Machining - Eastern Kentucky University
advertisement

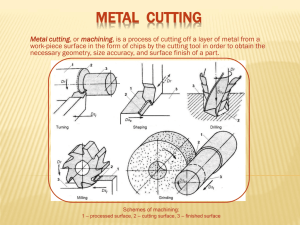
Machining Metal Cutting Process INT 201 Eastern Kentucky University Lecture References: 1) Degarmo E.P., Black J.T., Kosher R. (2003). Materials and Processes in Manufacturing, 9 th edition. Wiley 2) Repp, V. (1994). Metalwork: Technology and Practice, 9th edition. McGraw-Hill 3) Groover, M. (2004). Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing: Materials, Processes, and Systems, 2 nd edition. Wiley 4) Chen, C.S. (2001) ITEC 502: Advanced Design and Manufacturing [Course]. Iowa State University Lesson Objectives 1. REVIEW: Fundamentals of Machining 2. Identify the basic parameters associated with machining (milling) 3. Understand how these basic parameters are used to create and remove chips 4. Understand that machine parameters are directly related to type of material and the machine Machining Fundamentals REVIEW •Machining is a process of removing unwanted material from a workpiece in the form of chips. •Making and removing chips •Importance of lubricants •$60 billion spent annually on metal removal operations Machining Fundamentals Basic machine processes Machining Fundamentals • Milling Machines SPINDLE TRANSVERSELY TABLE LONGITUDINALLY COLUMN KNEE VERTICALLY BASE Basic Machining Parameters Basic Machining Parameters • Cutting Speed • Spindle Speed (RPM) • Feed Rate • Metal Removal Rate • Chip Load • Machine Horse Power Basic Machining Parameters Machining variables such as cutting speed, RPM, table feed rates, metal removal rates, and depth of cut all depend on: • Work material • Tool material • Specific process/equipment Cutting Speed (SFPM) • Cutting speed is the distance a point on the circumference of the milling cutter travels in one minute • Measured in Surface Feet per Minute (SFPM) • Calculated at the outside diameter of the cutter Cutting Speed (SFPM) • Different cutting speeds should be used when machining different metals – With cutting speeds too fast, cutter will overheat and dulls rapidly – With cutting speeds too slow, time is wasted and production costs will increase Cutting Speed (SFPM) • Factors affecting cutting speeds in milling: – Material properties, cutting tool (HSS, carbide, cast alloy), cutting fluids • Cutting speed recommendations for various materials and tooling combinations can be found in sources including: Tooling Mfg. & Engineering Handbooks (Machinist Handbook, etc) Material Low-Carbon Steel Stainless Steel Aluminum (and its alloys) Brass Suggested Cutting Speed Range SFPM 80-100 60-80 400-1000 200-300 Cutting Speed Formula SFPM = (π * D * N)/12 where SFPM = Surface Feet Per Minute π = Circumference constant per inch of Diameter D = Diameter of the cutter, measured in inches N = revolutions per minute of the spindle (RPM) 12 = 12 inches per foot (conversion calculation to feet) Cutting Speed Example If a 2 inch dia., 6 tooth milling cutter is turning at 100 revolutions per minute (RPM), what is the calculated cutting speed of the cutter (SFPM)? SFPM ( D N)/12 SFPM ((3.14) (2 inches) (100 RPM))/ 12 in/ft SFPM (628)/12 52.33 surface ft/min Spindle Speed (RPM) The speed of the milling machine is measured at the spindle and is measured in REVOLUTIONS PER MINUTE (RPM) Finding N (RPM) SFPM * 12 N *D Same equation; different arrangement SFPM = (π * D * N)/12 Determining RPM • When milling with a 3” diameter, 8 tooth milling cutter with a recommended cutting speed of 250 SFPM tooling material combination, what is the recommended RPM? N SFPM *12 250 SFPM *12 3,000 318.5 320 RPM π*D 3.14 * 3 in 9.42 Feed Rate • The linear distance moved along any machine axis, by the cutting tool in inches per minute. • Feed rate in milling is determined by multiplying: – Number of teeth on the cutter – Chip load per tooth – Speed of the cutter (N) Chip Load Chip Load or Feed per Tooth – The Chip Load is the amount of material removed by each tooth of the milling cutter during one revolution –Chip load recommendations for various materials and tooling combinations can be found in machining and engineering handbooks Milling Feed Rate Formula F = N * Ct * T where F = Feed rate in inches per minute N = Spindle RPM Ct = Chip Load per tooth [feed per tooth] T = Number of teeth on cutter Calculating Feed Rate A 6 inch dia., 12 tooth milling cutter is turning at 250 RPM. The recommended chip per tooth is 0.004”. What is the feed rate? F = N * Ct * T = 250 RPM * 0.004”/tooth * 12 teeth F = 12” per minute Metal Removal Rate Metal Removal Rate (MRR) is the volume of material removed from the work piece in one minute. Limited to available machine power How much material is removed in 1 minute MRR Formula MRR = W * D * F where MRR = Cubic inches removed per minute W = Width of Cut D = Depth of Cut F = Feed rate MRR Graphic Volume = In3 / min Depth Feed Rate Width MRR Example What is the MRR of a surface 3 inches wide that is to be milled with a 6 tooth milling cutter. Each depth of cut is 0.125 inches and the table feed rate is 4 inches per minute 3” Feed Rate = 4”/min .125” MRR Example 3” Feed Rate = 4”/min .125” MRR = W*D*F MRR = (3”) * (0.125”) * (4” per minute) MRR = 1.5 cubic inches per minute (in3/min) of material removed Horse Power (specific) HPs • HPs = Horse power required to remove 1 cubic inch (in3/min) of material per minute • All machined materials have a HPs rating • HPs is used to determine the HP required for machining. • The standard HPs = 1 – Materials with HPs > 1 require more than 1 HP/minute to remove 1 in3 of material – Materials with HPs < 1 require less than 1 HP/minute to remove 1 in3 of material • HPs can be found in machining and engineering handbooks Horse Power Formula HP = HPs * MRR where HP = Horse Power required to make a desired cut HPs = specific Horse Power of material MRR = Material Removal Rate HP Example How much Horse Power is required to machine a part with a desired MRR of 3.94 in3/min and a specific Horse Power (HPs) of 1.8? HP = HPs * MRR HP = 1.8 * 3.94 HP = 7.1 Review What is the maximum MRR of a material with a 1.6 HPs on a 1.2 HP machine? How much material can be removed from the same material on a 7.1 HP machine? Review Machining variables such as cutting speed, RPM, table feed rates, metal removal rates, and depth of cut all depend on: • Work material • Tool material • Specific process/equipment WHY?