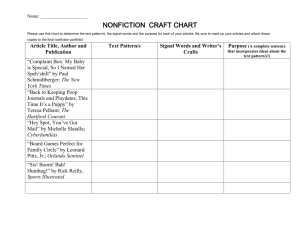
Chapter 5: Nonfiction Prose
advertisement

CHAPTER 5 PowerPoint Presentation by JoAnn Yaworski Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose Nonfiction prose is about real people, places, events, and social issues. • Presents factual information • Expresses a viewpoint • Appears in three major forms Informational Nonfiction Literary Nonfiction Visual Communication Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) Informational Nonfiction Business documents Literary Nonfiction Biographies Visual Communication Film Speeches Essays Photography Magazines Diaries Television Newspapers Memoirs Computer art Research reports Letters Painting Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) Reasoning skills are important in reading and interpreting nonfiction prose: • Comprehension: understanding the literal meaning • Application: applying information and ideas from a passage • Analysis: analyzing content, style, and structure • Synthesis: making connections between separate sources of information Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) There are three main types of nonfiction prose: • Informative essays: educate the reader about a selected subject • Critical essays: present an in-depth analysis of a subject • Reviews: briefly describe the content of a work of art and evaluate its strengths and weaknesses Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) Recognizing the difference between facts and opinions is important in understanding nonfiction prose: • Fact: a statement that can be proved Christmas Day falls on December 25. • Opinion: a statement that reflects a writer’s personal views Christmas Day is the best holiday of the year. Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) Recognizing descriptive language enables you to determine a writer’s views on his or her subject. The play was wild, witty, and wonderful. The play was unimaginative and predictable. The script was delightful and sophisticated. The script was strained and clumsy. Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) Suggestions for reading nonfiction prose: • Find the main idea. • Look for facts, examples, and evidence that support an author’s opinion. • Read the summaries and descriptions. • Note characteristics of style and structure. • Draw conclusions from the ideas and supporting details. Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose Informational nonfiction comes from a variety of sources: • Essays • Magazine articles • Newspaper articles • Speeches Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) Business-related documents are an everyday type of informational nonfiction: • Mission and goal statements • Employee handbooks • Training manuals • Legal documents Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose Literary nonfiction includes the following works: • Biographies • Memoirs or selected events • Diaries • Letters • Essays • Commentaries • Reviews of works of literature Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose Nonfiction prose includes commentaries on areas of visual communication: • Visual arts: sculpture, painting, photography • Performing arts: music, dance, theater, film, television Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) In commentaries about the visual arts . . . • Authors recreate the physical appearance of the art in words. • Authors interpret the emotions or the message that the art seems to convey. Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose (Continued) In reviews of the performing arts . . . • Reviewers write essays describing and expressing their opinions about an artist or a performance. Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. CHAPTER 5: Nonfiction Prose THE END Practice the skills you learned in this chapter by taking the Chapter Review Quiz or the GED Practice Quiz. Copyright © 2003 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.