Hookworms - Winona State University
advertisement

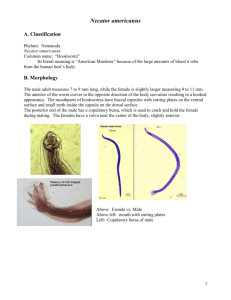
Hookworms Presented by: Mahamoud Ahmed & Faisal Farea The disease induced by hookworms…was never suspected to be a disease at all. The people who had it were merely supposed to be lazy, and were therefore despised and made fun of, when they should have been pitied. ---Mark Twain Taxonomy Kingdom: animalia Phylum:Nematode Class: secernentea Order: Strongiloidae Family: Ancylostomatidae Genus: Necator/Ancylostoma Species: A. duodenale and N. Americanus Hookworms are the voracious blood feeders of the nematode world. Two principal species that infect around 900 million people on earth are: Necator americanus known as the american killer also known the new world hookworm. Ancylostoma duodenale known as the old world hookworm. Definitive host Human No Intermediate host Neactor americanus N. americanus is the most common species in humans in most of the world. About 95% of the hookworms in the southern United States are this species. N. americanus has a pair of dorsal and a pair of ventral cutting plates surrounding the anterior margin of the bucal capsule Males have bursa diagnostic for the genus. The needlelike specules have minute barbs at their tips and are fused distally. Ancylostoma duodenale Associated with miners because mines offer an ideal habitat for egg and juvenile development due to constancy in temperature and humidity. It was known to cause a serious anemia in miners. Has two ventral plates, each with large teeth that are fused at their bases. A pair of small teeth is found in the depths of the capsule. The needlelike specules have simple tips and are never fused Comparison of hookworms Bucal cavity Size of female Size of male Position of vulva Egg production Penetration through skin Longevity Necator amricans Ancylostoma duodenale Dorsal and ventral cutting plates 2 ventral plates and two large teeth 9-11mm 7-9mm Mid-body 9000/ day Yes 10-13 8-11mm 1/3 from posterior 25000/ day Yes 15 years 5 years morphology The eggs are bluntly rounded, thin shelled, and are almost indistinguishable between the different species. Measuring 60 by 40µm, the eggs of Ancylostoma being slightly larger than those of Necator. The adult parasites are small cylindrical worms, (Ancylostoma duodenale being slightly larger than Necator americanus) The male worm is equipped with a characteristic copulatory bursa, used to catch and hold the female during mating. Geographic distribution A.duodenale is the indigenous hookworm of the north-temperate zone of the eastern hemisphere. it is confined in southern Europe, northern Africa, India, China and southern Asia. N.americanus is the new world worm. the “American killer,” was first discovered in Brazil and then Texas, but it was later found indigenous in Africa, India, Southeast Asia, China, and southwest Pacific islands. Question #1 The male is equipped with copulatory bursa, used to catch… a) food b) female c) prey Life cycle Life cycle Eggs are passed with feces. Eggs hatch in about 48 hours under favorable conditions such as (moist soil, protection from direct sun rays and temperature about 25°C. The first-stage larva feed upon bacteria in the feces about three days and then molt to second-stage larva. First and second stage larva have a rhabditiform esophagus. After 510 days they molt and become filariform third-stage larva that are infective. These infective larva can survive 3-4 weeks in favorable environmental conditions. 25 -15°C at 0°C death occurs rapidly. They move to the surface of the soil and wave back and forth which increases the chance to contact host. When they contact with the human host, the larva penetrate the skin and are carried through the veins to the heart and then to the lungs, break through into air sacs, to the trachea and are swallowed. The larva reach the small intestine, where they reside and mature in to adults. Hookworms have evolved strategies to evade the host’s defense system, and several of these has been discovered. Ancylostoma spp. Secrete a neutrophil inhibition factor that interferes with activation of neutrophils. N. americanus secretes acetyl cholinesterase, which inhabits gut peristalsis and possibly is an anti-inflammatory factor. Question #2 What conditions are required for the eggs to hatch? Moist soil & warm temp. Symptoms/pathogenesis Itching of skin as a result of penetration by the larvae. Congestion in lungs in heavy infections. Anemia due to loss of blood, particularly if diet is deficient. Diarrhea Persons with chronic hookworm disease are debilitated. Chronic heavy hookworm infection can damage the growth and development of children. Hookworm infection has been known to be fatal, particularly in infants. Hookworm infection/disease Depends on three factors. 1)Number of worms present 2)Species of hookworm 3)Nutritional conditions of the infected person. In general fewer than 25 N.americanus in person will cause no symptoms. 500-1000 result in severe symptoms, and more than 1000 may lead fatal consequences. Ancylostoma spp. Suck more blood than N.americanus fewer worms cause greater disease. 100 worms cause severe symptoms. Transmission Hookworm infection is contracted from contact with soil contaminated by hookworm, by walking bare foot or accidentally swallowing contaminated soil. Children are at high risk because they play in dirt and often go bare foot. Hookworms can’t be spread person to person. Diagnosis/treatment Recovery of the eggs in stool samples. Mebendazole or albendazole. It should not be given to pregnant women. Question #3 T/F hookworm infection can be transmitted person to person? False Prevention Proper sanitation practices. Appropriate fecal disposal. Do not walk barefoot or contact with bare hands in areas where hookworms is common or there are likely to be feces in the soil or sand. Questions from the article Which stage of larvae feed on bacteria? Rhabditiform. To become infective stage the rhabditiform has to molt? a) 2 times b) 3 times C) 1 time d) 4 times. Cont..questions. Which part of the world the N.americanus is found? Central/south. Africa, s. Asia, Australia and pacific islands. Which of the worms suck more blood? A.duodenale Works cited http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/DPDx/HTML /Para_Health.htm http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/DPDx/HTML /Para_Health.htm http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/parasit ology/nematodes.htm