Lecture 2 Introduction to Employee Benefits
advertisement

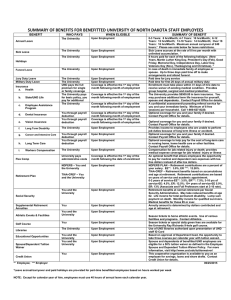
Lecture 2 Introduction to Employee Benefits • • • • Why study employee benefits? Define “employee benefits” Show the significance of employee benefits Identify factors that have contributed to the growth of group insurance • Describe job opportunities in the field • Current issues in employee benefits Why Study Employee Benefits? • To assist you in making personal choices involving employee benefits • To recognize the importance of employee benefits for companies • To prepare for work in this specialty – Pricing and developing – Negotiating – Implementing Definition of Employee Benefits Narrow Employer provided benefits for: Death Accident Sickness Retirement Unemployment Broadest All benefits and services, other than wages, provided to employees Five Traditional Categories of Employee Benefits • Legally required social insurance programs – Social Security, Workers’ Compensation • Payments for private insurance and retirement plans – Medical, disability, life insurance • Payments for time not worked – Vacations, parental leave, sabbaticals • Extra cash payments to employees – Educational expenses, suggestion awards • Cost of services to employees – Subsidized cafeterias, adoption assistance, parking Significance of Employee Benefits For 1995 the Average Cost per Employee was $14,659 (42.0% of Payroll) Selected Categories Medical $3668 Holidays and Vacation 3564 Legally Required Benefits 3109 Retirement and Savings 2620 Life insurance 140 Source: U.S. Chamber of Commerce Survey Significance of Employee Benefits continued Estimated total employer cost in 1995: $1.5 trillion or 41.8% of payroll Estimated value for 1929: 3% of payroll Estimated value for 1965: 21.5% of payroll In addition, employee payroll deductions equaled 13.1% of payroll in 1995 Significance of Employee Benefits continued • Social insurance plans – Social Security coverage almost universal • Cost is 15.3% of payroll – 90% of workers covered for unemployment – 95% of workers covered for workers’ comp. • Group life – $4.7 trillion coverage in force – 1 million contracts with 145 million certificates Significance of Employee Benefits continued • Group disability income insurance – Over 75% covered for short term disability – About 25% covered for long term disability • Group medical expense insurance – Premiums for medical expense coverage exceed 14% of GNP – About 185 million people covered under group medical insurance • Retirement plans – Approximately 104 million people covered – Assets of private pension plans exceed $3.6 trillion Factors Influencing the Growth of Employee Benefits • • • • • • • Industrialization Influence of organized labor Wage controls Cost advantages Tax advantages Inflation Legislation Employment Opportunities in Employee Benefits • • • • • • • • • Marketing Human resources Finance Insurance Accounting Communications Actuarial science Social science Medical Current Issues in Employee Benefits • • • • • • • • • Impact of terrorism on group life insurance “Janitor insurance” – abuses of COLI Health care costs Health care quality Mental health parity DNA testing Social Security reform Medicare prescription drug coverage Long term care insurance Current Issues in Employee Benefits (cont.) • • • • • • Mismanagement of 401(k) plans Investing in your employer’s stock Accounting treatment for stock options Cash balance pension plans Impact of pension investments on firm profits Unfunded pension liabilities