Intro to C# and .NET
advertisement

Introduction to C#
Tom Roeder
CS 215 2006fa
Goals of the course
Introduce C# language
ECMA standard
originally developed by MSR
not just Java + C++
many extensions
Introduce .NET framework
future of Windows
base of Microsoft’s C# implementation
Non-goals
Teach you to program
Introduce object oriented languages
should be very comfortable writing OO code
we will not cover much if any basic programming
not even teach you OO style (except wrt C#)
expected to write all code in OO style
Give you a detailed grade
S/U only
even homework
S/U Details
Requirements for the course
Assignments are S/U
come to lecture
participate
do three assignments
will not be giving a detailed grade
show me that you understand the concepts, and can write
C# code
All three assignments will be online soon
must be completed by the end of the course
Administrative Details
Class time MWF 12:20-1:10
office hours: W 10:30-12 or by appointment
Prerequisites: CS 211/212
tmroeder@cs.cornell.edu (4112 Upson)
really: experience in OO coding/concepts
Academic Integrity
Do not submit work that is not your own
minimum penalty: U in the course
Useful Tools
Visual C#
Express: Google “Visual C# Express”
in Visual Studio: MSDNAA
Mono: http://www.go-mono.com
must be version 2005: we need C# 2.0
Open Source impl for Linux: not quite at 2.0
Rotor: http://msdn.microsoft.com/net/sscli
Shared Source impl for Windows (through 2.0)
Used to work on BSD / OS X, too
Useful Tools
Portable.NET: http://www.dotgnu.org
CMS: http://cms.csuglab.cornell.edu
yet another open source impl
we will use this for homework
turn on your email notifications!
Course Webpage:
http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs215
will post lectures online
as well as any errata for the homework
CSUGLab
You all will have accounts
MSDNAA access: let me know if you don’t
currently have it
http://www.csuglab.cornell.edu/userinfo.html
Visual Studio .NET 2005 should be installed there
Syllabus
Syllabus (10 more lectures)
C# constructs: 5 lectures
Types, Delegates, Generics, Reflection, Iterators
.NET Memory Management: 1 lecture
Topics: 4 lectures
C# 3.0, Threading, Security, MSIL, MSH
Quiz 1
Each class will begin with a quiz
not for credit but for knowledge
but I will collect them and see what you know
Today’s quiz will be on prerequisites
OO programming, mainly to do with Java
If you don’t know Java, but do have OO
experience, it’s OK
talk to me after if you have trouble
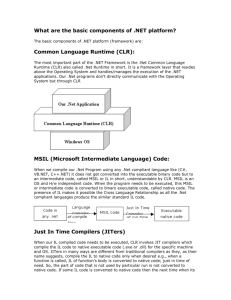
What is .NET?
A Framework in which to run code
A Common Language Runtime (CLR)
runs all programs
C# compiles to Microsoft Intermediate Language
MSIL runs on CLR
Virtual Machine like Java
code written in many languages compiles to MSIL
A Common Language Specification (CLS)
A Common Type System (CTS)
What is .NET?
Web Services
Sharepoint
Building Blocks (e.g. for Services)
...
...
.NET Applications
Enterprise Servers
Languages:
SQL Server
C#, Visual Basic, etc
BizTalk
...
Runtime
Common
Type
System
Common
Language
Runtime
Services: .NET and COM+
.NET Framework
Operating System
From MSDN
What is the CLR?
Base Class Library Support
Thread Support
COM Marshaler
Type Checker
Exception Manager
Security Engine
Debug Engine
MSIL to Native
Compilers (JIT)
Code
Manager
Class Loader
From MSDN
Garbage
Collector (GC)
What is the CTS?
A set of common types
any language that runs in CLR should implement
no syntax specified
Languages often define aliases
For example
CTS defines System.Int32 – 4 byte integer
C# defines int as an alias of System.Int32
What is the CTS?
From MSDN
What is the CLS?
A specification of language features
For example
how methods may be called
when constructors are called
subset of the types in CTS are allowed
Code that takes UInt32 in a public method
UInt32 is not in the CLS
Can mark classes as CLS-compliant
not marked is assumed to mean not compliant
The Class Libraries
The common classes used in many programs
like Java Class Library
eg.
System.Console.WriteLine
XML, Networking, Filesystem, Crypto, containers
Can inherit from many of these classes
Many languages run on .NET framework
C#, C++, J#, Visual Basic
even have Python (see IronPython)
Assemblies
Code contained in files called “assemblies”
code and metadata
.dll as before
to run: public static
types
private: local directory, not accessible by others
void Main(string[] args)
eg. Wolfram .NETLink
shared: well-known location, can be GAC
strong names: use crypto for signatures
then can add some versioning and trust
COM vs .NET
Historically, COM provided this integration
support for interfaces and interaction
given a GUID, lookup the type library
dynamically instantiate class
do RPC to make calls in many cases
Difficult to get right
software engineering problems
not type safe at all
ASP.NET and ADO.NET
Use .NET languages in web pages
thus can write typesafe code
server-side or client-side
Sharepoint interactions
can log in
Use the CLR to access databases
in the manner of ODBC
provides classes for access
Windows PowerShell
New shell originally for MS Vista
available for WinXP/2k3
native .NET
instantiates arbitary .NET classes and accesses them
Also can access COM objects
Allows better interaction with programs
Can it surpass bash and others?
First C# Program
using System;
namespace Test {
int a = 137;
class Hello {
public static void Main(string[] args) {
Console.WriteLine(“Hello {0}”, a);
}
}
}
Constructions of Note
using
namespace
like import in Java: bring in namespaces
disambiguation of names
like Internet hierarchical names and Java naming
class
like in Java
single inheritance up to object
Constructions of Note
Console.Write(Line)
Takes a formatted string: “Composite Format”
Indexed elements: e.g., {0}
can be used multiple times
only evaluated once
{index [,alignment][:formatting]}
also can use as in Java
“Test “ + a
More C# : basic inheritance
class A {
protected int a;
public virtual void print() {
Console.WriteLine(“a = “ + a);
}
}
class B : A {
public override void print() {
Console.WriteLine(“a really = “ + (a + 137));
}
}