Plants chapter 23
advertisement

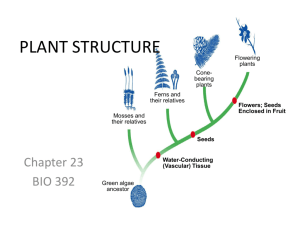
3/26 Get out: Plant Book Reminder: Test Corrections before/after school 3/27 Get out plant book Open to chapter 23 for notes Reminder – test corrections need to be completed by next Tuesday! If you missed test come see me EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIPS OF PLANTS Where did plants come from? Why are they so different? How have they changed over time? Angiosperms Gymnosperms Ferns Bryophytes Cone-bearing plants Ferns and their relatives Flowers; Seeds Enclosed in Fruit Mosses and their relatives Seeds Water-Conducting (Vascular)Tissue Green algae ancestor Flowering plants CHAPTER 23: PLANT STRUCTURES What are the 3 main organs and their functions: 1. Roots- absorb water and nutrients 2. Leaves – site of photosynthesis & gas exchange (O2 and CO2) 3. Stems- support; connect root + leaves; carry H2O + nutrients PLANT TISSUES 1. Dermal: outer covering of plant cuticle: thick waxy covering, conserves H20 root hairs: small cells on roots, increase surface area for water absorption PLANT TISSUES 2. Vascular: transport system used to move water and nutrients throughout the plant. xylem: transports water phloem: transports nutrients and products of photosynthesis PLANT TISSUES 3. Ground: composed of cells that lie between the dermal and vascular tissue. Structures : ROOTS Used for: 1) Absorption of minerals and water from the soil. 2) Storage of starches (vegetables) 3) Anchor to ground 4) 2 main types of roots: • taproot—grow long and deep to reach water below the surface. Ex. Carrots, radishes STRUCTURES: ROOTS fibrous—branched root system that grows close to the surface helps prevent soil from being washed away by rain. *Plants can have taproots, fibrous roots or both* Apical Meristem: area of root where cell division and growth occurs. Structures: STEMS: • Function: produce leaves, branches, and flowers; used for support and transport of substances between leaves and roots. Note: Wood = layers of xylem found in the stem. The tree rings show years of growth or “tree age”. Bark = composed of several layers including phloem. 3/31 Get out plant book Reminder – Plant Book Quiz tomorrow Come to enrichment if you aren’t finished If you still need to make up the test come see me now! Structures: Leaves Function: Absorb light and carry out photosynthesis Special structures •Stomata—opening in leaf to allow exchange of O2, CO2 and water vapor • Guard cell —regulates opening of the stomata and respond to conditions in the environment (wind, temperature) to maintain homeostasis within leaf. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Light Energy Equation: CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 Xylem: transports water needed for reaction to occur. Phloem: transports glucose from leaves to roots for storage. Stomata & Guard Cells: regulates the amount of gases & H2O needed for photosynthesis to occur. Leaf: contains chloroplasts, chlorophyll, + enzymes needed for photosynthesis PLEASE MAKE ADJUSTMENT IN PLANT BOOK FORMAT TRANSPIRATION 2)Transpiration •loss of water through stomata •When water is abundant, it flows from roots to leaves and guard cells respond by opening stomata to release excess water •When water is scarce, guard cells respond by closing stomata to limit transpiration •High transpiration rates can lead to wilting. http://youtu.be/mc9gUm1mMzc MONOCOT VS. DICOT Monocot: 1 seed leaf; parallel veins; flower multiples of 3, Fibrous roots Dicot: 2 seed leaves; branched veins; flower multiples of 4 or 5, tap root 4/1 Get out Plant Book for Quiz (not a joke) Reminder – Test next Monday If you did not bring your station lab to me for a stamp, do so now! If you missed a lab: Fern and moss Plant dissection Come see me ADD TO NOTES: TURGOR PRESSURE Turgor Pressure: Pressure exerted on the sides of the plant cell wall due to an expanded vacuole. What are some conditions which could cause Turgor Pressure to decrease, thus causing a plant to wilt? Plant System Interactions: VASCULAR TISSUE: XYLEM & PHLOEM -Products of Photosynthesis -Uptake of water by the root system -Hormones used for pollination, fruit ripening, flower development -Phototropism -Thigmotropism -Gravitropism What do the transport, reproductive, and plant response systems of plants have in common? • Transport • Reproduction • Plant Responses 4/4 Pick up: Whiteboard OLC worksheet Get out Pen or pencil Cell phone (not a trick)