Targets for the individual and the organisation
advertisement

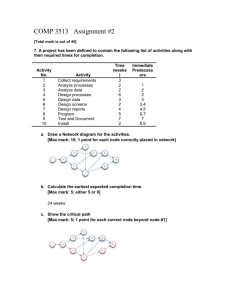
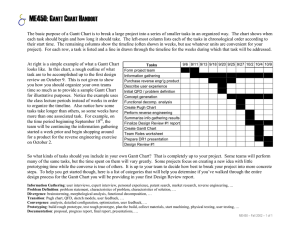
Targets for the individual and the organisation By Rachel , Claire , Kirsten and Natalie Personal development plan A Personal Development Plan or PDP is individual aims and objectives set by the employee(s). It is a formal record that concentrates on the employee’s personal strengths and weaknesses. Once the employee has identified their weaknesses a target is set that will help them improve on their weakness and a time limit will be set of when they would like to achieve this by. • The PDP is often used within a staff appraisal and is considering when putting staff on training. • With some organisations they also encourage their employees to record personal aims, although they do not have to do this. This may enhance the employee’s confidence because they will feel better about reaching their targets. The PDP is often discussed annually, then reviewed perhaps once or twice a year to help monitor performance. Action plan • An action plan is a document which shows what should be done and by who. This document usually has expected completion dates. The action plan is usually prepared when a team project needs to be planned. • In an action plan it:• Lists the tasks and the order that they should be done • Shows a guided time of how long it should take per task • This shows who will do which task • And it also has notes that gives extra details on the task Setting own targets • Setting priorities list • First set a ‘to do’ list displaying all the tasks that need to be done and then set a priorities list in the order that is most important to the least important task that needs to be dealt with. These priority lists are often associated with Action Plans. These targets could be set to high (urgent), medium (should be done) and low (could be done). • Personal development plan • This is a formal document that records the aims and objectives of an individual. It isn’t a necessary of the job but it helps the individual to meet the targets set. Smart targets • When setting own targets these need to be: • S- Specific, state exactly what has to be done with the task assigned. • M-Measureable, putting a number or value against a target (e.g. to improve by a percentage) as it is then a form of measuring a target • A- Agreed, targets that have been discussed and approved by line managers and team members • R- Realistic, select a challenging but achievable target and consider what resources you are going to use to achieve these targets • T- Timed, set a deadline or time scale to work towards for when a task/target has to be done for Setting departmental targets • Managing Targets • When managing targets you tend to only use two types of targets: ACTION PLANS and GANTT CHART. These are very useful and helpful when trying to communicate to employees or stakeholders. An action plan is something that is prepared when a longer term objective needs to be planned, This will include lists of the tasks in order which they have to be done and it will have on it estimated/actual time that each task will take. • • • • • A Gantt chart is a type of bar chart that shows a project schedule, it also has start and finish dates of the terminal elements and summary elements of a project Gantt charts can be used to show current schedule statuses. • Advantages • Main advantage of a Gantt chart is that you are visualizing your project schedule making this easier when communicating to employees or stakeholders. • Disadvantages • The main disadvantage is that it should be maintained and updated all the time but this could be an advantage as well. Dealing with changing priorities of people and tasks There are main ways in which you can deal with changing priorities: Establish a yearly enterprise wide planning process Doing this will set prioritization for at least a year, everything will scheduled. Assure the one who sets priorities for IT sets The higher you are the management scale priorities for all the more likely you are to have your priorities implemented. Establish a prioritization timeframe Get your leader to set a timeframe for about 3-6 months. After this time has gone the rest should be set. Assure your project resource capacity is Plan for between 80% to 90% capacity, this always 90% filled, not 100% way you can be agile enough to address scope changes or emergency efforts. Have IT leaders who can have this discussion The leaders of your department need to be skilled in negotiation to have this frank discussion Monitoring and evaluating progress Monitoring target can be done in many different ways. Managers can support their employees in different ways as well: o Checking them at regular intervals. o Putting a more experienced member of staff with them as a mentor. Gantt chart compares planned and actual progress and identifies if set milestones have been achieved Line managers checks at regular intervals that work is progressing as expected Sample checks when some but not all task will be examined Meeting targets or goals Set regular meetings and ask for updates from staff Audits or system checks that review current producers and make changes to gain greater efficiencies Buddy system when an employee is paired with someone with more experience for help and advice Thank you for listening