Exam-4-REVIEW
advertisement

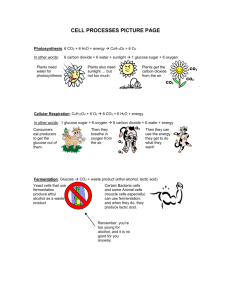
EXAM 4 REVIEW TEST TOMORROW!!!!!!!! Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide Glucose + Oxygen Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Glucose + Oxygen C6H12O6 + O2 Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Inorganic inorganic Glucose + Oxygen C6H12O6 + O2 ORGANIC inorganic Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Inorganic inorganic Glucose + Oxygen C6H12O6 + O2 ORGANIC inorganic Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Inorganic inorganic Plants absorb water through their roots from the ground Glucose + Oxygen C6H12O6 + O2 ORGANIC inorganic Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Inorganic inorganic Plants absorb water through their roots from the ground CO2 from the air. Animals exhale CO2 Glucose + Oxygen C6H12O6 + O2 ORGANIC inorganic Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Inorganic C6H12O6 + O2 ORGANIC inorganic Plants absorb water through their roots from the ground Glucose + Oxygen Glucose is chemical energy, or FOOD CO2 from the air. Animals exhale CO2 inorganic Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Inorganic C6H12O6 + O2 ORGANIC inorganic Plants absorb water through their roots from the ground Glucose + Oxygen inorganic Glucose is chemical energy, or FOOD CO2 from the air. Animals exhale CO2 Oxygen is a waste product. The plant does not need oxygen so it releases it into the air for us to breathe Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide H2O + CO2 Inorganic inorganic Plants absorb water through their roots from the ground LIGHT ENERGY Glucose + Oxygen C6H12O6 + O2 ORGANIC inorganic Glucose is chemical energy, or FOOD CO2 from the air. Animals exhale CO2 Oxygen is a waste product. The plant does not need oxygen so it releases it into the air for us to breathe How do plants capture light energy? How do plants capture light energy? Plants have special light absorbing molecules called pigments that can capture light energy from the sun. The main pigment of photosynthesis is chlorophyll In which organelle does photosynthesis take place? In which organelle does photosynthesis take place? CHLOROPLAST What is the purpose of photosynthesis? What is the purpose of photosynthesis? • To change light energy from the sun into chemical energy • To change inorganic materials into organic products that can be used as FOOD energy. What is the organic product of photosynthesis? What is the organic product of photosynthesis? •GLUCOSE!!! What is the organic product of photosynthesis? •GLUCOSE!!! C6H12O6 Where do organic molecules store energy? Where do organic molecules store energy? • In the bonds between the atoms of the molecule. How can energy be released from an organic molecule? How can energy be released from an organic molecule? • By breaking the bonds! Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis H2O + CO2 C6H12O6 + O2 In which organelle is glucose MADE? In which organelle is glucose MADE? •CHLOROPLAST In which organelle is glucose broken down? In which organelle is glucose broken down? •MITOCHONDRIA Glucose? Chloroplast- MAKES IT Mitochondria- BREAKS IT What does a plant do with extra glucose? What does a plant do with extra glucose? • Plants store extra glucose as a large polymer called STARCH What does a plant do with extra glucose? • Plants store extra glucose as a large polymer called STARCH • VACUOLE What macromolecule are starches and sugars (glucose)? What macromolecule are starches and sugars (glucose)? •CARBOHYDRATES What is an autotroph? What is an autotroph? • Organisms that makes its own food energy What is a heterotroph? What is a heterotroph? • An organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms Enzymes… What are 2 factors that affect enzyme activity? What are 2 factors that affect enzyme activity? •Temperature •pH What happens to an enzyme when it goes too far past its optimum temperature or too far out of its pH range? What happens to an enzyme when it goes too far past its optimum temperature or too far out of its pH range? LOSES ITS SHAPE • The enzyme and can no longer catalyze a chemical reaction Explain how an enzyme works like a lock and key. Explain how an enzyme works like a lock and key. • Each enzyme has a specific shape that fits a specific substrate. How many different chemical reactions can an enzyme catalyze? • JUST ONE type of chemical reaction! • Each enzyme only fits ONE type of reactant that fits its specific shape!