JOINTS Fibrous Joints • Composed of articulating bones joined by
advertisement

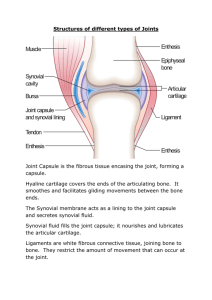
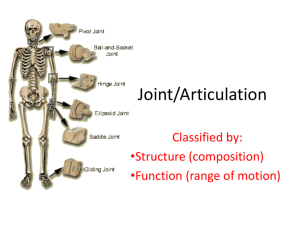
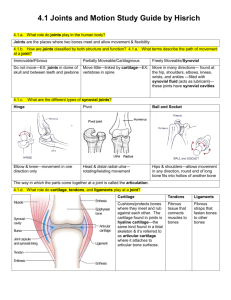
JOINTS Fibrous Joints • • • • • • Composed of articulating bones joined by dense collagen fibers Little elasticity Allow no empty spaces between surfaces Fibrous connective tissue forms union of irregular bones along full common borders Allows no movement and called synarthrosis Three types of fibrous joints: suture; syndesmosis; and gomphosis o Suture example: bones of cranium in adult, no movement o Syndesmosis example: interosseous ligament between tibia and fibula, slight movement o Gomphosis example: root of tooth attaches to jaw, no movement Cartilaginous Joints • • • • • • • Cartilage is tissue also made of collagen Similar to bone and fibrous tissue but lacks calcium No blood or nutrient supply to cartilage Flexible and strong and good shock absorber Three types of cartilage: hyaline; elastic; and fibrocartilage Two types of cartilaginous joints: synchondrosis and symphysis There are no empty spaces between surfaces of cartilaginous joints Synchondroses • • • • A cartilaginous joint during youthful years that absorbs calcium in adulthood and loses flexibility Epiphysial plate is an example Bwtween first rib and sternum and between manubrium and body of sternum Once complete is immovable or synarthrotic Symphyses • • • Primarily made of cartilage but has greater elasticity and flexibility than synchondrosis Example: pubic symphysis; articulation of vertebral body with one above/below A slight degree of movement is allowed called amphiarthrotic or amphiarthrosis Synovial Joints • • • • • • • Most common type in body Freely movable Examples: shoulder, hip, knee etc. Called diarthrosis or diarthrotic joint movement Six types responsible for specific functional movement Movements occur on three planes; the number of planes a joint moves on is the degree of movement or freedom Elements allow movement and simultaneous joint integrity and stability: o Articular cartilage; synovial cavity; joint capsule; synovial membrane; synovial fluid and ligaments Articular cartilage is hyaline; covers ends of bones for smooth slick surface; shock absorber Joint cavity is empty space between two bones to allow movement Joint capsule is enclosed sac that surrounds all other structures of the joint • Made of fibrous connective tissue and attaches to periosteum Synovial membrane is thin inner lining of joint capsule • Covers everything but areas of articular cartilage • Made of loose connective tissue with blood supply and creates synovial fluid for lubrication and sources of food and healing Ligaments help hold joint together with joint capsule • Some ligaments are inside joint capsule, others outside • No blood supply so poor healing potential Other elements not found in all synovial joints include: • Meniscus • Bursa • Tendon sheaths • Labrum • Muscle