File
advertisement

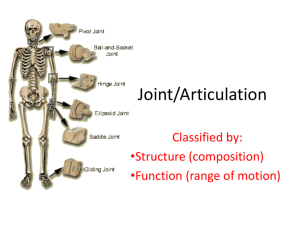
Joint Connection between two bones Joints allow motion Bear body weight Provides stability Types of Joints Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial Fibrous joint Has thin layer of periosteum between the bones e.g. – sutures of skull 3 types of fibrous joints: Synarthrosis thin layer of fibrous periosteum between two bones no motion between bones Syndesmosis great deal of fibrous tissue small amount of twisting or stretching e.g.- distal tibiofibular jint distal radio ulnar joint Gomphosis between tooth & wall of its dental socket in mandible & maxilla Cartilaginous joint Hyaline or fibrocartilage is present between bone surfaces Vertebral joints: disc of fibro cartilage directly connect bones 1st sternocostal joint: direct connection made by hyaline cartilage Synovial (diarthrodial) joint No direct union between bone ends Joint surfaces covered with hyaline (articular) cartilage Outer layer of capsule by strong fobrous tissue Diarthroidal Joint Classification Nonaxial Uniaxial Biaxial Triaxial Nonaxial Linear movement Flat surfaces of bone glide over each other Uniaxial Angular movement (hinge) One plane around one axis Biaxial Movement in 2 different directions allowed Triaxial(multiaxial) Motion occurs at 3 axes Joint Structure Bone Ligament- bands of fibrous tissue Hold ends of bones together Flexible, but not elastic Joint Capsule Surrounds Protects 2 layers: Outer fibrous layer Inner layer Synovial membrane Synovial fluid http://www.allaboutmydoc.com/surgeonweb/surgeonId.2729/clinicId.1432/theme.theme3/country.US/language.en/page.article/docId.20262 Cartilage – 3 Types Hyaline (articular) cartilage Fibrocartilage Meniscus Intervertebral discs Labrum Elastic cartilage Ear Tendon Connects muscle to bone Tendon sheaths Aponeurosis Flat tendinous sheet Linea alba Bursa Fluid filled sac Located in areas of friction Lined with synovial membrane Natural vs. Acquired PLANES of the BODY Sagittal plane Divides body into left and right halves Flexion/extension Frontal plane Divides body into front and back halves Adduction/abduction Transverse (Horizontal) plane Divides body into top and bottom halves Rotation Cardinal Planes – divide the body equally Axis Point through center of joint around which the body part rotates Movement Occurs In a Plane, Around an Axis Sagittal axis Frontal axis Vertical axis Degrees of Freedom Number of planes in which a joint can move Uniaxial joint – one degree of freedom, motion at one axis Biaxial joint – 2 degrees of freedom, motion at 2 axes Triaxial joint – 3 degrees of freedom, motion at 3 axes Thank You