CAUSES OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION
advertisement

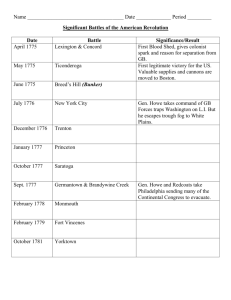
AP: CAUSES OF THE AMERICAN REVOLUTION COLONIAL PROBLEMS: 1. PEQUOT WAR (RI, MASS) KING PHILIP--PILGRIMS 2. SLAVE REVOLT • STONO REBELLION (SC) • SLAVE CODES •3. EAST-WEST DISPUTES (VA) • BACON’S REBELLION •4. NAVIGATION ACTS – – SHIPPING LAWS TO MAINTAIN MERCANTILISM ENUMERATED ARTICLES (CASH CROPS) FRENCH AND INDIAN WAR • Statistical Comparison between English and French colonies 1750: • Population: • Troop strength: • Indian Allies: • The start of the war: • Governor of New France—Marquis Duquesne de Menneville, • forts from Lake Erie to the Ohio River and beyond.—1751 • 1753 Lt. Gov. Va. Lord Fairfax—George Washington to survey part of the “Ohio Territory” for land speculation. • French building Ft. Duquesne (Pittsburgh). • ALBANY CONGRESS—1754 – Purpose: – Result: • July 1754—George Washington > inform the French they were trespassing on Va. Soil. When he arrived the fort was almost complete. Quickly Washington built Ft. Necessity and attacked Ft. Duquesne. • He lost—this started the French and Indian War FRENCH AND INDIAN WAR The war: 7 Years’ War—Eng., Prussia v. Fr, Sp. Russia, Holland and Austria 1755-1758 the French were winning. “Guerilla Warfare” **1755--Force of 1400, William Braddock, and colonial militia to capture Ft. Duquesne. 900 were killed or captured. The war turned England’s way when William Pitt was chosen as Prime Minister of Parliament. Blockade of European coastline. Launch a pre-emptive strike against Spain. Attack New France **1759 Battle of Quebec Gen James Wolfe v. Gen. Louis Montcalm “Plains of Abraham” 1759 Battle of Montreal 1760 King George II dies, King George III crowned. 1761 William Pitt resigns as PM, replaced by Lord Bute. 1761 Havana, Cuba and Manila, Philippines **1763 Treaty of Paris RESULTS OF FRENCH AND INDIAN WAR • TREATY OF PARIS 1763 • 1. Internal problems in Parliament – – – – William Pitt’s resignation De Facto PM Lord Bute Election of George Grenville 1st Wilkes Affair • 2. Anti-American resentment in England • 3. War Debt • 4. Pontiac’s Rebellion THE LAWS • • • • • • • • PROCLAMATION OF 1763 CURRENCY ACT 1764 SUGAR ACT 1764—Lord George Grenville – INDIRECT TAX – SUGAR, COFFEE, MOLASSES – CRACKDOWN ON SMUGGLERS-ADMIRALTY COURTS – TAXATION WITHOUT REPRESENTATION QUARTERING ACT 1765 STAMP ACT 1765—Lord Grenville – SUGAR ACT DID NOT BRING ENOUGH MONEY TO PAY DEBT OR PAY TROOPS STATIONED IN WILDERNESS. – DIRECT TAX ON ALL OFFICIALLY PRINTED DOCUMENTS – STAMP ACT CONGRESS (9/13) – SONS OF LIBERTY – COLONIAL-WIDE BOYCOTT DECLARATORY ACT (Lord Rockingham’s government) STAMP ACT REPEALED TOWNSHEND ACTS 1767 (aka Revenue Acts ()— (Lord Charles Townshend) – INDIRECT TAX-glass, lead, paper, paint and tea. – BOARD OF CUSTOMS COMMISSIONERS – CIRCULAR LETTER—2 REGIMENTS TO BOSTON America’s Response to Revenue Acts: Dickinson Letters Virginia resolves -TROUBLE IN MASSACHUSETTS NEWSPAPER STIRRED UP TROUBLES. -REGULATORS IN SC 1769 BOSTON MASSACRE MARCH 5, 1770 TOWNSHEND ACTS REPEALED EXCEPT ON TEA LORD HILLSBOROUGH CHANCELLOR OF THE EXCHEQUER 2ND WILKES CRISIS PLACEMEN Gaspee Incident Committees of Correspondence created 1772 LORD NORTH PRIME MINISTER TEA ACT 1773 Br. East India Tea Co. BOSTON TEA PARTY DEC. 16, 1773 COERCIVE ACTS (INTOLERABLE ACTS) Boston Port Act Massachusetts Government Act Quartering Act Administration of Justice Act Quebec Act SHOT HEARD ‘ROUND THE WORLD COMMITTEES OF CORRESPONDENCE – Keep other colonies abreast on activities in Massachusetts. – Organize boycotts and colonial-wide meeting in Philadelphia. •1st CONTINENTAL CONGRESS Sept. 1774 – Accomplishments •LEXINGTON AND CONCORD April 1775 – Reason for attack – Retreat to Boston Call out the instigators FIRST MAJOR BATTLES •FT. TICONDEROGA May 1775 •2ND CONTINENTAL CONGRESS May 1775 •COMPARISON OF THE ARMIES: •June 1775—Battle of Bunker Hill •Mar. 1776--DORCHESTER HEIGHTS •Thomas Paine publishes Common Sense Jan. 1776 •June 1775—Feb 1776 Continental Army invades Quebec •(Gen. Montgomery, Gen. Benedict Arnold) •1st CHARLESTON June 1776 •DECLARATION OF INDEPENDENCE America’s darkest hours: 1776-1777 • BRITISH TROOPS RETURN 30,000 strong under Gen. William Howe, navy commander by Adm. Richard Howe—New York City Nathan Hale-Capture NYC, chase Gen. Washington out of NY, GW retreats across NJ into Pa. Americans deserted by the 100s • AMERICA’S DARKEST HOUR – Thomas Paine published The American Crisis pamphlet in which he criticizes Americans of being “Sunshine Patriots”. • TRENTON AND PRINCETON – Marquis de Lafayette becomes Washington’s Aide-deCamp – Hessians, Christmas 1776, Jan. 1777 BRITISH PLAN TO WIN THE WAR 4 SIMULTANEOUS ATTACKS: 1777 Gen. John Burgoyne from Montreal Col. St. Leger, Iroquois Under Joseph Brant and Tories from Canada. Gen. Clinton to Ft. West Point from NYC. Gen. William Howe to capture Philadelphia from NYC. RESULTS OF THE PLAN Col. St. Leger, Joseph Brant captured a patriot fort at Oriskany but then failed to win at Ft. Stanwix. Defeated by Benedict Arnold and Gen. Herkimer. July 1777 Gen. Howe defeated Gen. Washington twice, captured Philadelphia. Germantown and Brandywine Creek Washington retreated to Valley Forge. July 1777 Gen. Clinton never left NYC. Gen. Burgoyne recaptured Ft. Ticonderoga Short on supplies sent Hessians into Vermont—defeated at Battle of Bennington Aug.-Sept. 1777 Oct. 7, 8, 1777 Battle of Freeman’s Farm Oct. 9, 1777 Burgoyne surrounded at Saratoga by Gen. Horatio Gates (Benedict Arnold, and Col. Daniel Morgan) asked for terms of surrender (10/16/1777). Largest Br. defeat of the war. 1. France agreed to a reciprocal treaty--Treaty of Alliance and Amity 1778 A. Recognized American independence. B. Promised troops and aid 2. England asked for peace with “home rule” for America. 3. Increased American morale 4. Spain declared war on England, 1779 5. Holland declared war on England 1780. 6. Gen. Howe resigned as Commanding General, turned control over to Gen. Henry Clinton. Clinton withdrew the troops in Philadelphia to NY City. AMERICAN POLITICS DURING THE WAR • Creation of State Governments: Colonial Charters--Constitutions – Republicanism and Popular Sovereignty – System of checks and Balances • Three branches of government • Bicameralism • Most of the power granted to the Legislative Branch. – Limited Government • Especially tight control over the Executive (Governor) – Civil Liberties • Guarantee of personal liberty and freedoms. • Articles of Confederation 1777 – John Dickinson (Md.) – Outline of Government • One branch, unicameral, parliamentary--Legislature – Powers granted • Fight a war, deliver the mail, make peace, ask for money, make treaties, • Limited power to make laws (9/13 majority), make amendments (13/13 majority), control of Ohio Territory. • Powers denied: No taxing power, no trade regulation, no interference into state matters. – Ratification 1781 (13/13) WAR SHIFTS SOUTH AND WEST • VALLEY FORGE – Gen. Frederich Von Steuben – Significance of Valley Forge – June 1778—Battle of Monmouth Courthouse (Molly Pitcher) Washington attacked Clinton’s army as it withdrew from Philadelphia to New York. Continentals win. England decided to consolidate its forces in the largest cities. Last major battle in the north. Largest land battle of the Revolution. • American Capt. George Rogers Clark captures 3 Br. Forts in Ohio Territory. (Gives US claim to Ohio Terr.) – From Ft. Nelson in Kentucky in 1778 – Ft. Kaskaskia 1778 (Illinois on the Mississippi River) – Ft. Vincennes (Indiana) 1779 BATTLES IN SC: 8. CORNWALLIS AND WHAT IS LEFT OF TARLETON’S TORIES DEFEAT GEN. GREENE AT GUILFORD’S COURTHOUSE. Cornwallis retreats toward Wilmington NC, then to Virginia.—Pyrrhic Victory, “Friendly Fire” 6. MAJ. FERGUSON (BR) BUTCHERED BY “OVER THE MOUNTAIN BOYS” AT KING’S .MOUNTAIN 1780. Led by Col. Shelby. 7. 6 7. TARLETON LOSES TO COL. DANIEL 3. MORGAN (AMER) AT COWPENS (SARATOGA 3. COL. TARLETON MASSACRES SC MILITIAMEN AT THE OF THE SOUTH) JAN. 1781. WAXHAWS 1780. He was chasing members of SC’s Provincial Government who had escaped Charleston. TARLETON’S QUARTER!!! 5. SC “guerilla fighters” Low Country- Francis Marion Midlands- Thomas Sumter Upstate- Andrew Pickens 1780—harassed Br. forces all over SC. . 4.4CORNWALLIS DEFEATS GEN. GATES AT CAMDEN 1780 Humiliating defeat reaffirms Br. idea that colonial militia are cowards. Gen. Gates replaced by Gen. Nathaniel Greene. 2 2. CORNWALLIS CAPTURES CHARLESTON, April 1780 Largest American defeat of Revolutionary War. 1. Gens. Clinton and Cornwallis --Savannah falls 1778. 1 OTHER NOTABLE EVENTS • Benedict Arnold betrays the American cause. May 1780. – Exchanged plans for the capture of Ft. West Point for a commission in the British army. – Maj. John Andre executed by Continental Army for spying in retaliation for the hanging of Nathan Hale earlier in the war. John Paul Jones --“Bon Homme Richard” -defeated the HMS Serapis “I have not yet begun to fight” WORLD TURNED UPSIDE DOWN FRENCH ARMY AND NAVY ARRIVE IN AMERICA 1780—Count Rochambeau, Adm. De Grasse WASHINGTON STILL CAMPED AT MONMOUTH COURTHOUSE, NJ. WASHINGTON ATTACKS CORNWALLIS AT YORKTOWN. Based on the insistence of the Marquis de Lafayette--Americans lay siege for 1 month. Combined US and French forces under Rochambeau. French fleet Admiral de Grasse. CORNWALLIS SURRENDERS Oct. 1781 PEACE NEGOTIATIONS— Paris—US, Eng., Sp., Holland., and Fr. PEACE TREATY OF PARIS-- Sept.3, 1783. WAR IS OVER. WASHINGTON STOPS COUP D’ETAT AT NEWBURGH, NY. • • • THE CRITICAL PERIOD 1783-1787 AMERICA UNDER THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION SUCCESSES – WON THE WAR – TREATY OF PARIS 1783 – LAND ORDINANCE OF 1785 – LAND ORDINANCE OF 1787 PROBLEMS – DEBT • VETERAN’S PENSIONS • WAR BONDS • BONUSES • LOANS FROM FOREIGN COUNTRIES – STATES AUTONOMY • MONEY • ALLIANCES – ECONOMIC • LACK OF OVERSEAS MARKETS • “DUMPING” BY ENGLAND • HYPER-INFLATION, DEPRESSION • TREVITT V. WEEDEN, 1786: RHODE ISLAND STATE SUPREME COURT CASE – SHAYS’S REBELLION 1786 MASSACHUSETTS TAX REVOLT – ALL CAUSED BY THE INHERENT WEAKNESSES OF THE ARTICLES: • NO POWER TO TAX • NO POWER TO REGULATE TRADE • NO EXCLUSIVE POWER TO PRINT AND COIN MONEY • NO POWER TO INTERVENE IN STATE PROBLEMS ORDINANCE OF 1785 CALL FOR A NEW CONSTITUTION • VIRGINIA (Mt. Vernon) CONFERENCE 1785 • ANNAPOLIS CONVENTION 1786 • CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION MAY 1787 • PURPOSE: GEORGE WASHINGTON • WHERE: • STATES PRESENT: • DELEGATES PRESENT: • NOTABLE ABSENTEES: • ORGANIZATION OF CONVENTION • PROPOSALS: • VIRGINIA PLAN BEN FRANKLIN • NEW JERSEY PLAN • “GREAT COMPROMISE” (CONNECTICUT COMPROMISE) • 3/5S COMPROMISE • SLAVE TRADE/COMMERCE CLAUSE COMPROMISE • RATIFICATION PROCESS AND ARGUMENTS: • FEDERALIST PAPERS (Madison’s Federalist Paper #10) • PROMISE BY FEDERALISTS TO ANTI-FEDERALISTS OF A BILL OF RIGHTS. JAMES MADISON ALEXANDER HAMILTON JOHN JAY WASHINGTON’S PRESIDENCY (1789-1797) • FIRST JOB: PUT THE NEW GOVERNMENT IN TO ACTION: – ESTABLISH THE PRESIDENCY– HIS CABINET– CONGRESS PROPOSED AND THE STATES APPROVED A “BILL OF RIGHTS”. • 5 MAJOR ISSUES OF WASHINGTON’S PRESIDENCY: – 1. DEBT: HAMILTON’S 5 PART PLAN – 5% Tariff on all imports – Assumption of state debts » (Compromise on location of new capital city) – Pay off bonds at face value – Raise excise taxes gradually -- 25% whiskey tax » 1794 Whiskey Rebellion – Bank of the US – 2. INDIAN PROBLEMS ON THE FRONTIER • Treaty of Greenville – 3. FRENCH REVOLUTION 1789 • Citizen Genet 4. WAR BETWEEN FRANCE AND ENGLAND 1793 Neutrality Proclamation • Jay’s Treaty Pinckney’s Treaty – 5. CREATION OF POLITICAL PARTIES • Washington’s Farewell address: • Sept. 1796– announced that he was not running for a 3rd term. • Listed his accomplishments: Boundaries firmly set Indian hostilities over. Avoided war. US was expanding– 3 states added. Debt paid. Urged America: Unity at home. Neutrality abroad Washington was eulogized by Congress: “First in War, First in Peace and First in the hearts of his Countrymen” A modern day Cincinnatus.