ch2powerpt_f04
advertisement

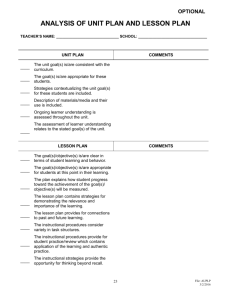
Designing and Planning Technology Enhanced Instruction Chapter 2 Lever-Duffy EDMD 3300, Fall 2004 What is the Learning Environment? The learning environment includes all conditions that impact the learner Physical space and its characteristics can impact learning Dunn and Dunn’s research suggests different aspects of the physical space appeal to different learning styles What is the Learning Environment? Non physical aspects of the learning environment include: – Teaching strategies selected by teachers – Technologies selected to support instruction – Plan for interaction among students – Assessment strategies – Attitude and role of the teacher in the learning process Why Is Planning Important? To build the best possible learning environment, all aspects of it must be planned A systems approach to planning calls for a step-by-step process that designs, creates, evaluates and revises all aspects of instruction The Design-Plan-Act! (D-P-A) system ensures all necessary steps are addressed Instructional Planning The DESIGN Phase The Design phase allows the teacher to take a strategic look at the delivery of instruction In this phase, the broad steps necessary are considered and refined An instructional design model is often used in this phase to ensure no steps are missed The Dynamic Instructional Design (DID) model will assist you in creating your design The DID Model KNOW THE LEARNER STAT E YOUR OBJECTIVES ESTABLISH THE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT IDENTIFY TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES IDENTIFY AND SELECT TECHNOLOGIES SUMMATIVE EVAULATION Figure 2.2, p. 39 Lever-Duffy DID Model Clarification The DID Model Know the Learner To identify the instruction necessary, you must first know the people you are teaching You should consider: – – – – Physical and cognitive developmental stage Cultural and language differences Incoming skills and current knowledge base Personal characteristics (learning styles, dominant intelligences, etc) – Group characteristics and dynamics The DID Model State your Objectives Performance objectives state what the student will be able to DO at the conclusion of instruction Performance objectives have 4 components: • The Stem • The Target Performance • The Measurement Conditions • The Criterion for Success Example: The student will be able to identify the subject and verb in a sentence written on the board with 95% accuracy. ABC’s of Objectives Objective components can also be illustrated: • • • • Audience Behavior Condition Degree Example: Given a calculator and scratch paper The student will be able to multiply simple fractions (reducing the answer to simplest terms), answering 9/10 exercises correctly. The DID Model Objectives should address different levels of thinking Blooms Taxonomy offers a guide for six levels of cognition 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Knowledge – Recall of facts Comprehension – Interpreting facts Application – Apply information to new situations Analysis – Recognizing components within data Synthesis – Creating new ideas for the data provided Evaluation – Making thoughtful value judgments The DID Model Establish the Learning Environment – Adjust the physical space to support learners – Encourage and support a positive climate that includes a feeling of safety, confidence, and positive attitude – Prepare to keep learners active and engaged – Prepare well organized and articulated lesson plans The DID Model Identify Teaching and Learning Strategies Decide upon the methods that are most likely to help the stated objectives Utilize the steps of the Pedagogical Cycle to help determine strategies The steps of the Pedagogical Cycle include – – – – Providing pre-organizers Using motivators Bridging to past knowledge Sharing objectives and expectations The DID Model Identify Teaching and Learning Strategies The steps of the Pedagogical Cycle also include – Introducing new knowledge via varied teaching methods – Reinforcing knowledge – Providing practice experiences – Offering a culminating review Pedagogical Cycle Provide Preorganizer Culminating Review Use Motivators Provide Practice Bridge Prior Knowledge Reinforce Knowledge Share Objectives Adapted from Figure 2.4 p. 50 Lever-Duffy Introduce New Knowledge The DID Model Identify and Select Support Technologies – Determine which technology tools will build the desired learning environment – Examine technology options – Evaluate appropriateness of the technologies under consideration – Experiment with the technologies selected The DID Model Evaluate and Revise the Design – You have already adjusted continually throughout the DID model in response to formative feedback – Summative feedback is the evaluation that occurs at the end of the process – Using the feedback from this final evaluation, revise the design to make it even better Instructional Planning The PLAN Phase Once you have completed your design, it is now time to PLAN your lessons Lesson Plans provide day-to-day snapshot of what will happen in the classroom Each component of the lesson plan grows out from a component of the design so they will parallel each other Instructional Planning The PLAN Phase The essential components of the Lesson Plan include – Readying the Learners – Target specific daily objectives – Prepare the lesson Prepare the classroom Detail the steps of the Pedagogical Cycle Identify technologies and materials Check for success Instructional Planning The ACT Phase Once you have completed your lesson plan, it is now time to take ACT to get ready to teach The Instructional Action Plan (IAP) is your lesson’s To-Do list The IAP will detail everything you need to do in order to carry out your planned lesson successfully Instructional Planning The ACT Phase The Instructional Action Plan includes – – – – – – Identifying learner preparation activities Getting the classroom ready Preparing all teaching and learning materials Creating your personal prompts Practice with your support technologies Preparing your formative and summative feedback tools – Preparing follow-up activities Planning for Technology in Teaching & Learning Remember… Technology is a tool that supports your design and your plans Technology should make it possible to something done before better or make it possible to do something that wasn’t previously possible Many technologies are available, choose wisely and well Connect! Journal Entry: Sept 7, 2004 Reflect on class so far, what evidence of the DID model do you see in practice? Be specific in the things that you identify. How can you apply the DID model to your Group Tutorial Assignments? Be specific in your suggestions.