Practice
advertisement

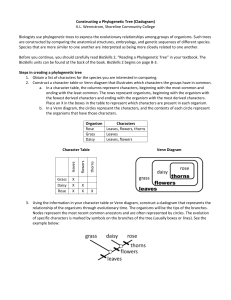
Warm-Up: The shaded sequence of nucleotides is for a gene from DNA that is similar to what you might find from a living human (Living DNA). The rest are sequences from five different ancestors. Sort the sequences starting with the living human to the most distant ancestor. Date 1/15-16 1/20-21 Session # Activity Page # Evidence of Evolution Notes 32 Genotype vs Phenotype Quick Write 33 Taxonomy Notes 34 Cladograms 35 h/w: read pages 43B-49B, 54B-56B, 62B-67B Evolution Vocab 2 definitions & images &/or examples 8.L.4 Understand the evolution of organisms and landforms based on evidence, theories and processes that impact the earth over time. 8.L.4.1 Summarize the use of evidence drawn from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy to form the basis for biological classification systems and the theory of evolution TLW analyze evolutionary relationship between organisms using evidence of evolution and phylogenetic trees to complete several w/s activities. Kingdom Card Sort There are 6 major classifications of living organisms. With your partners, sort the set of organism cards into six different groups. Be prepared to discuss the criteria you used to decide which group to place on organism in. Kingdoms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protists Fungus Plants Animals Modern System a Nested Hierarchy-Seven Levels of Organization Kingdoms are divided into phylum Phylum are divided into a smaller groups called classes. Classes are divided into an orders. Orders are divided into families Family are divided into a genus Genus are divided into species Classification Hierarchy of Organisms The more closely two different species are related, the more levels of classification they share. To classify organisms, modern taxonomist consider the evolutionary history of the organism. The fossil record often provides clues to evolutionary relationships It cannot be read like a story book because some fossil records are incomplete Taxonomists consider other evidence to confirm information contained within the fossil record with other lines of evidence, like… ……….Comparative Anatomy (Homologous structures, vestigial structures), embryology, DNA, shared chemicals & chemical processes. Practice using taxonomy classifications to determine relatedness of different species Cladogram or Phylogenetic Tree • Using patterns of shared traits, biologists construct a branching diagram called a cladogram (or phylogenetic tree.) • It shows show the sequence in which different groups of organisms evolved P 36 Phylogenetic trees allow us to predict characteristics of living organisms not yet studied. •The Pacific Yew produces a chemical called taxol that is used in treating cancer. 100,000 lbs of bark would be needed for clinical trials, and bark collection kills the tree. Based on the evolutionary relationships among yew species, biologists expected that close relatives of the Pacific Yew might produce similarly effective compounds •The leaves of the European Yew contain a related compound that can also be used to efficiently produce Taxol. Taxol is now widely available for cancer treatment. Which organisms are most closely related? Practice Green plants (viridiplntae) break down into what 2 groups? Practice In land plants which of the two taxa (groups) is the oldest? Practice What vascular plant came next? Practice What type of plants occurred next ? http://lcmrschooldistrict.com/roth/PowerPoint_Lectures/chapter18/vi deos_animations/cladogram_interpretation.html Practice Phylogenetic Tree Worksheet Quick Write p33 Summarize 2 types of evidence we have learned and how it is used to classify organisms and support the theory of evolution