three categories— proportional, progressive, and regressive. Three Types of Taxes (cont.) • Three general types of taxes exist in the United States today. – Proportional tax • If the percentage tax rate is constant, the average tax rate is constant. • Medicare tax fund Three Types of Taxes Three Types of Taxes (cont.) – Progressive tax • Marginal tax rate – Regressive tax Profiles in Economics: Monica Garcia Pleiman In which category of taxes does a homeowner’s property tax fall? A. Proportional tax B. Progressive tax C. Regressive tax D. None of the above 0% A A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B C 0% D Section Preview In this section, you will learn that federal, state, and local governments rely on different revenue sources. Content Vocabulary • Internal Revenue Service (IRS) • payroll withholding system • corporate income tax • excise tax • estate tax • property tax • tax assessor • natural monopoly • gift tax • indexing • customs duty • FICA • user fee • payroll tax • intergovernmental revenue Academic Vocabulary • implemented • considerably The second most important federal revenue source is the individual income tax. A. True B. False A. A B. B 0% B A 0% Federal, State, and Local Revenue Systems • The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the branch of the U.S. Treasury Department in charge of collecting taxes today. Federal Government Revenue Sources Individual income taxes, FICA, and borrowing constitute the main sources of government revenue. Federal Government Revenue Sources (cont.) • Four largest sources of government revenue are – Individual income taxes • Tax is mostly collected through a payroll withholding system. • Tax code takes into account indexing. Federal Government Revenue Sources Federal Government Revenue Sources (cont.) – FICA or Federal Insurance Contributions Act tax • Social Security and Medicare are part of payroll taxes. – Borrowing by selling bonds to investors – Corporate income tax – Excise tax The Global Economy & YOU Total Tax Revenue as a Percentage of GDP Federal Government Revenue Sources (cont.) – Estate tax and gift tax – Customs duty – Miscellaneous fees like a user fee Why is indexing so important to the tax code? A. Lowers the tax on those who pay a gift tax C 0% A C. Keeps workers from paying more in taxes because of inflation A. A B. B 0% C 0% C. B B. Helps defray costs related to Medicare and Social Security State Government Revenue Sources States rely on funds from the federal government in addition to income taxes and sales taxes. State Government Revenue Sources (cont.) • Largest sources of state governments revenue – Intergovernmental revenue – Sales tax implemented by most states – Individual income taxes by most states – Other revenue sources State and Local Government Revenue Sources Which of the following states does not charge a general sales tax or individual state income tax? A. New Hampshire 0% D 0% A D. Delaware C C. Washington A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B B. Alaska Local Government Revenue Sources Local governments rely mostly on intergovernmental revenue and property taxes. Local Government Revenue Sources (cont.) • Largest sources of local governments revenue – Intergovernmental transfers from state and federal governments – Property tax • Tax assessor determines valuations of property State and Local Taxes as a Percentage of State Income Local Government Revenue Sources (cont.) – Utility revenues from natural monopolies – Sales tax – Other revenue sources Which of the following property does not fall under the property tax laws? A. Real estate B. Farm animals 0% D A 0% C D. Jewelry A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B C. Automobile Section Preview In this section, you will learn that one consequence of tax reform was to make the individual tax code more complex than ever. Content Vocabulary • payroll withholding statement • accelerated depreciation • investment tax credit • alternative minimum tax • capital gains Academic Vocabulary • concept • controversial • flat tax • value-added tax (VAT) Do Americans pay more in taxes than do people in other developed countries? A. Yes B. No C A 0% A. A B. B 0% C 0% C. B C. About the same Examining Your Paycheck The income taxes you pay are summarized on the stub that is attached to your paycheck. Examining Your Paycheck (cont.) • The payroll withholding statement attached to your paycheck lists deductions taken. Biweekly Paycheck and Withholding Statement What is the FICA tax percentage deducted from your paycheck? A. 6.20% B. 5.5% 0% D A 0% C D. Varies by individual A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B C. 7.65% Tax Reform Numerous changes have been made to the federal income tax code since 1981. Tax Reform (cont.) • The Economic Recovery Tax Act, signed by Ronald Reagan in 1981, included large tax reductions for individuals and businesses. • Businesses also got tax relief from accelerated depreciation and investment tax credit. Tax Table for Single Individuals, 2006 Tax Reform (cont.) • In 1983 the alternative minimum tax was passed. • In 1993 government added tax brackets in order to balance the budget. • The Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997 was both economical and political. – Capital gains tax was reduced. Total Government Receipts per Capita, Adjusted for Inflation Tax Reform (cont.) • Temporary tax reform in 2001—based on the federal government collecting more taxes than it was spending • Temporary tax reform in 2003—due to slow economic growth, accelerated many of 2001 reforms • If the present trend of government spending more than it collects in taxes continues, it will be difficult to preserve tax cuts due to expire in 2011. What do you think Congress should do now regarding taxes? A. Keep everything the same B. Reduce government spending C. Increase taxes D. Change the tax structure all together 0% A A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B C 0% D Alternative Tax Approaches The need for new federal revenues will influence future tax reform. Alternative Tax Approaches (cont.) • Two alternative forms of taxation – Flat tax – Value-added tax (VAT) The Value-Added Tax Alternative Tax Approaches (cont.) • Advantages to the flat tax – Simplicity to taxpayer – Closes most loopholes – Reduces need for many workers in IRS and tax preparers Alternative Tax Approaches (cont.) • Disadvantages to the flat tax – Removes many incentives built into current tax code – Don’t know what rate is needed to replace revenues collected today – Unsure if flat tax would stimulate economic growth Alternative Tax Approaches (cont.) • Advantages to the VAT – Tax is hard to avoid – Tax incidence is widespread – Easy to collect – Encourages saving Alternative Tax Approaches (cont.) • Disadvantage to the VAT – Virtually invisible—other factors can change the product’s price. • Desires to simplify the tax code, unexpected expenditures on war and natural disasters, and political change all result in tax reform. Why is it difficult for politicians to change the tax code completely? A. Hard to give up power of modifying behavior and influencing allocation of resources D. All of the above 0% D C 0% A C. They find it hard to grant concessions to special interest groups. A. A B. B C. 0%C 0% D. D B B. They support their own pet projects. Types of Taxes All taxes in the United States can be broken down into three categories: proportional, progressive, and regressive Government Revenue Sources Federal, state, and local revenue sources differ. Much of the federal revenue is sent on to state and local governments. Alternative Tax Approaches Because the federal tax code has become so large and cumbersome, people have discussed the flat tax and the valueadded tax as two alternatives. Monica Garcia Pleiman (1964– ) • president and CEO of OMS, a technology consulting firm • publisher of Hispanic lifestyles magazine Latino SUAVE • cofounder of the Latina Chamber of Commerce xxx – insert new DFS trans 1 sin tax relatively high tax designed to raise revenue and discourage consumption of a socially undesirable product incidence of a tax final burden of a tax tax loophole exception or oversight in the tax law allowing taxpayer to avoid paying certain taxes individual income tax federal tax levied on the wages, salaries, and other income of individuals sales tax general state or city tax levied on a product at the time of sale tax return annual report by a taxpayer filed with local, state, or federal government detailing income earned and taxes owed benefit principle of taxation belief that taxes should be paid according to benefits received regardless of income ability-to-pay principle of taxation belief that taxes should be paid according to level of income, regardless of benefits received proportional tax tax in which percentage of income paid in tax is the same regardless of the level of income average tax rate total taxes paid divided by the total taxable income Medicare federal health-care program for senior citizens progressive tax tax in which the percentage of income paid in tax rises as the level of income rises marginal tax rate tax rate that applies to the next dollar of taxable income regressive tax tax in which the percentage of income paid in tax goes down as income rises validity justification evolved developed gradually Internal Revenue Service (IRS) branch of the U.S. Treasury Department that collects taxes payroll withholding system system that automatically deducts income taxes from paychecks on a regular basis indexing adjustment of tax brackets to offset the effects of inflation FICA Federal Insurance Contributions Act; tax levied on employers and employees to support Social Security and Medicare payroll tax tax on wages and salaries deducted from paychecks to finance Social Security and Medicare corporate income tax tax on corporate profits excise tax general revenue tax levied on the manufacture or sale of selected items estate tax tax on the transfer of property when a person dies gift tax tax paid by the donor on transfer of money or wealth customs duty tax on imported products user fee fee paid for the use of good or service intergovernmental revenue funds that one level of government receives from another level of government property tax tax on tangible and intangible possessions such as real estate, buildings, furniture, stocks, bonds, and bank accounts tax assessor person who examines and assesses property values for tax purposes natural monopoly market structure in which average costs of production are lowest when a single firm exists implemented put into effect considerably to a noticeable or significant extent payroll withholding statement document attached to a paycheck summarizing pay and deductions accelerated depreciation schedule that spreads depreciation over fewer years to generate larger tax reductions investment tax credit tax credit given for purchase of equipment alternative minimum tax personal income tax rate that applies to cases in which taxes would otherwise fall below a certain level capital gains profits from the sale of an asset held for 12 months or longer flat tax proportional tax on individual income after a specified threshold has been reached value-added tax (VAT) tax on the value added at every stage of the production process concept general idea controversial disputed To use this Presentation Plus! product: Click the Forward button to go to the next slide. Click the Previous button to return to the previous slide. Click the Home button to return to the Chapter Menu. Click the Transparency button from the Chapter Menu, Chapter Introduction, or Visual Summary slides to access the Economic Concepts transparencies that are relevant to this chapter. From within a section, click on this button to access the relevant Daily Focus Skills Transparency. Click the Return button in a feature to return to the main presentation. Click the Economics Online button to access online textbook features. Click the Reference Atlas button to access the Interactive Reference Atlas. Click the Exit button or press the Escape key [Esc] to end the chapter slide show. Click the Help button to access this screen. Links to Presentation Plus! features such as Graphs in Motion, Charts in Motion, and figures from your textbook are located at the bottom of relevant screens. This slide is intentionally blank.